Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
35.6894875
139.69170639999993
Collection information
Japan,Tokyo
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | ゲンノショウコ, Gennoshōko, Geranii Herba (JP18), Geranium Herb (JP18) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 玄草 | ||||||
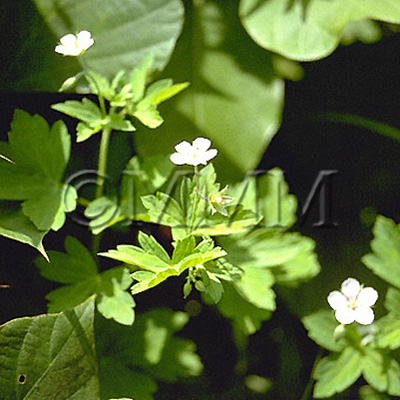
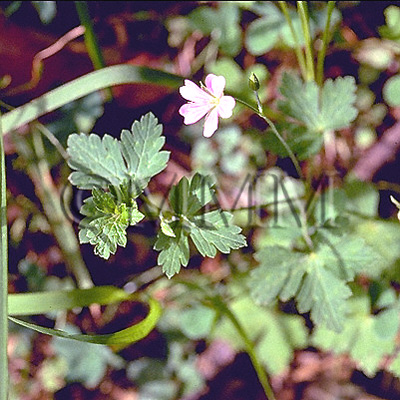
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
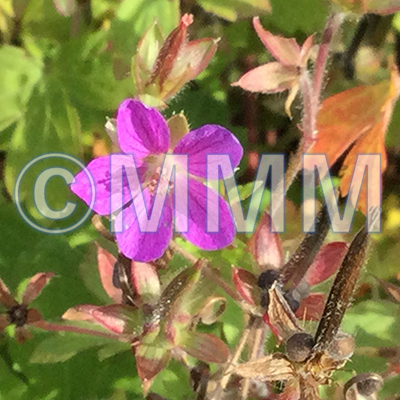
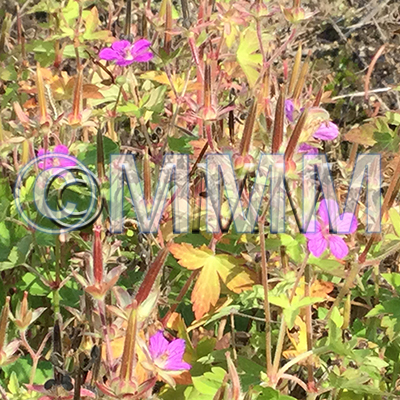
| Original plant name | Geranium thunbergii Siebold et Zuccarini, (Gennoshōko) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Geraniaceae | ||||||
| Used part | aerial part | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Gennoshoko has few foreign substances. The stem is purplish brown. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an astringent and antidiarrheal, Geranii Herba is applied for diarrhea due to colitis and abdominal pain. As a stomachic, it is used as tea. External use of its decoction is for swelling and skin disease. | ||||||
| Medical system | Folk medicine | ||||||
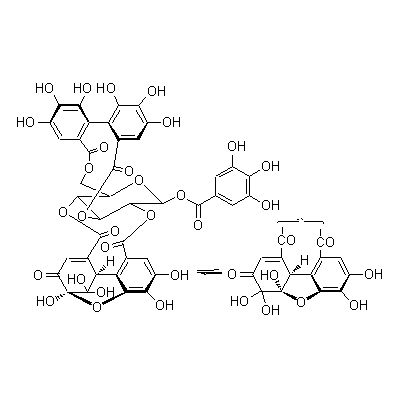
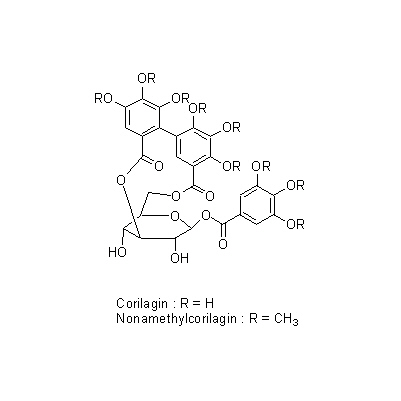
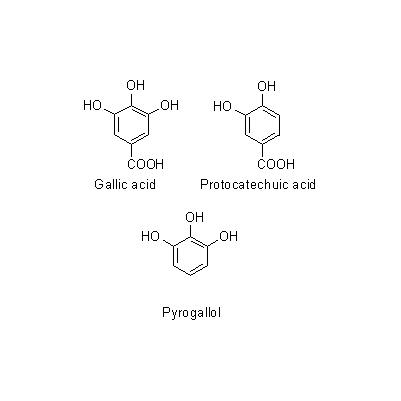
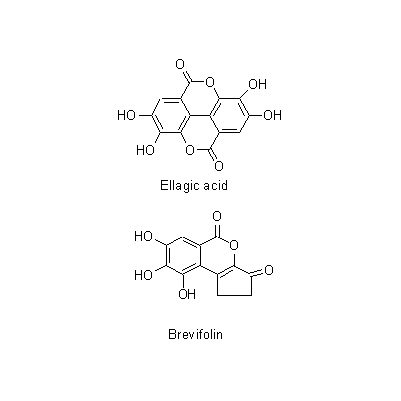
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Succinic acid Flavones & Flavonols (*C1): Quercetin, Kaempferol monorhamnoside, Kaempferitrin Hydrolyzable tannins & related compounds (*C1): Geraniin, Ellagic acid, Brevifolin, Undecaacetae corilagin, Nonamethylcorilagin Other aromatic derivatives (*C1): Gallic acid, Protocatechuic acid, Pyrogallol | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Hypertonia of smooth muscle, suppression of longitudinal muscle movement. Astringent (geraniin). Disinfection (dysentery bacillus typhosus, Salmonella typhi, colibacillus, enteritis). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | U77906 | ||||||
| Disease | Diarrhea, Constipation, Colitis, Leukorrhea | ||||||
| Formulation | |||||||
| Related drugs | Laoguancao (see "Remarks") | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 24-26. | ||||||
| Remarks | There are two kinds of Gennoshōko depending on the color of the flower (white and red). The one with a white flower is more common for medicinal use. It is used regularly as folk medicine and also used as a raw material for domestic medicines. In China, the whole plant, including the fruit, of congeners such as Erodium stephanianum Willd. (Jap. name: Kikubafūro) Geranium wilfordii Maxim. (Jap. name: Mitsubafūro), G. carolinianum L. (Jap. name: Americafūro), and so on are called "Laoguancao" (老鸛草) (Jap. name: Rōkansō). They are used as medicine. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/01/31 | ||||||