Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
27.894504
102.26444900000001
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Xichang
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
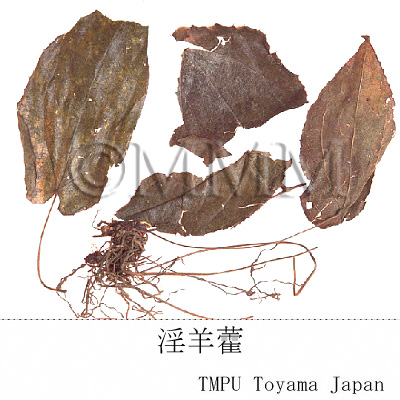
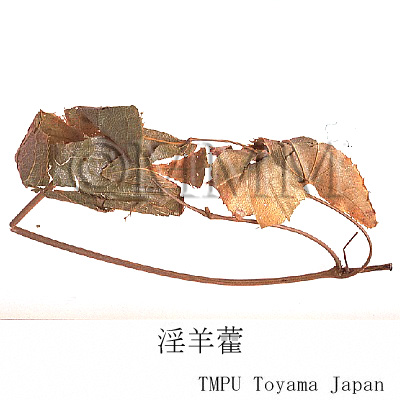
| Common name | 淫羊藿, Yinyanghuo, Epimedii Herba (JP18), Epimedii Folium (CP2020), Epimedium Herb (JP18), Epimedium Leaf (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
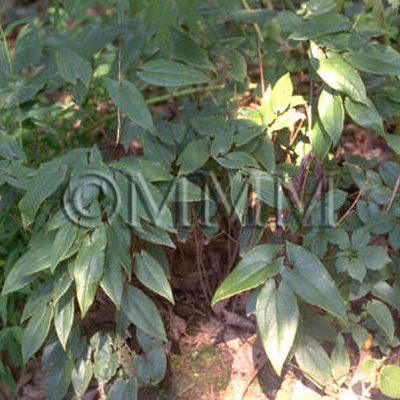
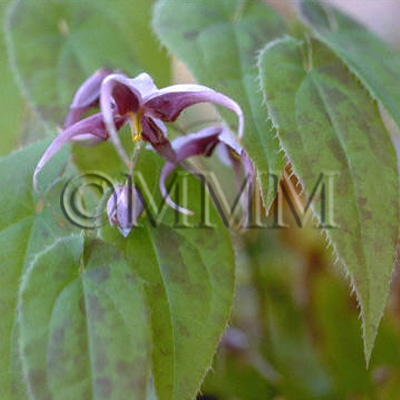
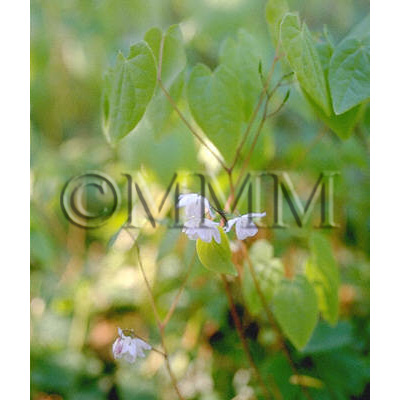
| Original plant name | Epimedium koreanum Nakai1, Epimedium grandiflorum Morren var. thunbergianum Nakai2, Epimedium pubescens Maximowicz, Epimedium brevicornu Maximowicz, Epimedium wushanense T.S. Ying, Epimedium sagittatum Maximowicz3 or Epimedium sempervirens Nakai4, (Kibanaikarisō1, Ikarisō2, Hozakiikarisō3, Tokiwaikarisō4) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Berberidaceae | ||||||
| Used part | whole plant or leaf | ||||||
| Quality for selection | The one with fresh bluish leaves is of good quality (NI). The leaves with petioles and rhizomes isthe second class (TN). | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | It is used as an aphrodisiac and tonic to treat impotence, weakness of the waist and knees, partial paralysis, and rheumatism. Generally, it is taken by soaking in liquor "Xian ling pi jiu". | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Replenishing Yang(vital function) drugs | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent, sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and kidney meridians. [Actions] To tonify the kidney yang, strengthen sinew and bone, dispel wind-dampness. [Indications] Debilitation of kidney yang, impotence and seminal emission, limp wilting sinew and bone, painful impediment caused by wind-dampness, numbness, spasm and climacteric hypertension. | ||||||
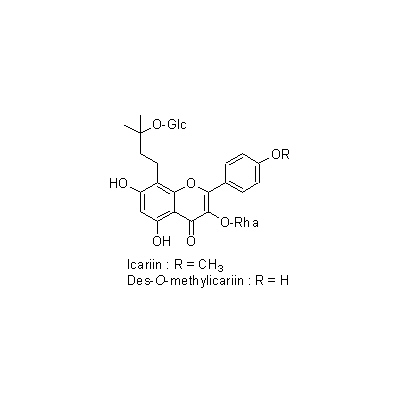
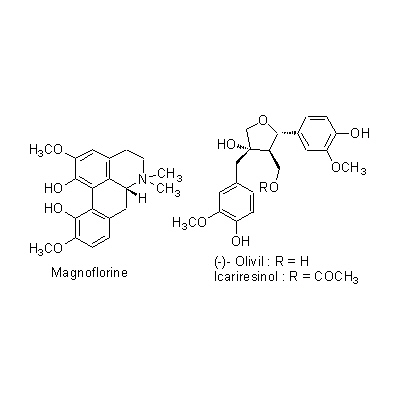
| Chemical constituent | Lignans & Neolignans (*C1): 葉/ leaf: (-)-Olivil, Icariresinol Flavones & Flavonols (*C1): 茎,葉/ stem, leaf: Icariin 根/ root: Des-O-methylicariin 茎,葉/ stem, leaf: Epimedine A,C Alkaloids (*C1): 根/ root: Magnoflorine | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| DNA sequence | L75869, L75875, AF328970 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Impotence, Infertility, Partial paralysis, Rheumatism, Paralysis, | ||||||
| Formulation | , | ||||||
| Related drugs | Epimedii Radix | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1) Nat.Med.,48(2),141-154;48,(4),253-263(1994). B2) Shoyakugaku Zasshi,45(2),109-118(1991). C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. Ⅱ, pp 48-50. | ||||||
| Remarks | The Chinese pharmacopoeia (2020 ed.) defines the aerial part of Epimedium brevicornum Maxim., E. sagittatum Maxim., E. pubescense Maxim. and E. koreanum Nakai as "Yinyanghuo" (淫羊藿). The ones produced in Sichuan Prov. are mainly E. Pubescens, E. acuminatum Franch., E. wushanense, E. sutchuenense Franch. and E. davidii Franch. The ones from northeastern China and the northern part of the Korean Peninsula are thought to be E. koreanum Nakai, and E. cremeum Nakai (Jap. name: Kibanaikarinsō). Japanese ones are the dried aerial part or the leaves of E. grandiflorum Morr. var. thunbergianum Nakai (Jap. name: Ikarisō, from Nagano Pref.) and E. sempervirens Nakai var. hypoglaucum Ohwi (Jap. name: Urajiroikarisō, from Niigata Pref.). In Japan, the underground part is called "Ikarisō kon" and is sold separately. (B2) | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/29 | ||||||