Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
40.842356
111.74999500000001
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Hohhot City
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
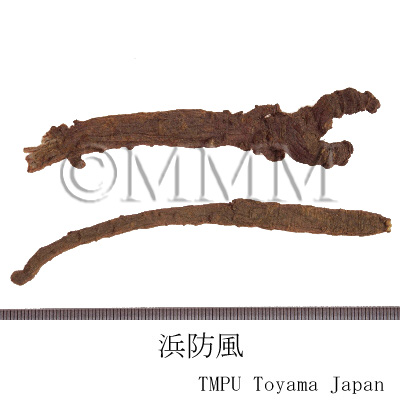
| Common name | 浜防風 (北沙参), Hamabōhū (Beishashen), Glehniae Radix cum Rhizoma (JP18), Glehniae Radix (CP2020), Glehnia Root and Rhizome (JP18), Coastal Glehnia Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 北沙参 (Beishashen) | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
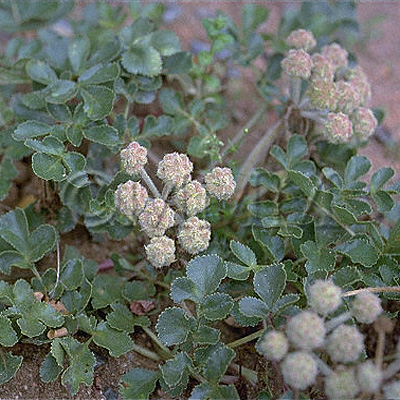
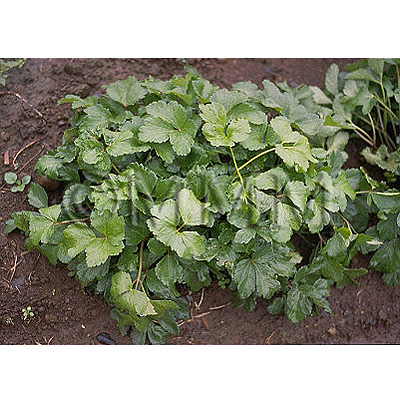
| Original plant name | Glehnia littoralis F. Schmidt ex Miquel, (Hamabofu) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Umbelliferae | |||||
| Used part | root and rhizome | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Hamabofu is yellowish-white and has a fragrant odor. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a diaphoretic, antifebrile and painkiller, beishashen is applied for cold and other disease. It is an ingredient of Tososan. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for replenishing Yin-vital essence | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; sweet and mild bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and stomach meridians. [Actions] To nourish yin and clear the heat, boost the stomach and engender fluid. [Indications] Lung heat and dryness cough, phlegm and cough with blood caused by consumptive disease, stomach yin deficiency, heat disease consuming fluid, dry throat and thirst. | |||||
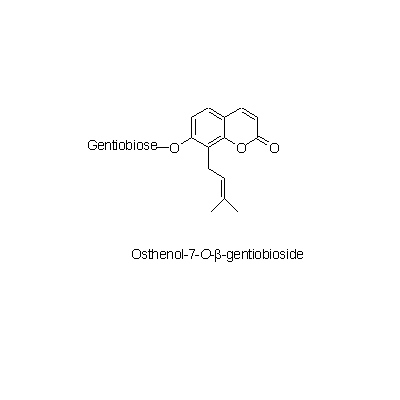
| Chemical constituent | Coumarins (*C1): Psoralen, Imperatorin, Bergapten, 8-Geranyloxypsoralen, Osthenol-7-O-beta-gentiobioside | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antipyretic, mild analgesia (ethanol extract). | |||||
| DNA sequence | D63490, D44568 | |||||
| Disease | Dry cough, Few sputum, Fever, Phlegm-free, Sputum with blood, Heat, Thirst | |||||
| Formulation | ||||||
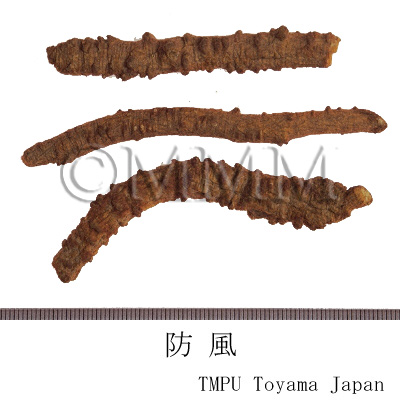
| Related drugs | Saposhnikoviae Radix | |||||
| References | (JP18): The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. (CP2020): Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 81-83. | |||||
| Remarks | In Japan, "Hamabōhū" is blended in substitution for "Bohū" (Saposhnikoviae Radix) in Kampo formulation. In China, the barked root of "Hamabōhū" is called "Beishashen" (Jap. name: Hokushajin). Generally, "Beishashen" is called "Shashen" (Jap. name: Shajin), while in Japan, "Nanshajin", the root of genus Adenophora of family Campanulaceae, is called "Shajin". | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/03/23 | |||||