Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
30.572815
104.06680099999994
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Sichuan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 忍冬, Rendong, Lonicerae Folium cum Caulis (JP18), Lonicerae Japonicae Caulis (CP2020), Lonicera Leaf and Stem (JP18), Japanese Honeysuckle Flower (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 忍冬藤, 金銀藤, 銀花藤 | |||||
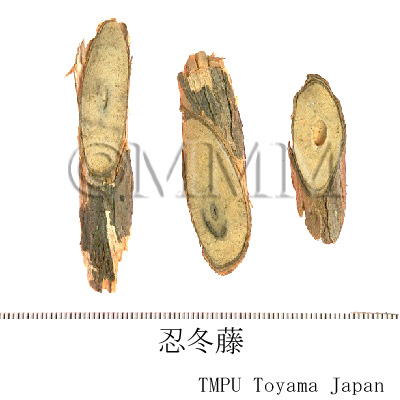
| crude drug image |
| |||||
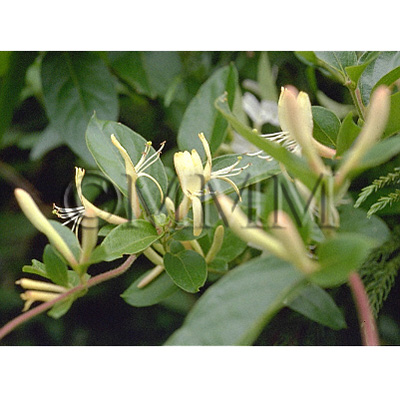
| Original plant name | Lonicera japonica Thunberg, (Suikazura) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Caprifoliaceae | |||||
| Used part | stem or stem with leaves | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Rendong is fresh and bright green. (NI) Ginkatō, produced in Giangsu Prov., is the best quality. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JHMC (1989), JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antifebrile, antidote, diuretic and antiinflammatory, Rendong is applied to treat swelling, hemorrhoids, gonorrhea, oliguria and poisoning of toadstool, in folk. The concentrated decoction may be used for swelling and hemorrhoids. It is also applied for muscle and bone pain. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Febrifugal and detoxicant drugs | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and stomach meridians. [Actions] To clear heat and remove toxin, disperse wind and unblock the collaterals. [Indications] Warm disease with fever, heat-toxin blood dysentery, swelling abscess, , sore and ulcer, wind-dampness heat impediment, red, swelling, heat and painful joint. | |||||
| Chemical constituent | Flavones & Flavonols (*C1): Lonicerin (= Luteolinrhamnoglucoside) Tannins (*C1): タンニン | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Increase in blood sugar. | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF207727,AF207728,AF207729,AF207730,AF207731,AF207732,AF207733,AF207734 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Pyogenic dermatosis, Swelling and pain of the throat, Diarrhea, Hematochezia, Fever, Rash, Chill, Swelling and pain of joint | |||||
| Formulation | Jizusoippo, Kagawagedokuzai, Shikonboreito, Katsuketsugedokuto, Shogedokuto | |||||
| Related drugs | Lonicera Flower | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 172-173. | |||||
| Remarks | In China, Rendong is generally called Jinyinteng (Jap. name: Kingintō) and the infant branch with leaves is called Jinhuateng (Jap. name: Ginkatō). In Japan, it is sold under the name of Nindō, which has less effect in removing toxic heat than Jinyinhua (Jap. name: Kinginka) but stronger effect in expelling wind and promoting flow of meridians. It is widely used as folk medicine as well. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||