Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
35.6894875
139.69170639999993
Collection information
Japan,Tokyo
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 甘茶, Amacha, Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium (JP18), Sweet Hydrangea Leaf (JP18) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Hydrangea macrophylla Seringe var. thunbergii Makino, (Amacha) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Saxifragaceae | |||||
| Used part | leaf and spray | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Amacha is dark green or yellow-green. There should be no foreign substances besides leaves. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII | |||||
| Clinical application | As a sweetener and corrigent, Amacha is used as a ingredient for domestic medicine and mouth refrigerant. | |||||
| Medical system | Folk medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Japan | ||||
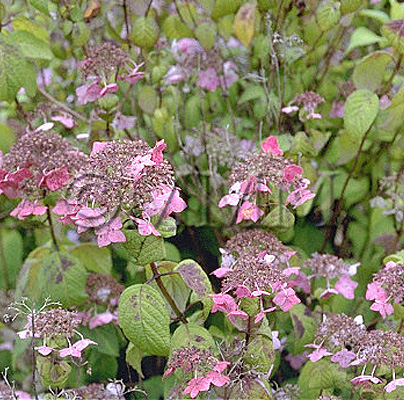
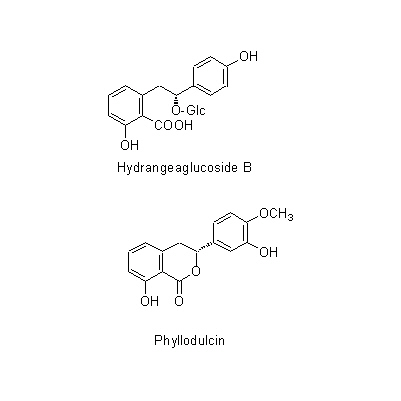
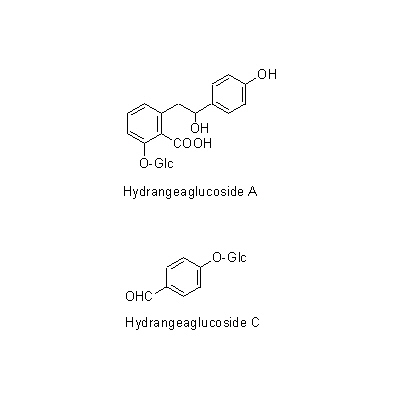
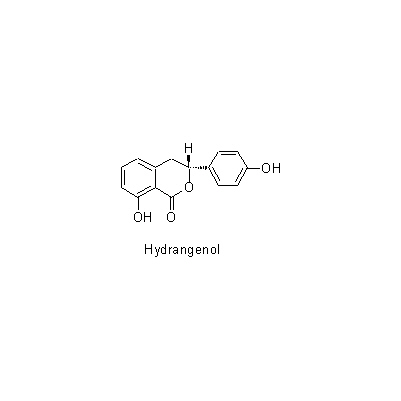
| Chemical constituent | Phenylpropanoids (*C2): Chlorogenic acid Flavones & Flavonols (*C2): Kaempherol, Quercetin, Rutin Coumarins (*C2): Umbelliferone Isocoumarins (*C1,C2): d-Phyllodulcin, Hydrangenol Phenol derivatives (*C1): Hydrangea-glucoside A, Hydrangea-glucoside B, Hydrangea-glucoside C (*C2): p-Hydroxybenzoic acid, Gallic acid | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Not exactly known. | |||||
| Formulation | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 86-87. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, pp 292-293. | |||||
| Remarks | Since the leaves are kneaded and slightly fermented, they are crimpled. Though raw leaves have no sweetness, the process (kneading, fermenting and so on) results in phyllodulcin which is the hydrolysate and the component of sweetness. The history of its medicinal use is short. Amacha was used as amachato, the extract of Amacha, at Kanbutsue, the celebration for Buddha's birthday (April 8th) in Edo period. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/03/03 | |||||