Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
40.842356
111.74999500000001
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Hohhot City
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
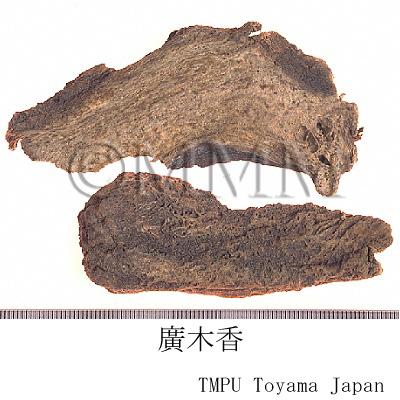
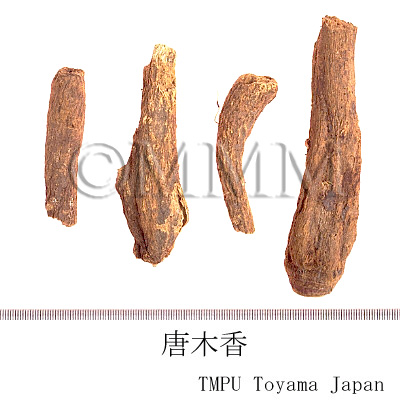
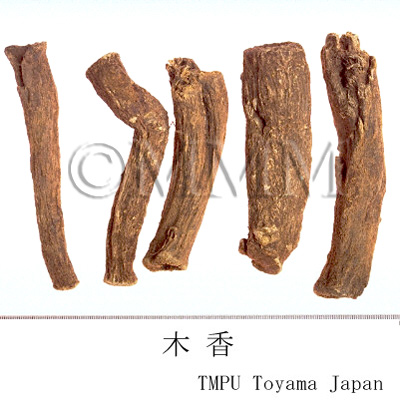
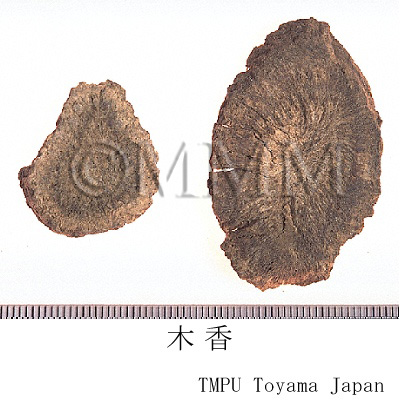
| Common name | 木香, Muxiang, Saussureae Radix (JP18), Aucklandiae Radix (CP2020), Saussurea Root (JP18), Common Aucklandia Root (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 唐木香, インド木香, 広木香, 雲木香, 老木香 | ||||||
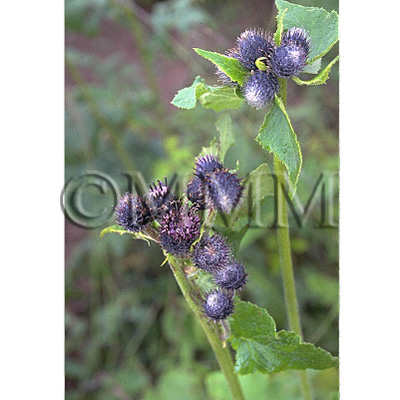
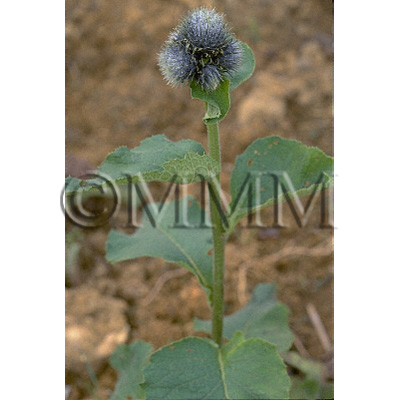
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
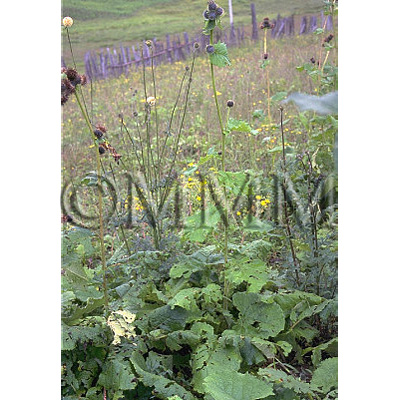
| Original plant name | Saussurea lappa Clarke (= Aucklandia lappa Decne.) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Compositae | ||||||
| Used part | root | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good one is enlarged, dense and has a strong odor. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a stomachic and intestinal remedy, it is applied to treat vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, indigestion and parasitic diseases. It is also used as an incense. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Carminatives for regulating flow of Qi | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent and bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, stomach, large intestine, triple energizers and gallbladder meridians. [Actions] To move qi and relieve pain, fortify the spleen to promote digestion. [Indications] Distending pain in the chest, hypochondrium, epigastrium and abdomen, tenesmus caused by diarrhea and dysentery, food accumulation, no desire for food and drink. | ||||||
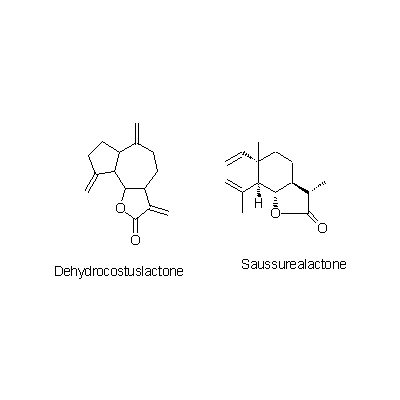
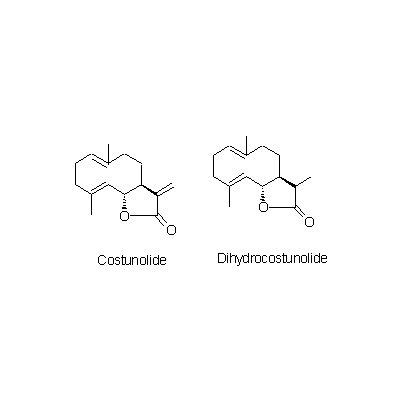
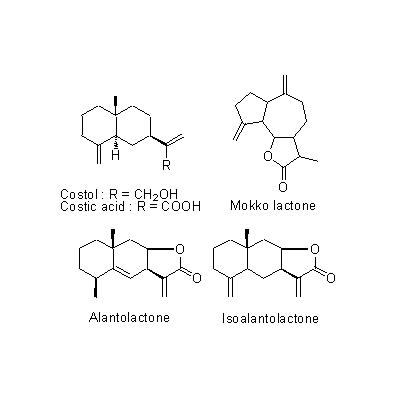
| Chemical constituent | Lipids (*C1): Aplotaxene Sesquiterpenoids (*C1-C4): alpha-Ionone, Dehydrocostus lactone, Saussurea lactone, Costunolide, Dihydrocostunolide, alpha-Costol, beta-Costol, gamma-Costol, beta-Costic acid, beta-Cyclocostunolide, Alantolactone, Isoalantolactone, Isodehydrocostus lactone, Isozaluzanin C, Mokkolactone, Saussureal Triterpenoids (*C1): Betulin Sterols (*C1): Stigmasterol | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antimicrobial effect (essential oil components: Hypococcus, Bacteroides), vasodilation, smooth muscle relaxation (saussurine). | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Nausea, Vomitting, Constipation, Diarrhea, Tenesmus, Dyspepsia, Anorexia | ||||||
| Formulation | Ureitsukito, Kagenshosaikoto, Kamikihito, Kikyoto, Kihito, Kyukihochuto, Kumibinroto, Kobokuto, Kowashakuyakuto, Goshitsusan, Sanshoin, Shichimibyakujutsuto, Jippito, Shakuyakuto, Jurokumiryukiin, Shobaito, Jinsoin, Zenshikunshito, Zenshibyakujutsusan, Chuseito, Chokoshiteito, Dosuibukuryoto, Dotaitsukeito, Naisoorento, Nyoshinsan, Haikanpo, Baimoto, Bunshoto, Boisan, Boito, Botanpisan, Honposhakuyakuto, Rogyokuto, Koshayoito | ||||||
| Related drugs | Aristolochiae Radix,Vladimiriae Radix,Inulae Radix,Inulae Racemosae Radix See "Remarks". | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 40-42. C2) Chem. Pharm. Bull., 12, 632 (1964). C3) Tetrahedron, 13, 319 (1961). C4) Phytochemistry, 31, 336 (1992). | ||||||
| Remarks | "Muxiang" (木香) derived from the root of Saussurea lappa Clarke (= Aucklandia lappa) Decne. of family Compositae is the genuine, and was called "Qingmuxiang" (青木香, Jap. name: Seimokkō) in ancient times. The present "Qingmuxiang" is derived from the roots of Aristolochia debilis Sieb. et Zucc. (Jap. name: Umanosuzukusa) and Aristolochia contorta Bunge (Jap. name: Marubaumanosuzukusa) of family Aristolochiaceae. "Chuanmuxiang" (川木香, Jap. name: Semmokkō) is the root of Vladimiria souliei (Franch.) Ling, which is usually prepared by burning the root head. It was once used as "Cangmuxiang" (蔵木香, Jap. name: Zōmokkō) Inula racemosa Hook. f. erroneously. "Tumuxiang" (土木香, Jap. name: Domokkō) is the root of Inula helenium L. of family Compositae. Other "Yueximuxiang" (越西木香)" in Chinese market is the root of Vladimiria denticulata Ling. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/01/23 | ||||||