Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
22.817002
108.36654299999998
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Guangxi Zhuangzu Autonomous Region
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.620202
112.45392600000002
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Luoyang
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
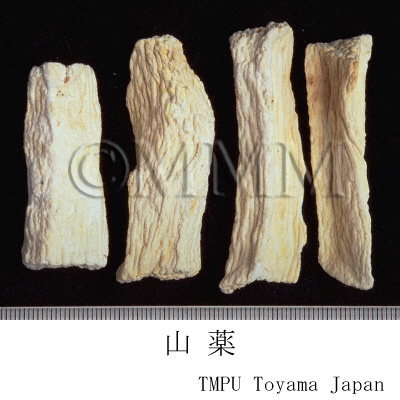
| Common name | 山薬, Shanyao, Dioscoreae Rhizoma (JP18, CP2020), Dioscorea Rhizome (JP18), Common Yam Rhizome (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 淮山薬, 淮山, 懐山薬, 光山薬, 毛条山薬 | ||||||
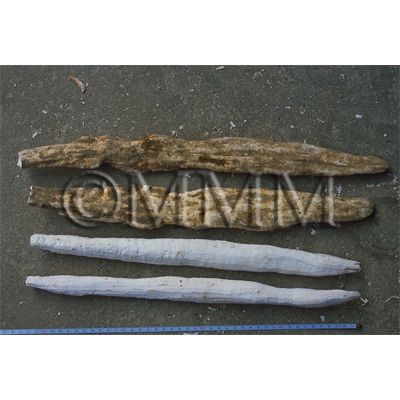
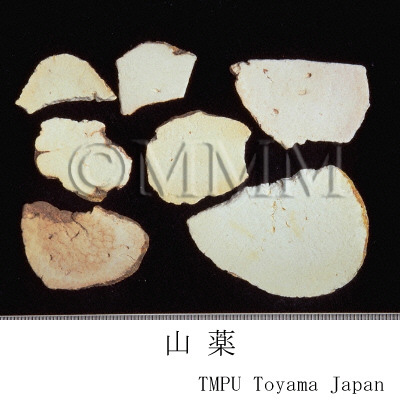
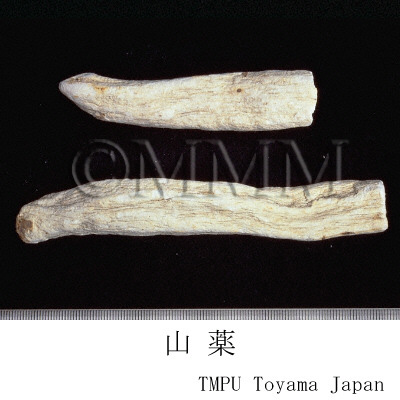
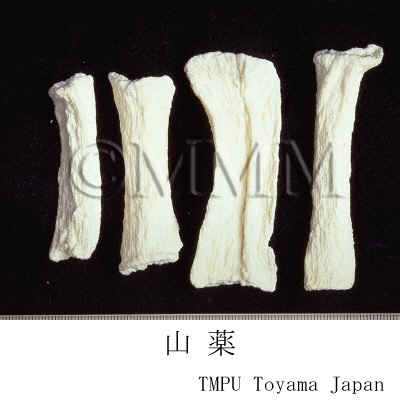
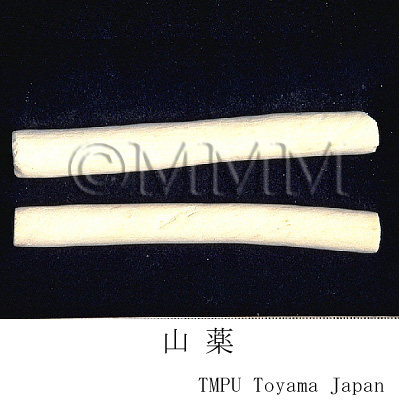
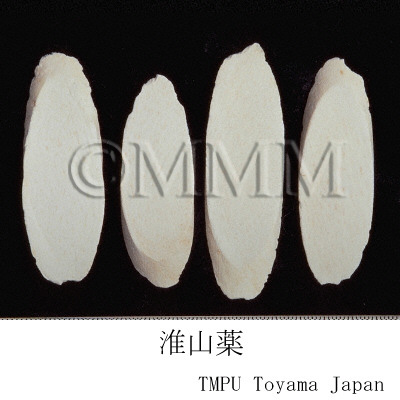
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
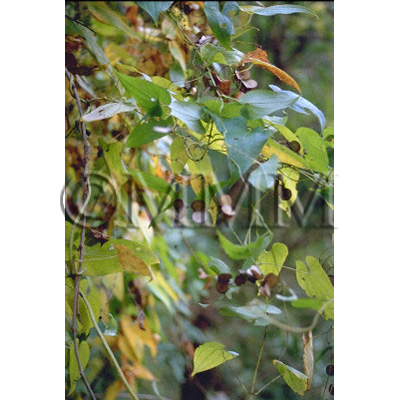
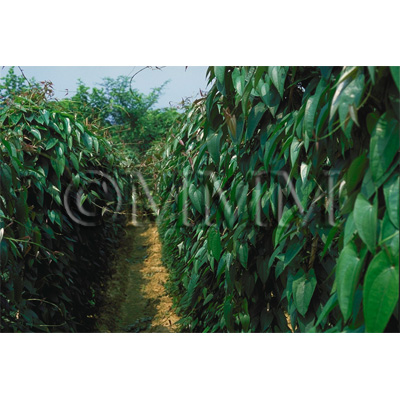
| Original plant name | Dioscorea japonica Thunberg1 or Dioscorea batatas Decaisne2 (= Dioscorea opposita Thunberg), (Yamanoimo1 or Nagaimo2) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Dioscoreaceae | ||||||
| Used part | rhizome without periderm | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Shanyao is dense, white and smooth. It has no worm-eaten part. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a tonic, antidiarrheal, for relieving thirst, Shanyao is applied for weakness of spleen and stomach, anorexia, fatigue, inflammation of the intestines, nocturnal enuresis and night sweat. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for replenishing Qi (vital energy) | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, lung and kidney meridians. [Actions] To tonify spleen and stomach, engender fluid to nourish lung, tonify kidney to astringe essence. [Indications] Cough caused by lung deficiency, seminal emission caused by kidney deficiency, vaginal discharge, frequent urination, deficiency heat and wasting-thirst. | ||||||
| Chemical constituent | Polysaccharides (*C1): Glucoprotein, 澱粉/Starch, Mannan Sterols (*C1): ステロ-ル/Sterols Amino acids (*C1, C2): Arginine, Phenylalanine, Valine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine Simple nitrogen containing compounds (*C1): Choline Other nitrogen compounds (*C1): Allantoin | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Not exactly known. | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AB017340, AB040208, AF069203, AF206903, D28327, AJ235803 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |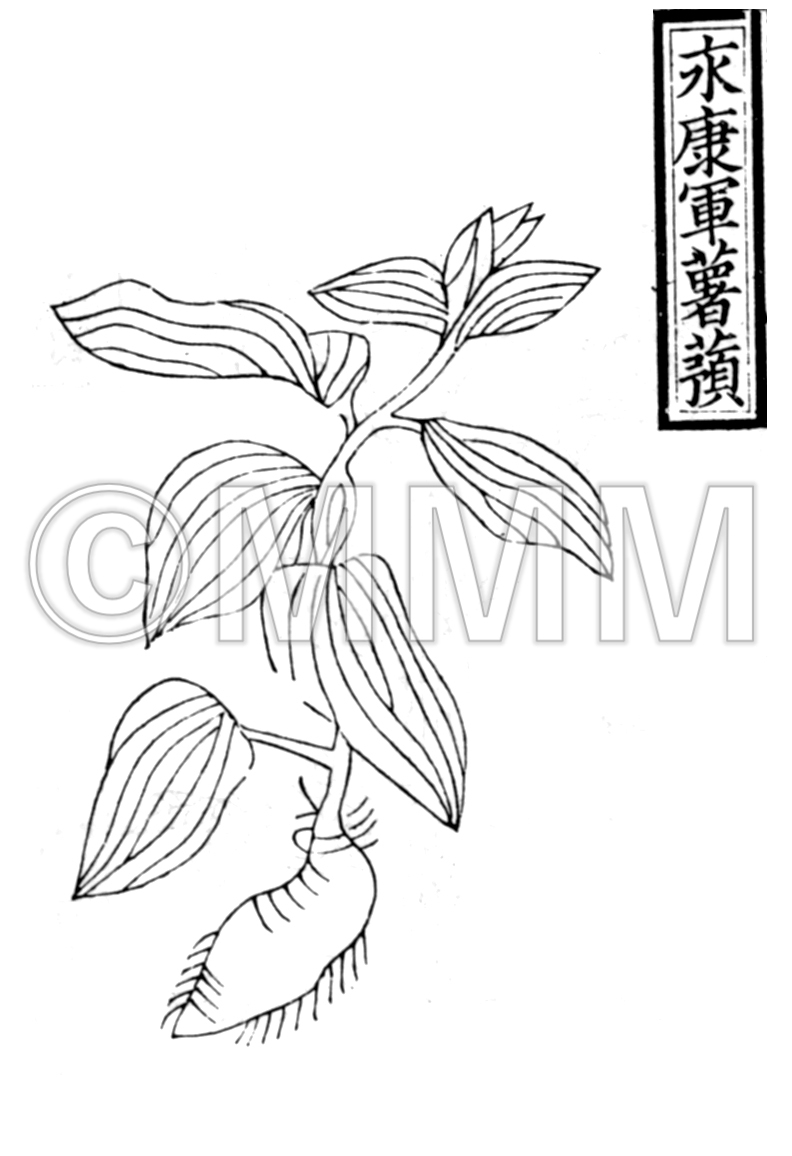  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Anorexia, Lack of energy, Muddy and watery stool, Full stomach, Enterocolitis, Thirst, Spermatorrhea, Frequent urination, Bed-wetting, Night sweats, Leukorrhea | ||||||
| Formulation | Kagenhachimotsuto, Keihito, Goshajinkigan, Shichikensan, Jinryobyakujutsusan, Hachimijiogan, Hokoeito, Rokumijiogan, Kogikujiogan | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, p 22. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 333. | ||||||
| Remarks | The Japanese Pharmacopoeia (18th edition) defines Dioscorea japonica (Jap. name: Yamanoimo) and D. batatas (Jap. name: Nagaimo) as Shanyao. In contrast, The Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. defines D. opposita as Shanyao. Shanyao in Henan Prov., which is called Waisanyaku or Waisan in Japan, is descended from D. opposita. Meanwhile, Shanyao in Guangxi Zhuangzu Autonomous Region is descended from D. alata L. (Jap. name: Daijo). Japanese Shanyao is made from Nagaimo which is cultivated for food. Nagaimo has been widely cultivated for food and has many types. They are roughly divided into groups of Nagaimo, Ichōimo and Tanbaimo. There are intermediate types between Nagaimo and Yamanoimo. Taiwanese Shanyao consists of species such as D. alata L., D. doryphora Hance, and there is also a fake product which is the tuber of Ipomoea batatas (L.) Poir of family Convolvulaceae (Jap. name: Amerikaimo). There is a difference in the process between Japanese and Chinese Shanyao. Japanese Shanyao is barked and then dried by heat. Chinese Shanyao is dried after being compressed in order to get rid of moisture (Maotiao Shanyao), or cut into chalk-like shape (Guang Shanyao). Japanese Shanyao is said to be of high quality. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/11/22 | ||||||