Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
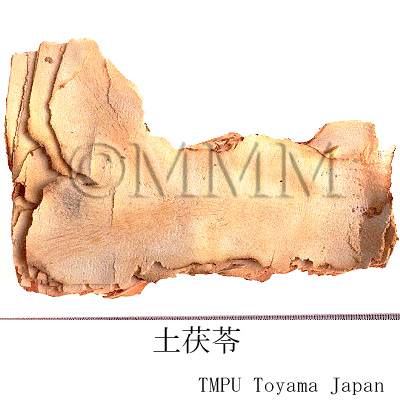
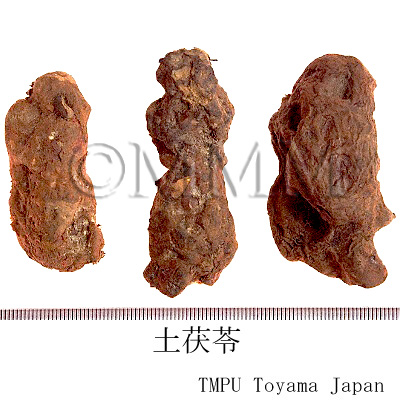
| Common name | 土茯苓, Tufuling, Smilacis Rhizoma (JP18), Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma (CP2020), Smilax Rhizome (JP18), Glabrous Greenbrier Rhizome (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 山帰来 (Sankirai) | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
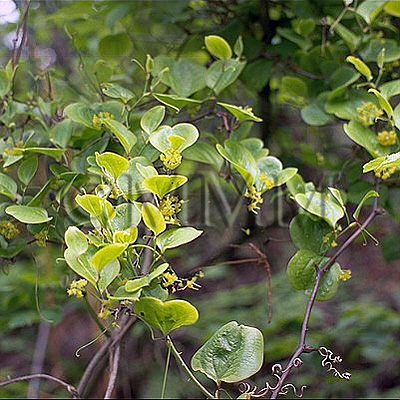
| Original plant name | Smilax glabra Roxburgh | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Liliaceae | |||||
| Used part | rhizome | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Tufuling is pale reddish brown. The inside is powder-like white. The one which has rotten or blighted parts is not good. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a remedy for poison, removing dampness, clearing heat and eliminating syphilis, it is used to treat chronic skin disease, dermatitis and contracture of limbs and muscle pain caused by syphilis or mercury poisoning. It is also used as a supplementary drug for acute hepatitis. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Febrifugal and detoxicant drugs | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral; sweet and bland. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and stomach meridians. [Actions] To remove toxin, remove dampness, relieve and comfort joints. [Indications] Spasm of limbs, pain in the sinews and bones caused by syphilis or mercury poisoning, dampness-heat strangury and the turbid, vaginal discharge, swelling abscess, scrofula, scabies, and tinea. | |||||
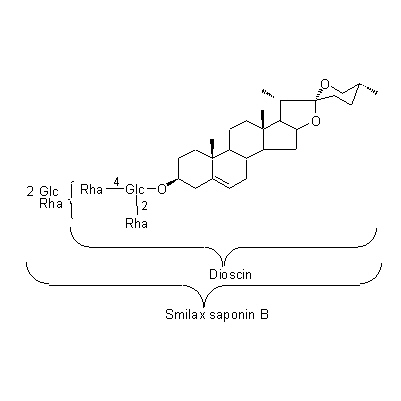
| Chemical constituent | Polysaccharides (*C1): 澱粉/starch Steroid saponins & Sapogenins S. china (*C1): Smilax-saponin A, Smilax-saponin B, Smilax-saponin C Phenylpropanoids S. glabra (*C2) 5-0-caffeoylshikimicacid Chromones S. glabra (*C2) Eurryphin Flavanones & Dihydroflavonols S. china (*C1): Astilbin, Distylin, Engeliten (= Engelitin) S. glabra (*C2) Smitilbin, Engeletin, Astilbin, Dihydroquercetin | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antiinflammation, antisyphilic, anticarcinogenesis (extract, resveratrol), suppression of autoimmune hepatopathy (eurryphin, resveratrol, smitilbin, eugeletin, astilbin).(C2) | |||||
| DNA sequence | AB040204, AF207022, D28333, U82645, L39853, L39854 | |||||
| Disease | Syphilis, Pyogenic dermatosis, Eczema, Psoriasis, Swelling and pain of joint | |||||
| Formulation | Kagawagedokuzai, Katsuketsugedokuto, Kikyogedokuto, Shogedokuto, Daibyakuchuin, Hachimitaikaho | |||||
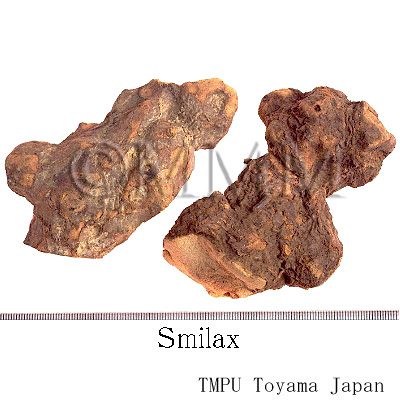
| Related drugs | Bakkatsu, the rhizome of S. china | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 13. C2)Planta Med., 65, 56-59(1999). | |||||
| Remarks | Japanese Sankirai (山帰来) is the rhizome of Smilax chinaL., (Jap. name: Sarutoriibara). It has been famous for treating syphilis. In Japan, it was used in Muromachi period according to an old record. It seems that the treatment method was developed shortly after syphilis came from South America. There is a myth that Sankirai, literally means returning from mountains, was named because syphilis patients returned alive from mountains after going there alone and taking the roots. However, this myth is questionable. Assumably, Sankiryo, another name for Tufuling, was the original name and had changed the accent into Sankirai (TN). In China the rhizome of S. china is referred to as Bakkatsu and used to eliminate dampness, promote urination and and reduce edema. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||