Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
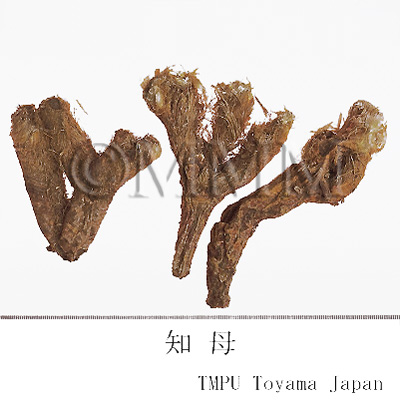
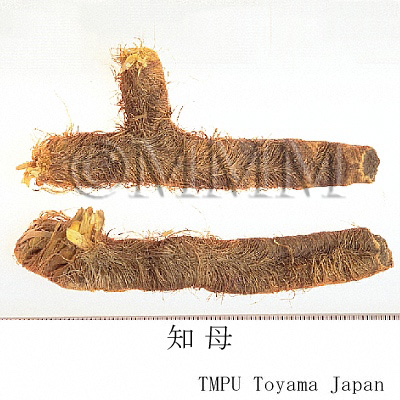
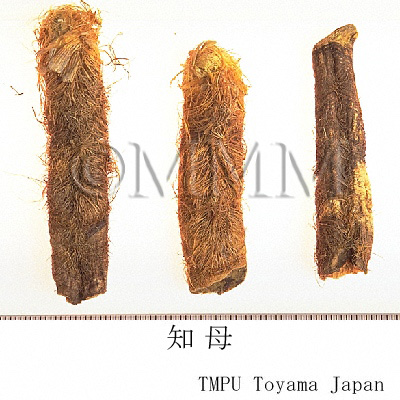
| Common name | 知母, Zhimu, Anemarrhenae Rhizoma (JP18, CP2020), Anemarrhena Rhizome (JP18), Common Anemarrhena Rhizome (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 毛知母,光知母,知母肉 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
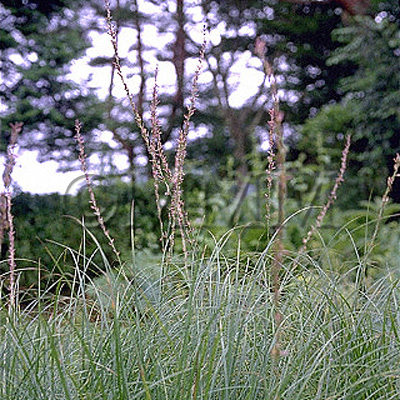
| Original plant name | Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge, (Hanasuge) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Liliaceae | |||||
| Used part | rhizome | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Zhimu is enlarged, moist and has yellow hair roots. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antifebrile, diuretic, tranquilizer, antiussive and antidiarrheal drug, zhimu is applied for high fever and excessive thirst. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for reducing intense internal heat | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter and sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Lung, stomach and kidney meridians. [Actions] To clear heat, purge fire, nourish yin to moisten dryness. [Indications] External contraction of febrile disease, high fever with vexation and thirst, lung heat with dry cough, bone-steaming and tidal fever, interior heat wasting-thirst, constipation caused by intestinal dryness. | |||||
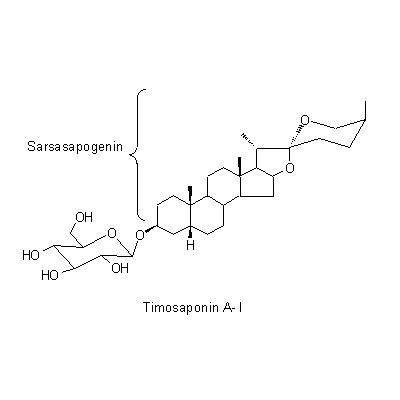
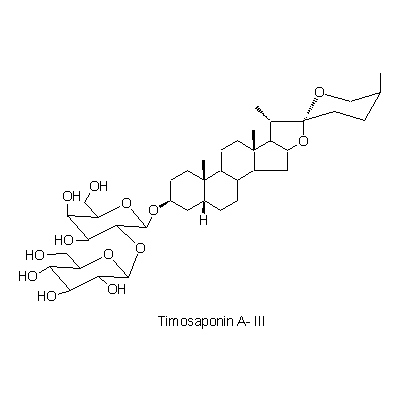
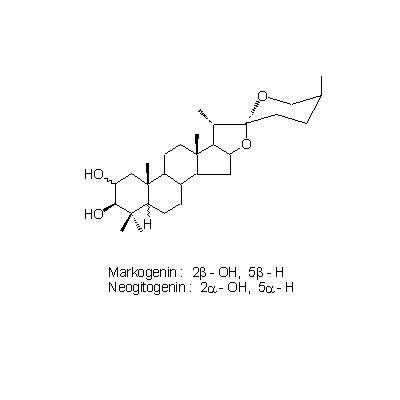
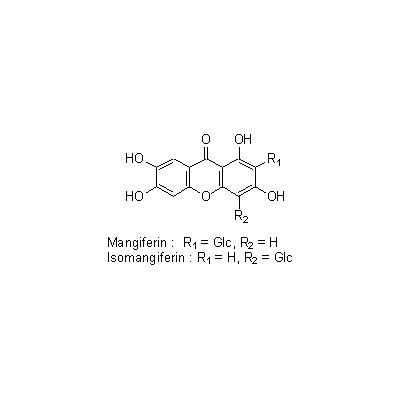
| Chemical constituent | Steroid saponins & Sapogenins (*C1): Timosaponin A-I, Timosaponin A-II, Timosaponin A-III, Timosaponin A-IV, Timosaponin B-I, Timosaponin B-II, Sarsasapogenin, Markogenin, Neogitogenin Xanthones (*C1): Mangiferin, Isomangiferin Amino acids (*C1): Pantothenic acid Pyridine alkaloids (*C1): Nicotinic acid | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Hypoglycemic (extract).Antipyretic and antibacterial (decoction).Hypotensive, suppression of respiratory center, hemolytic (timosaponins). | |||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | High fever, Thirst, Cough, Dry cough, Night sweats, Anhidrosis, Dysuria, Constipation | |||||
| Formulation | Ishoho, Ogibekkoto, Orenshodokuin, Kagenshahakusan, Kamishimotsuto, Kamihachimyakusan, Keishishakuyakuchimoto, Saikoyoeito, Sansoninto, Jiinkokato, Jiinshihoto, Shionsan, Jijintsujito, Shofusan, Joshitsuhokito, Shin'iseihaito, Jingyobekkoto, Seishinto, Seisoyoeito, Seinetsuhoketsuto, Chimobukuryoto, Tokinentsuto, Bakumondoinshi, Byakkokakeishito, Byakkokaninjinto, Hointo | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 87-89. | |||||
| Remarks | There are two types in "Zhimu (知母)", "Maozhimu" and "Guangzhimu". "Guangzhimu", in which yellowish brown fine roots of the surface have been removed, is appreciated as high quality in China, but it is not used in Japan. The rhizome of Aspidistra genus of family Liliaceae is a substitute for above in Zhuangzu Autonomous Region of Guangxi Province ("Maozhimu") and Taiwan ("Guangzhimu"). | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||