Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 附子, Fuzi, Aconiti Radix Processa (JP18), Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata (CP2020), Processed Aconite Root (JP18), Prepared Common Monkshood Daughter Root (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 加工附子, 塩附子, 炮附子, 黒附片, 白河附子 | ||||||
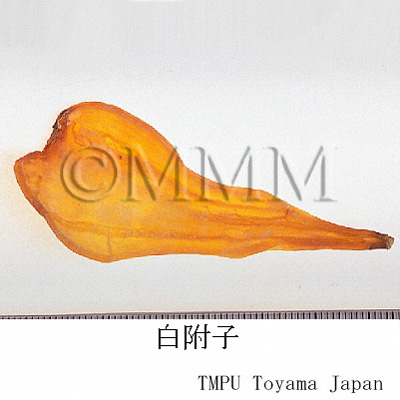
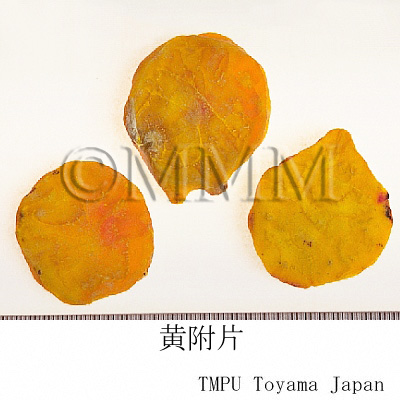
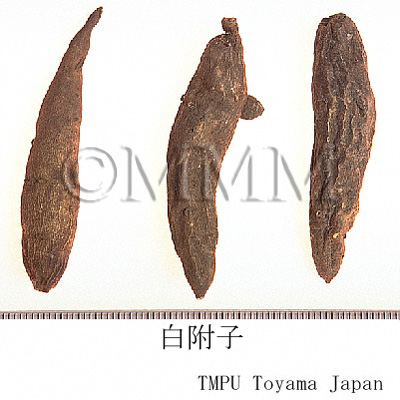
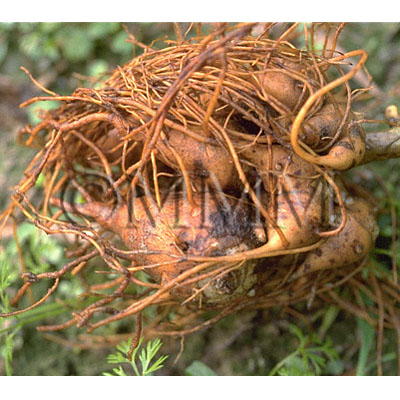
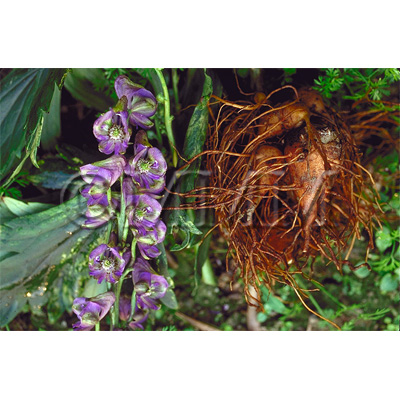
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
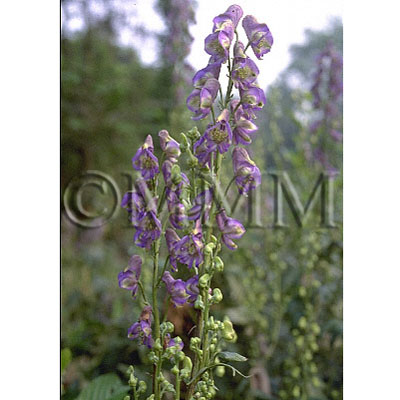
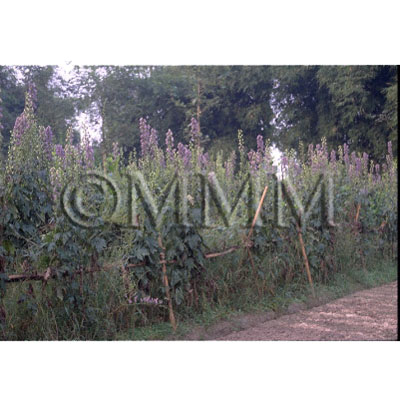
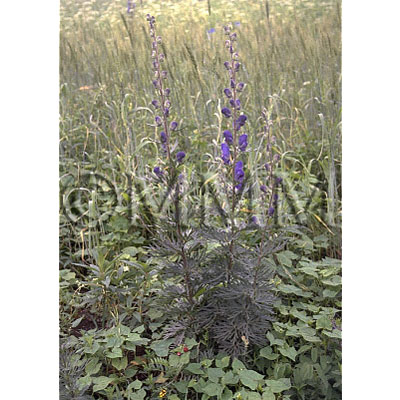
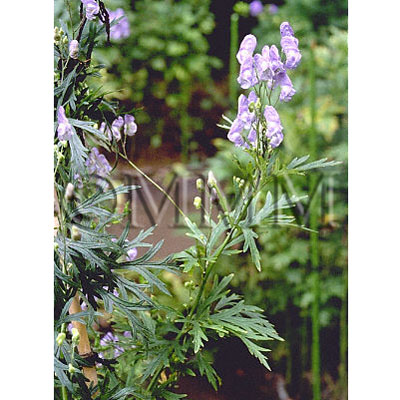
| Original plant name | CN production: Aconitum carmichaeli Debeaux1, JP production: Aconitum japonicum Thunberg2, (Hanatorikabuto1, Okutorikabuto2) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Ranunculaceae | ||||||
| Used part | tuber (lateral root), harvested from late June to early August. | ||||||
| Quality for selection | The best Fuzi is the size of hen's egg. (NI) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a tonic, diuretic, cardiotonic and painkiller, Fuzi is applied for metabolic dysfunction, joint paralysis and pain of limbs and disease due to relaxation of internal organs such as invalid's stomachache, diarrhea and pollution. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for dispelling internal cold | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Highly hot; pungent and sweet; toxic. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, kidney and spleen meridians. [Actions] To restore yang, induce resuscitation, tonify fire and assist yang, dissipate cold and relieve pain. [Indications] Yang collapse, coldness of limbs and faint pulse, deficiency of heart yang with chest impediment and heart pain, deficiency cold vomiting and diarrhea, cold pain in the epigastrium and abdomen, debilitation of kidney yang, impotence and uterine coldness, yin-cold edema, external contraction with yang deficiency, and cold-dampness arthralgia. | ||||||
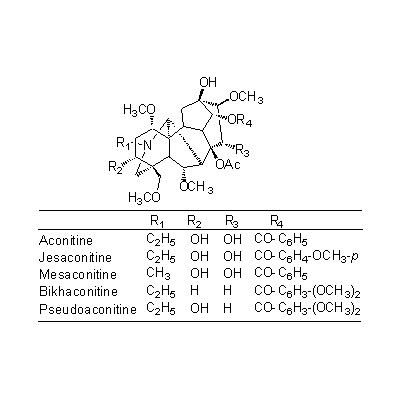
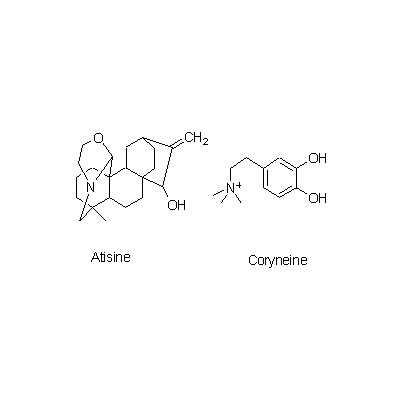
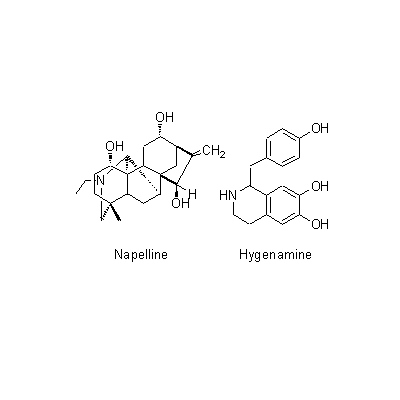
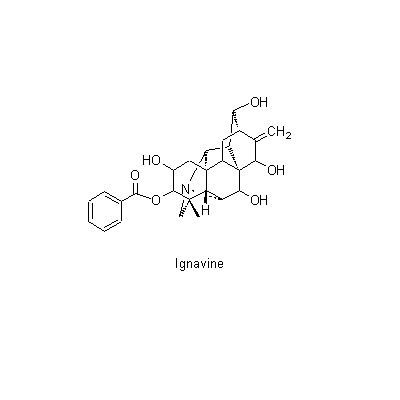
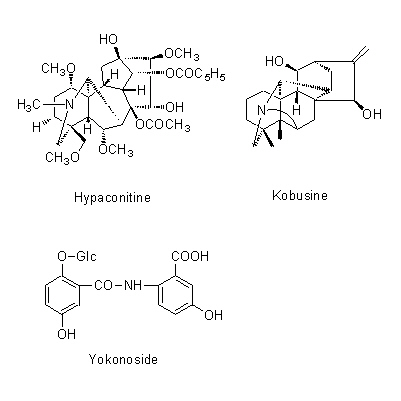
| Chemical constituent | Alkaloids A. carmichaeli (*C1): Aconitine, Hypaconitine, Mesaconitine, Carmichaeline, Talatisamine, Coryneine chloride A. japonicum (*C1): Aconitine, Mesaconitine, Hypaconitine, Hygenamine Aconitum spp. (*C2): Aconitine系 (type):Aconitine, Hypaconitine, Mesaconitine, Jesaconitine, Neopelline, Atisin系 (type):Atisine, Kobusine, Pseudokobusine, Telatisine, Songorine, Atidine, Napelline, Heteratisine, Hypognavine, Ignavine, 強心成分 (Cardiotonic compounds):Hygenamine, Coryneine, Yokonoside, etc. A. ferox (*C1): Pseudoaconitine A. heterophyllum(*C1): Atidine, Atisine, Hetisine, Heteratisine, Benzoylheteratisine A. napellus (*C1): Songorine, Napelline, Hypaconitine, Mesaconitine, Neopelline, Neoline, Aconine, Benzoylaconine, Aconitine, Napellonine | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Sedative,suppression of stress ulcer (extract).Sedative,hypotensive,induction of arrythmia (aconitine),cardiotonic (hygenamine, coryneine).Analgesic and antiinflammatory (mesaconitine). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AB020369, AB020370, AB020371, AB020372, AB020373, AB020374; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Pallor of the face, Cyanosis, Coldness of limbs, Weak pulse, Spontaneous sweating, Heaviness and powerlessness in lumber and knee, Frequent urination, Sexual problem, Muddy and watery stool, Lower back pain, Oliguria, Full stomach, Swelling and pain of joint, Numbness, Chill | ||||||
| Formulation | Akyobushito, Uzushakusekisigan, Unpito, Kaikyushokushoto, Kakkonkaryojutsubuto, Kankyobushito, Kanzobushito, Kinkohojutsubuto, Keikyososooshinbuto, Keishikajutsubuto, Keishikaryojutsubuto, Keishikyoshakuyakukamaobushisaishinto, Keishishakuyakuchimoto, Keishinieppiittokaryojutsubu, Keishibushito, Kobokuto, Goshajinkigan, Sanshoin, Shigyakuto, Shigyakukaninjinto, Shakukan'oshinbuto, Shakuyakukanzobushito, Shakuyakukanzobushidaioto, Shokanto, Shozokumeito, Jokinritsuansan, Shimbuto, Seikanto, Sogento, Daiobushito, Daisangoshichisan, Daitokato, Daibofuto, Danrito, Chikuyoto, Chokobukuryoto, Choburichuto, Tsumyakushigyakuto, Hachimigangoninjinto, Hachimijiogan, Hanbikokantan, Byakujutsubushito, Bukuryoshigyakuto, Hojinto, Hontonto, Maokaryojutsubuto, Maobushikanzoto, Maobushisaishinto, Yokuibushihaishosan, Rikakuto, Rokumotsubushito | ||||||
| Related drugs | wutou, tianxiong | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 91-97. C2) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, pp 304-305. | ||||||
| Remarks | The Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China defines "Fuzi (附子)" as the processed tuber (lateral roots) of Aconitum carmichaeli. The processed aconite root, which is compressed and heated, is used for many kinds of Kampo drug products. Since aconitum alkaloids have strong toxicity, there are many processes to reduce it. It is called "Yanfuzi (塩附子)," "Paofuzi (炮附子)," "Heifupian (黒附片)" or "Baifupian (白附片)" depending on each process. - Chinese "Yanfuzi (塩附子)", the tuber of Aconitum carmichaeli, is half dried after rinsed in the solution of salt water and bittern. - "Paofuzi (炮附子)" is the dried "Yanfuzi (塩附子)" after being peeled and divided lengthwise. - Both "Heifupian (黒附片)" and "Refupian (熟附片)" are made as follows : rinse roots in bittern, divide them lengthwise, stain with dye stuff, dry after steaming. - Though "Baifupian (白附片)" is the similar product to "Heifupian (黒附片)", it is barked and smoked by sulfur untill it becomes white at its final process. The Japanese "Shirakawa-bushi," the tuber of Aconitum japonicum, is made as follows : rinse it in salt water, coat with lime and dry. It is mentioned in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia that there are three ways in processing the aconite tuber. 1: Autoclaving. 2: Heating or autoclaving after rinsing in salt or rock salt solution. 3: Treating with calcium hydroxide after rinsing in salt solution. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | ||||||