Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
37.9025518
139.02309460000004
Collection information
Japan,Niigata Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
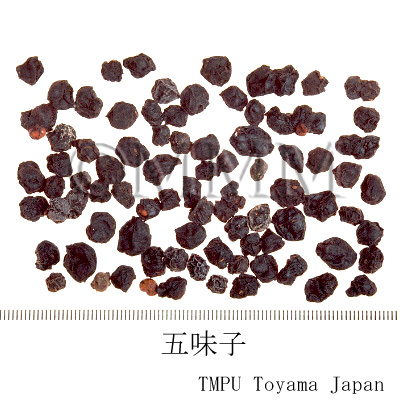
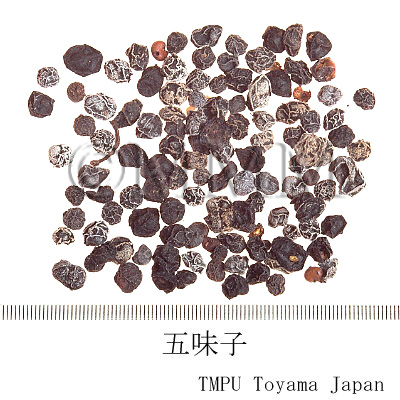
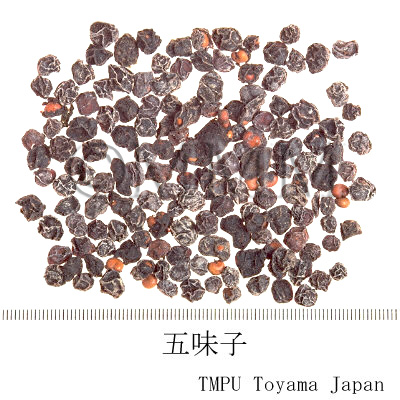
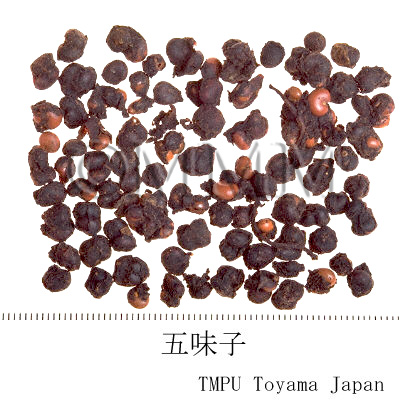
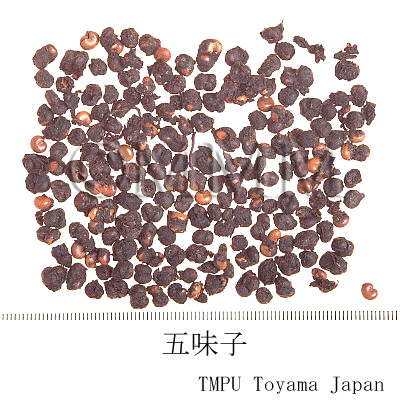
| Common name | 五味子, Wuweizi, Schisandrae Fructus (JP18), Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus (CP2020), Schisandra Fruit (JP18), Chinese Magnoliavine Fruit (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 北五味子 Baiwuweizi | ||||||
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
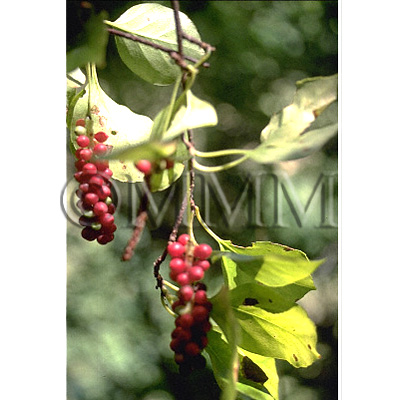
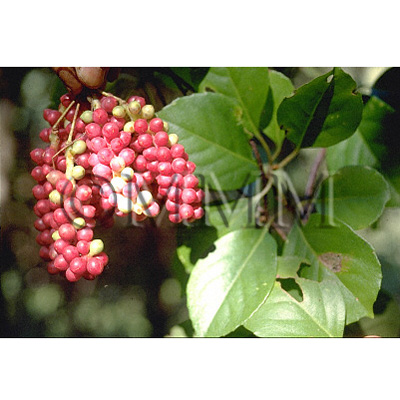
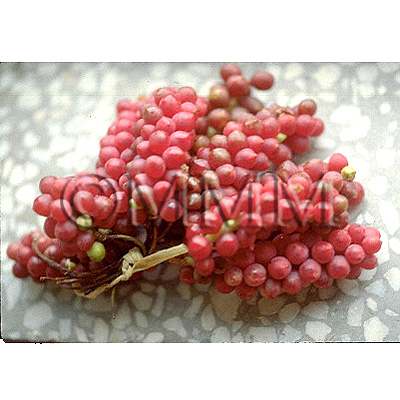
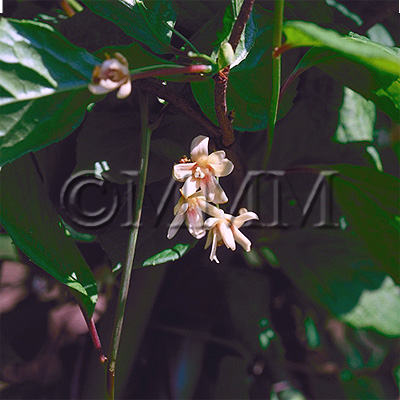
| Original plant name | Schisandra chinensis Baillon, (Chōsengomishi) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Schisandraceae | ||||||
| Used part | mature fruit | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Wuweizi is deep purple and has wrinkles on the surface. It tastes sweet. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an antibechic, astringent, antidiarrheal and tonic, wuweizi is applied for hepatic disorder and the diseases with thirst, cough, diarrhea and phlegm. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Astringents and haemostatics | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; sour and sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Lung, heart and kidney meridians. [Actions] To astringe and secure, tonify qi, engender fluid, tonify the kidney and calm the heart. [Indications] Chronic cough, dyspnea of deficiency type, dream emission, spermatorrhea, enuresis, frequent urination, chronic diarrhea, spontaneous sweating, night sweat, thirst caused by fluid consumption, interior heat wasting-thirst, palpitations and insomnia. | ||||||
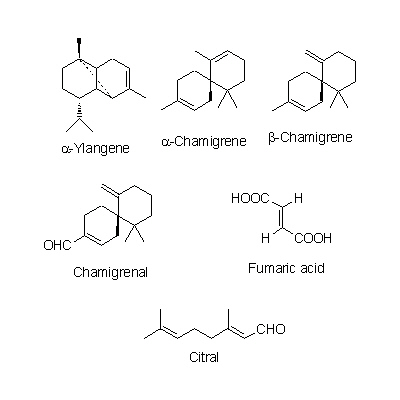
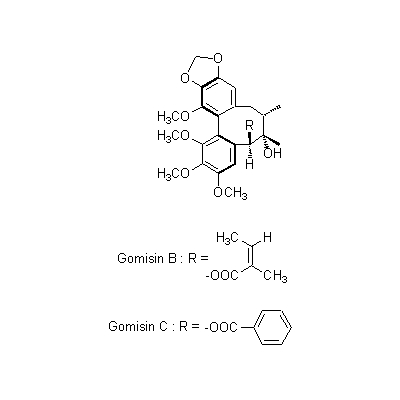
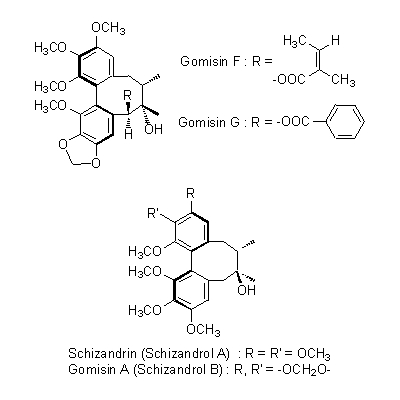
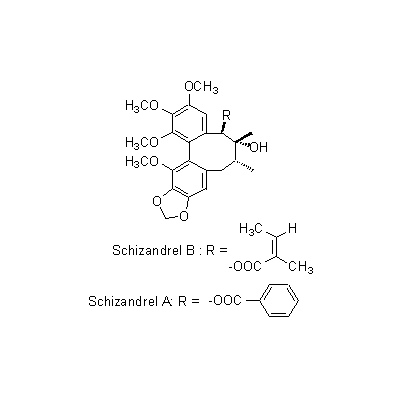
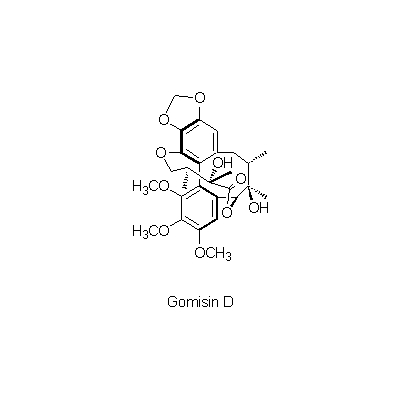
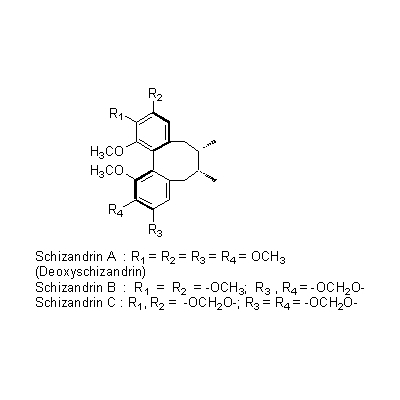
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Fumaric acid, Citric acid, Malric acid, Tartaric acid Monoterpenoids (*C1): Citral Sesquiterpenoids (*C1): Sesquicarene, alpha-Ylangene, alpha-Chamigrene, beta-Chamigrene, Chamigrenal Sterols (*C1): beta-Sitosterol Lignans & Neolignans (*C1): Schizandrin (= Schizandrol A), Gomisin A (= Schizandrol B), Gomisin B, Gomisin C, Gomisin D, Gomisin E, Gomisin F, Gomisin G, Schizandrin A (= Deoxyschizandrin), Schizandrin B, Schizandrin C, Schizandrel A, Schizandrel B (*C2): Pregomisin | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Suppression of gastric juice secretion,stimulation of bile secretion (schizandrin).sedative・analgesic,decreases body temperature,relaxation of muscles,suppression of stress-induced ulcer (schizandrin, gomisin A).Antitussive (gomisin A).Ataxia,induction of spasm,appearance of arousal brain wave (coal oil-ether extract). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AF163710, AF094561, AF238061, AF263441, L75842; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Cough, Dyspnea, Spontaneous sweating, Night sweats, Frequent urination, Incontinence of urine, Diarrhea, Thirst, Malaise, Lack of energy, Palpitation | ||||||
| Formulation | Kamishimotsuto, Kyukihochuto, Kyososan, Kobokumaoto, Shionsan, Shoseiryuto, Shoseiryukasekkoto, Shoseiryugomakyokansekito, Shomyakusan, Joshitsuhokito, Seishoekkito, Seinetsuhokito, Seinetsuhoketsuto, Seihaito, Chimobukuryoto, Ninjin-yoei-to, Ninjin-yoei-to, Baimoto, Bakumondoinshi, Fuhishomyakusankabyakukyu, Hohaito, Mibakuekkito, Yakammaoto, Yohaito, Ryokankyomishingeto, Ryokankyomishingeninto, Ryokankyomishingeninoto, Ryokangomikyoshinto | ||||||
| Related drugs | Nanwuweizi (see "Remarks") | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 201-204. | ||||||
| Remarks | In China, the fruit of Schisandra sphenanthera Rehd. et Wils. is called "Nanwuweizi". It is used similarly to the fruit of S. chinensis (Beiwuweizi). The Pharmacopoeia of People's Republic of China defines Wuweizi as these two species. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | ||||||