Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 款冬花, Kuandonghua, Tussilaginis Flos (Non-JPS2022), Farfarae Flos (CP2020), Coltsfoot Flower (Non-JPS2022), Common Coltsfoot Flower (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 霊台冬花,山西冬花 | |||||
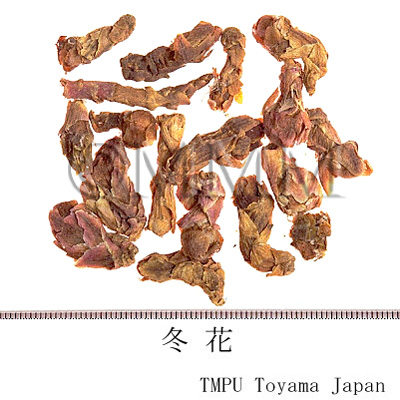
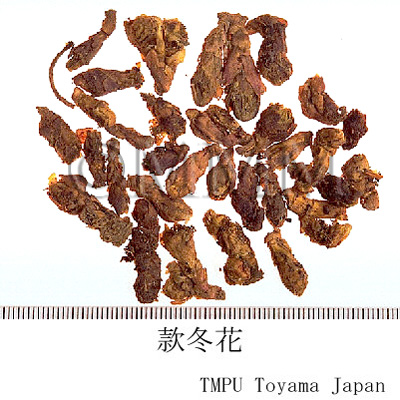
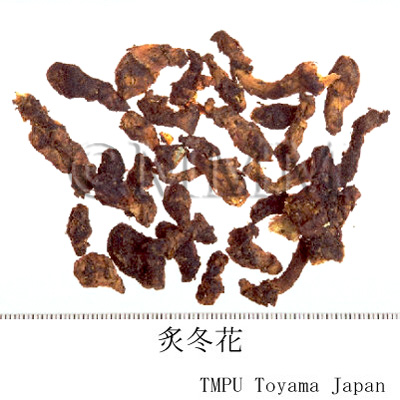
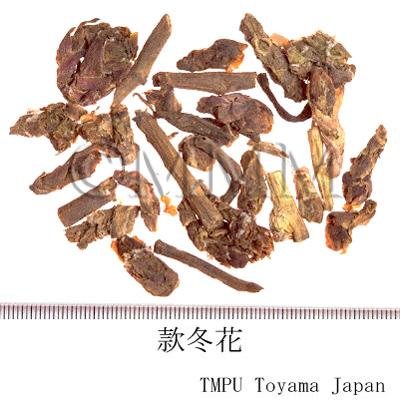
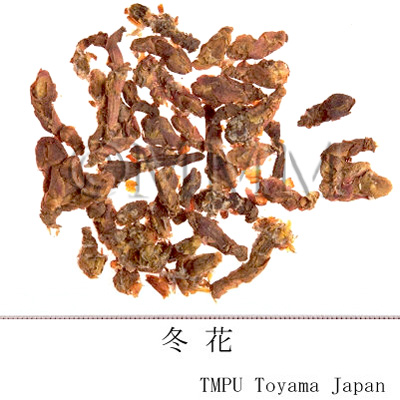
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Tussilago farfara Linn., (Fukitampopo) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Compositae | |||||
| Used part | flos | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good one is fresh and it consists of half-opend buds with no dirts. (NI) | |||||
| Official compendium | Non-JPS (2022), CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antitussive and expectorant, Kuandonghua is applied for cough, blocked airway, lung abscess, lung atrophy and hematemesis. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Antitussives and antiasthmatics | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent, mild bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Lung meridian. [Actions] To moisten the lung and direct qi downward, suppress cough and resolve phlegm. [Indications] Acute and chronic cough, panting and cough with profuse sputum, cough caused by consumptive disease with hemoptysis. | |||||
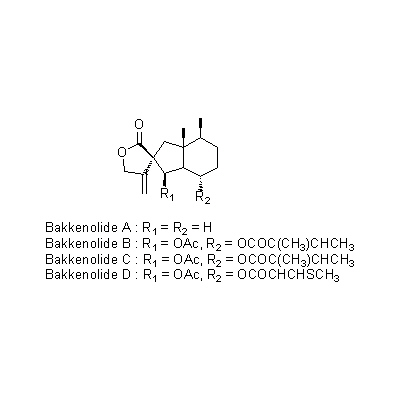
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids Petasites japonicus (*C1): Caproic acid, Caprylic acid Other aliphatic and related compounds Petasites japonicus (*C1): Angelic acid, Butylaldehyde, l-Nonane, Terpene alcohol Tussilago farfara (*C1): Parafin Monosaccharides Petasites japonicus (*C1): Fructose, Glucose Sesquiterpenoids Petasites japonicus (*C1): Bakkenolide A, Bakkenolide B, Bakkenolide C, Bakkenolide D Carotenoids Tussilago farfara (*C1,C2): Taraxanthin Sterols Tussilago farfara (*C1,C2): l-Phytosterol, Faradiol Flavones & Flavonols Petasites japonicus (*C1): Quercetin, Kaempferol Tannins Tussilago farfara (*C1): Tannin Others Petasites japonicus (*C1): 苦味質/Amaroid, KCl | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antipyretic (water extract). | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Cough, Sputum with blood | |||||
| Formulation | Hohaito, Yakammaoto, Chimobukuryoto | |||||
| Related drugs | Kuandongye: leaves of Tussilago farfara, Kuandonggen: roots of T. farfara, Wakantōka: flowers of Petasites japonicus and Fukinotō: flower buds of P. japonicus . | |||||
| References | Non-JPS2022: The Japanese standards for non-Pharmacopoeial crude drugs 2022. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 128-130. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p221. | |||||
| Remarks | The leaves of Tussilago farfara L. ( Jap. name: Fukitampopo), which directly grow from the root are called Kuandongye, and the root of it is called Kuandonggen. They are used as antitussive and expectorant, as well as Kuandonghua. Fukitampopo is well distributed in the continent of Eurasia. The leaves are called Farfarae Folium in Europe and are applied to relieve coughs such as bronchial catarrh. Long ago, Dioscorides said "If you put the beaten leaves on rubors on the skin, erysipelas and all the other inflammatory regions, they will be cured. It will cure the people who are orthopneic because of dry cough or other transient reasons, if they fumigate dried leaves and inhale the smoke through a pipe. The smoke also induces expectoration of abscess in the lung. The fumigated smoke of the roots has the same benefits. If a pregnant woman drinks the brewed roots with honey water, she will abort a dead fetus." Since then, these benefits have been handed down. Wakantōka, Japanese Kuandonghua, is the flos of Petasites japonicus (Sieb. et. Zucc.) Maxim., butterbur of family Compositae. Generally, it is sold as Fukinotō and is also used to alleviate cough and remove phlegm. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/09/01 | |||||