Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 黄精, Huangjing, Polygonati Rhizoma (JP18, CP2020), Polygonatum Rhizome (JP18), Solomonseal Rhizome (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
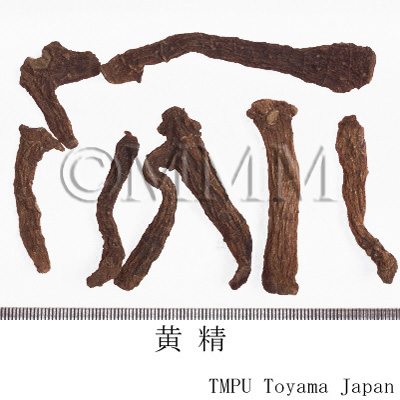
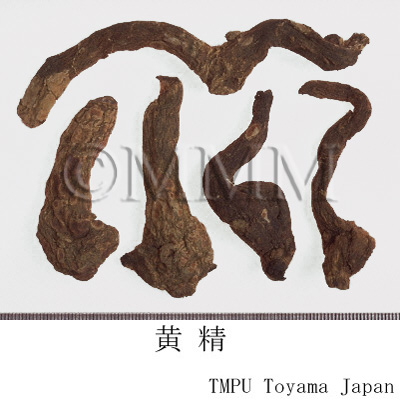
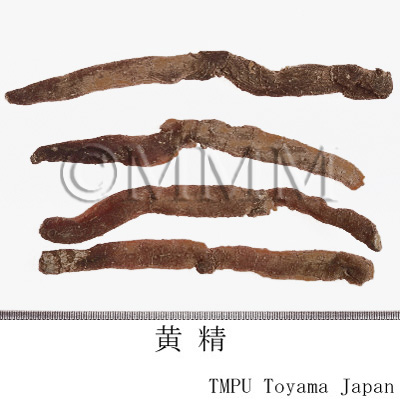
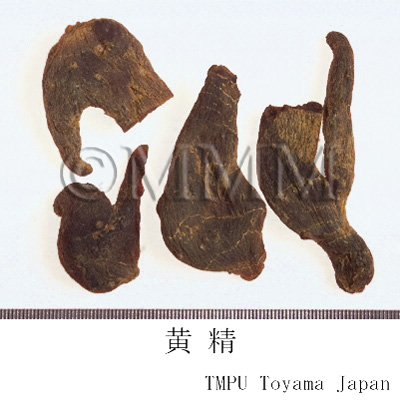
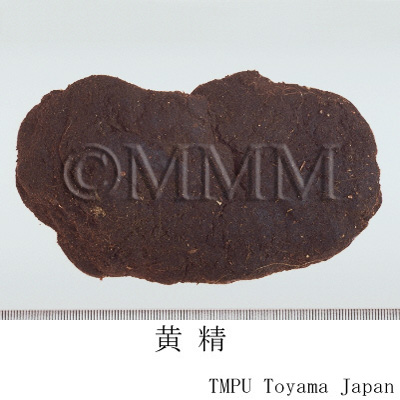
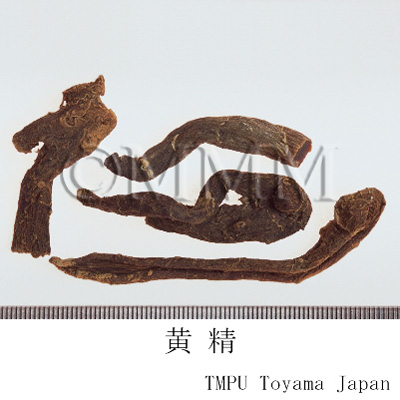
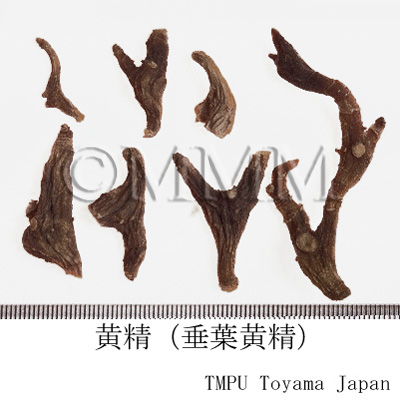
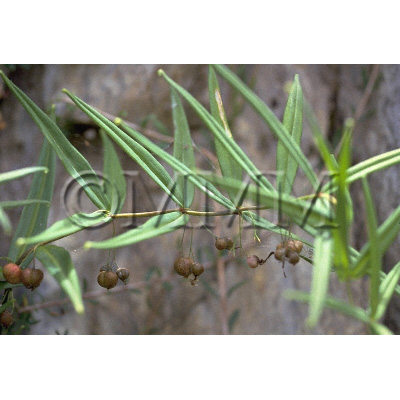
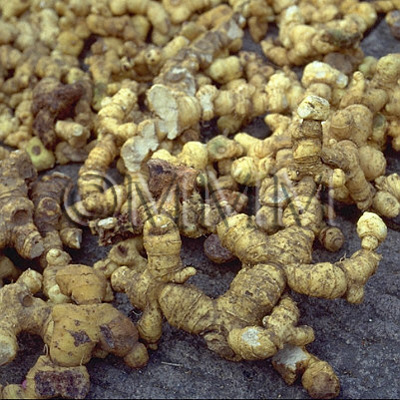
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
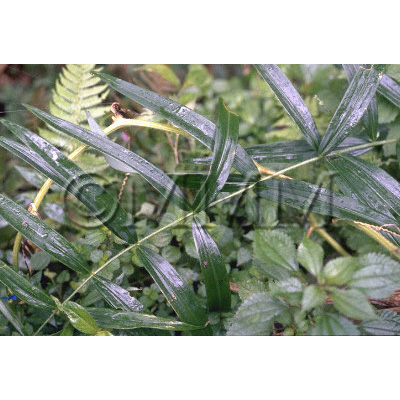
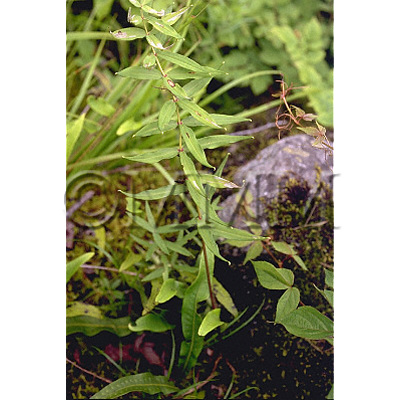
| Original plant name | Polygonatum kingianum Collett et Hemsley, Polygonatum sibiricum Redoute1, Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua or Polygonatum falcatum A. Gray2, (Kagikurumabanarukoyuri1, Narukoyuri2) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Liliaceae | ||||||
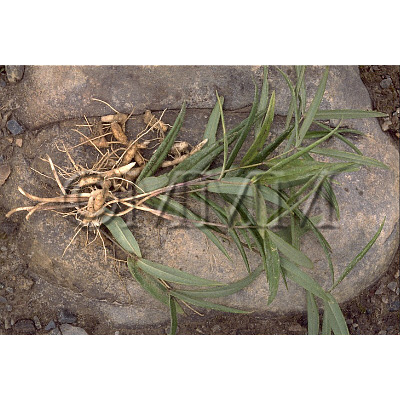
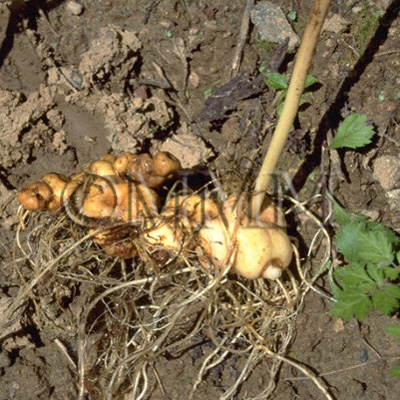
| Used part | rhizome | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Huangjing has large and clear stem traces. It has a thick parenchyma and no branch. (NI) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a tonic, Huangjing is applied for infirmity after illness, cough of pulmonary tuberculosis, thirst due to diabetes, fidgeting and hyperglycemia. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for replenishing Yin-vital essence | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, lung and kidney meridians. [Actions] To tonify qi and nourish yin, fortify the spleen, moisten the lung, and tonify the kidney. [Indications] Spleen stomach qi deficiency, fatigue and lack of strength, stomach yin deficiency, dry mouth, reduced food intake, dryness cough caused by lung deficiency, hemoptysis and cough caused by consumptive disease, deficiency of essence and blood, soreness and weakness in the low back and knees, premature graying, interior heat, and wasting-thirst. | ||||||
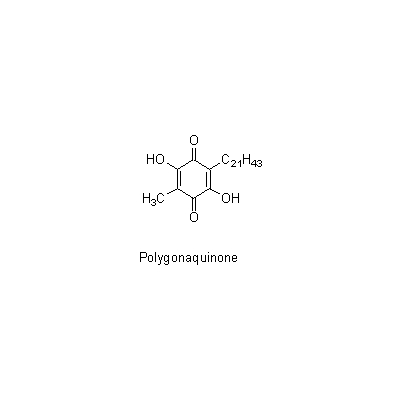
| Chemical constituent | Polysaccharides P. falcatum A. Gray ナルコユリ (*C1): Falcatan(D-Fructose:D-Mannose:D-Glucose:D-Galacturonic acid=25:10:5:1) Quinones P. falcatum A. Gray ナルコユリ (*C1): Polygonaquinone | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antibacterial, antifungal, reduction of blood pressure, decrease in blood sugar. Suppression of carbohydrate release from the liver (*p1). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AB017316, AB040207, AB029760 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Anorexia, Thirst, Constipation, Dry cough, Heaviness and powerlessness in lumber and knee, Lightheadedness | ||||||
| Formulation | not used in formula | ||||||
| Related drugs | Yuzhu (Polygonati Odorati Rhizoma) | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, p 150-152. B1)Shoyakugaku Zasshi, 45,99(1991);47,131(1993);47,144(1993);47,249(1993). P1)J.Trad.Med.,13,281(1996). | ||||||
| Remarks | The Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China defines Polygonatum kingianum, P. sibiricum, P. cyrtonema as the original plant of Huangjing. However, more than 10 kinds of congeners are used in the Chinese market, such as P. odoratum, P. macropodium, which are the original plants of Yuzhu. Though the benefit of Huangjing is similar to that of Yuzhu (Polygonati Odorati Rhizoma), the former has the advantage of invigorating qi and the latter has the advantage of invigorating yin. Clinically, they are used differently. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/06/09 | ||||||