Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.341574
108.93976999999995
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Xi 'an
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
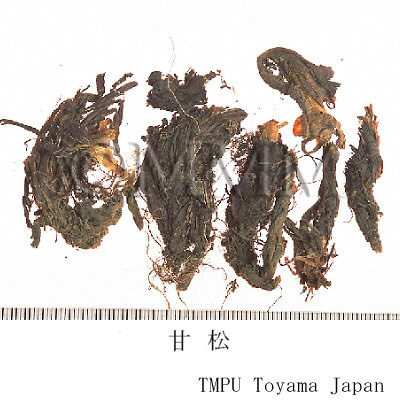
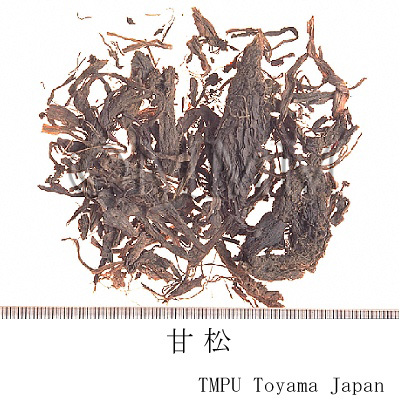
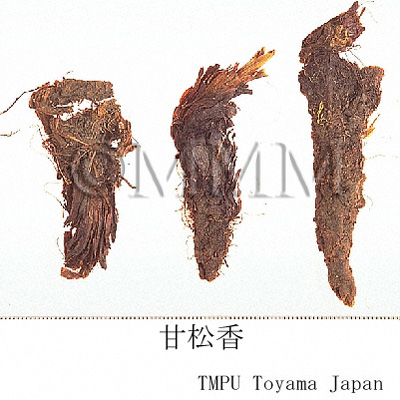
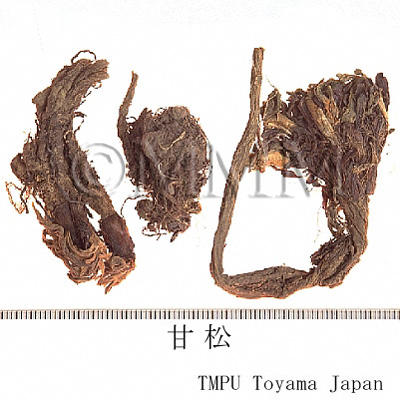
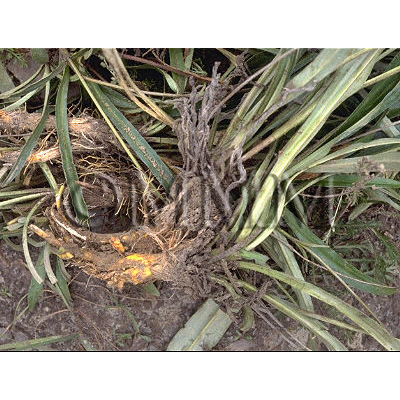
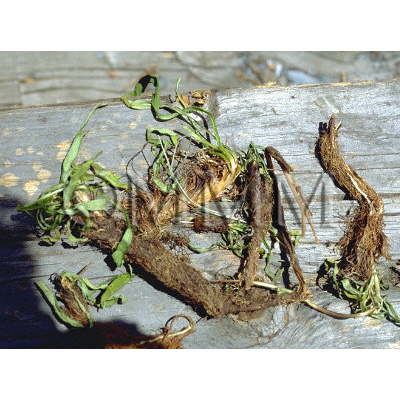
| Common name | 甘松香, Gansongxiang, Nardostachys Radix et Rhizoma (CP2020), Nardostachys Root (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 甘松(Gansong) | ||||||
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
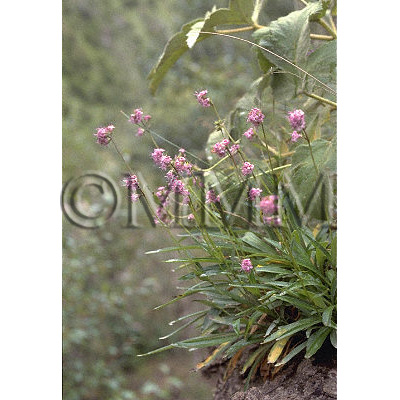
| Original plant name | Nardostachys chinensis Batalin, Nardostachys jatamansi DC. (= Nardostachys grandiflora DC.) (B1) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Valerianaceae | ||||||
| Used part | rhizome | ||||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an analgesic, sedative and stomachic, it is applied to treat chest and abdominal pain with a fullness sensation, stomachache, vomiting, lack of appetite and insistent diarrhea. Its decoction is used for hot compress which is applied for edema due to beriberi. Nowadays, it is used for incense more frequently than for a medicine. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Carminatives for regulating flow of Qi | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent and sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen and stomach meridians. [Actions] To regulate qi and relieve pain, resolve depression and enliven the spleen; topical application: to dispel dampness and disperse swelling. [Indications] Distention and fullness in the epigastrium and abdomen, anepithymia, vomiting, and topically toothache, beriberi with swelling and toxin. | ||||||
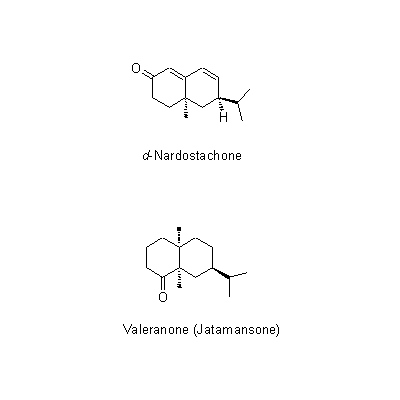
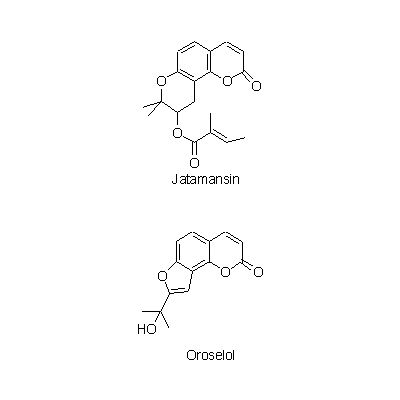
| Chemical constituent | Terpenoids (Essential oils) N. grandiflora (*C1): d-Nardostachone Sesquiterpenoids N. grandiflora (*C1): Valeranone Coumarins N. grandiflora (*C1): Jatamansin, Oroselol | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Sedation. | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AF446950 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Feeling of pressure in the chest, Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Anorexia, Beriberi edema, Diarrhea, Vomitting | ||||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | ||||||
| Related drugs | Jatamansi (Ayurveda), sPang-spos (Tibetan Medicine) | ||||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1)Nat.Med.,53(2),61-71(1999). C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 50-51. | ||||||
| Remarks | "Jatamansi" and "sPang-spos" are the root or rhizome of Nardostachys grandiflora. "Jatamansi" is applied for hysteria, schizophrenia, spasm, hypertension, loose hair, gray hair, dysmenorrhea, insomnia and excitement in Ayurveda (Traditional Indian Medicine). "sPang-spos" is used for removing heat and counteracting toxicity, removing edema with cold of deficiency type, bone-setting and draining pus in Tibetan Medicine. It is applied for epidemic fever, febrile illness and dermatitis. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/28 | ||||||