Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
37.9025518
139.02309460000004
Production area information
Japan,Niigata Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
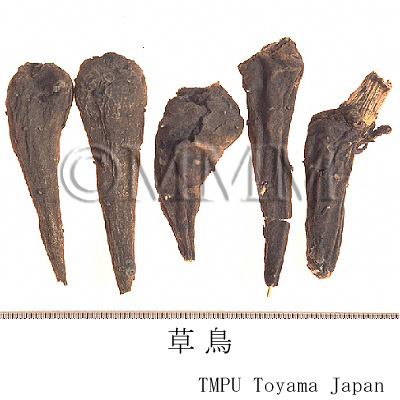
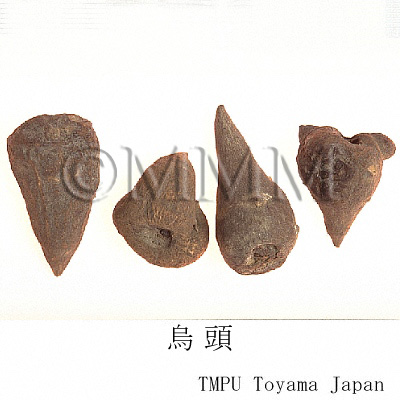
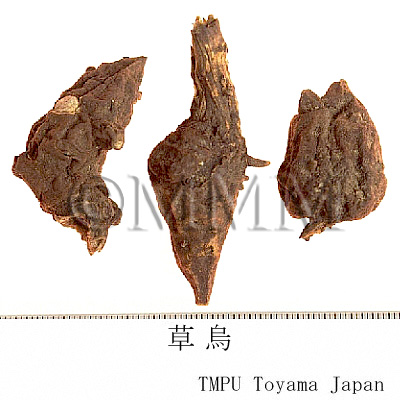
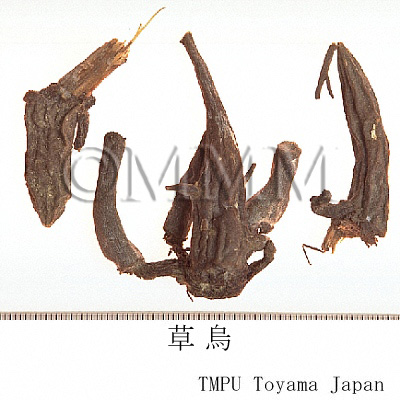
| Common name | 烏頭, Wutou, Aconiti Radix (CP2020), Common Monkshood Mother Root (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 川烏 (Chuanwu), 川烏頭 (Chuan wutou), 草鳥 (Caowu), 草烏頭 (Cao wutou) | ||||||
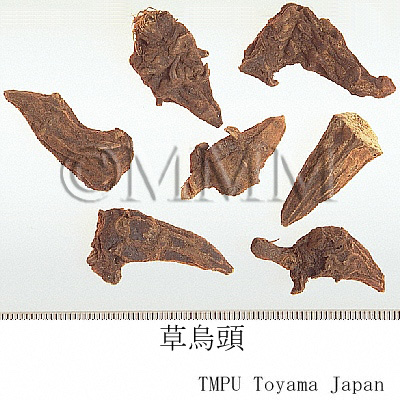
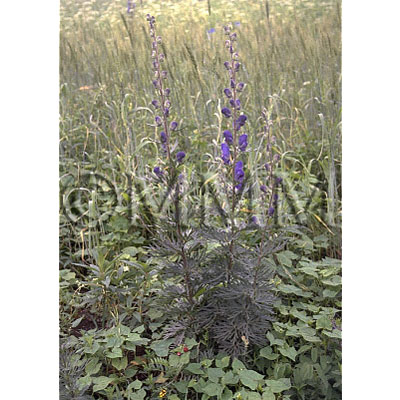
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
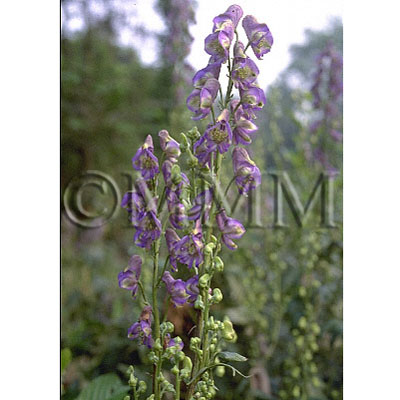
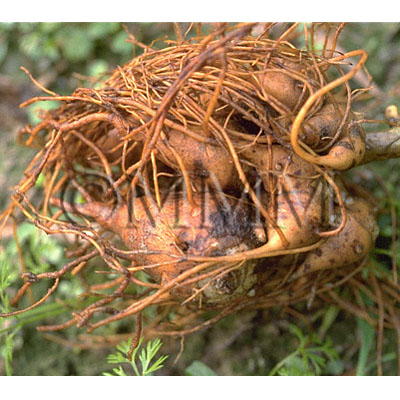
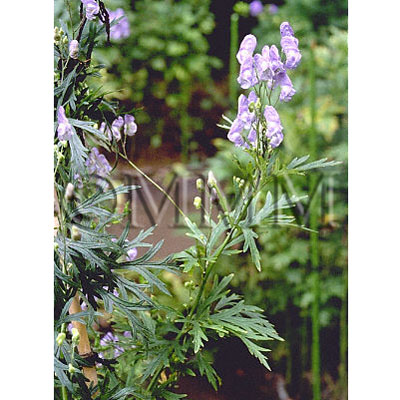
| Original plant name | Aconitum carmichaeli Debx.1,Aconitum kusnezoffii Reichb.2, CN products: Karatorikabuto (Chuan wutou1, Cao wutou2), and etc. | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Ranunculaceae | ||||||
| Used part | tuber (parent root for chuanwu) | ||||||
| Quality for selection | The bark of a good Wutou is black and the inside is white. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an antispasmodic and painkiller, Wutou is applied for arthritis, numbness of limbs and abdominal pain of sickly person. It is also used as diuretic and tonic. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for dispelling internal cold | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Hot; pungent, bitter; highly toxic. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, liver, kidney and spleen meridians. [Actions] To dispel wind and remove dampness, and warm the meridian to relieve pain. [Indications] Wind cold dampness impediment, joint pain, cold pain in the heart and abdomen, pain in cold abdominal colic, and it can be applied for anesthesia to relieve pain. As it is highly poisonous, it is processed before use generally . | ||||||
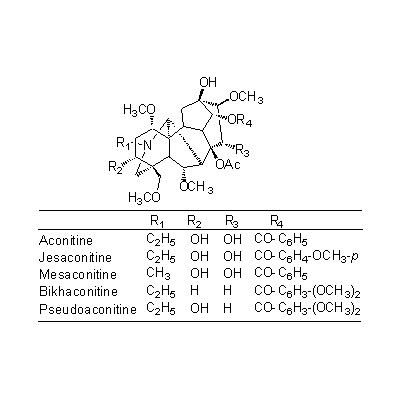
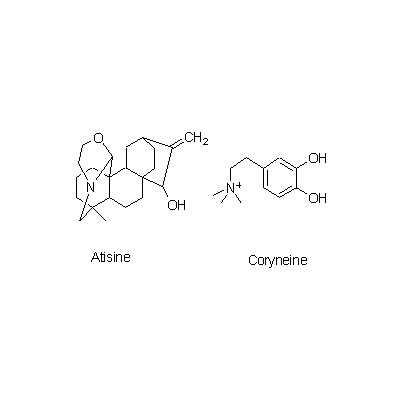
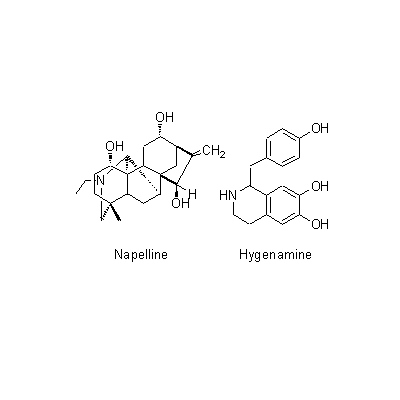
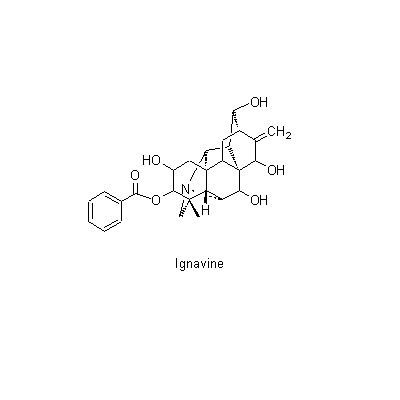
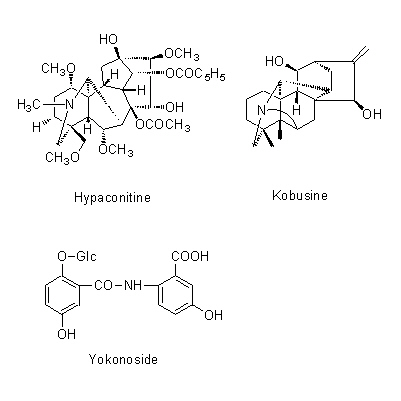
| Chemical constituent | Alkaloids A. carmichaeli (*C1): Aconitine, Hypaconitine, Mesaconitine, Carmichaeline, Talatisamine, Coryneine chloride A. japonicum (*C1): Aconitine, Mesaconitine, Hypaconitine, Hygenamine Aconitum spp. (*C2): アコニチン系:Aconitine, Hypaconitine, Mesaconitine, Jesaconitine, Neopelline, アチシン系:Atisine, Kobusine, Pseudokobusine, Telatisine, Songorine, Atidine, Napelline, Heteratisine, Hypognavine, Ignavine, 強心成分/cardiac component:Hygenamine, Coryneine, Yokonoside, etc. A. delavayii Franch. (*C1): Delavaconitine A. soongaricum (*C1): Aconitine, Songorine (= napellonine), Acetylsongorine | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Sedation, suppression of stress ulcer (extract). Sedation, reduction of blood pressure, arrhythmogenic effect (aconitine), cardiotonic effect (hygenamine, coryneine). Analgesia, antiinflammation (mesaconitine). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AB020369, AB020370, AB020371, AB020372, AB020373, AB020374 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Somatic pain, Swelling and pain of joint, Numbness, Frequent urination, Abdominal pain, Numbness | ||||||
| Formulation | Uzuto, Uzukeishito, Uzushakusekisigan, Sanshoin, Sekiganryo (keihi), Sekiganryo (hange) | ||||||
| Related drugs | Fuzi, the daughter root of Aconitum carmichaeli. | ||||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 91-97. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, pp 304-305. | ||||||
| Remarks | - The tubers of wild Aconitum have respective names depending on the production area and species, as follows: Sōuzu (Jap. name), Caowu, Wuyao, Jinniuqi, Dacaowu, Xiaoheiniu, Xuewu, Huangcaowu, Tengcaowu, Wanwuyao, Kaenshi (Jap. name), Tiebangchui. - Various kinds of Chinese Souzu: A. kusnezoffii (Heilongjiang), A. artemisaefolium Bar. et Skv. (Liaonig), A. paniculigerum Nakai, A. sczukini Turcz. (Northeast part), A. taipeicum Hand.-Mazz. (Shaanxi), A. karakolicum Rap., A. soongaricum Stapf (Xinjiang), A. sungpanense Hand.-Mazz. (Shaanxi, Gansu, Sichuan), A. hemsleyanum Pritz. (Sichuan, Hubei, Hunan, Shaanxi), A. stylosum Stapf, A. transsectum Diels, A. delavayi Franch. (Yunnan) and many other tubers of genus Aconitum. - Korean Sōuzu: Tubers of several Aconitum genus such as A. triphyllum Nakai (Jap. name: Mitsubatorikabuto). - Japanese Sōuzu: The tuber of A. japonicum Thunb. - The Pharmacopoeia of The People's Republic of China contains Chuanwu, the parent root of A. carmichaeli (harvested from late June to early August), and Caowu, the tuber of A. kusnezoffii (harvested in Autumn). Caowu is stronger in both toxicity and benefit than Chuanwu. Compared with Fuzi, Wutou has advantages of expelling wind and relieving pain, and has disadvantages of stimulating heart and dispelling cold. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/11/02 | ||||||