Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
36.6512986
138.18095570000003
Production area information
Japan,Nagano Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 敗醤草, Baijiangcao, Thlaspi Herba (CP2020: 菥蓂), Boor's Mustard Herb (CP2020: 菥蓂) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 敗醤根, Baijianggen, Patriniae Radix | |||||
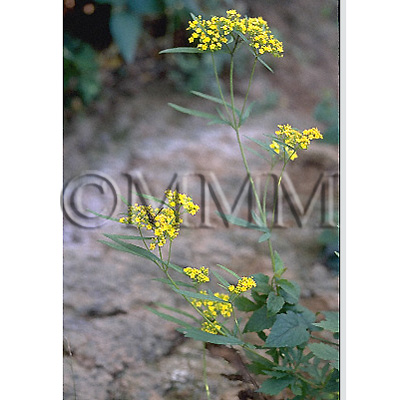
| crude drug image |
| |||||
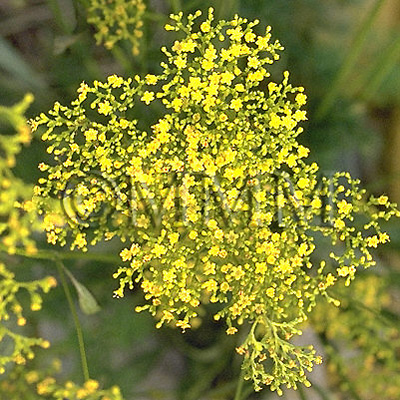
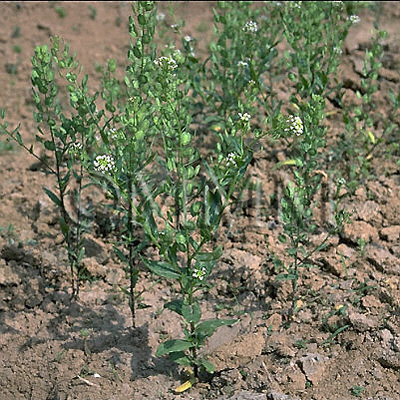
| Original plant name | Patrinia villosa Juss.<オミナエシ科/Valerianaceae>1, Thlaspi arvense L.<アブラナ科/Brassicaceae>2, Sonchus brachyotus DC.<キク科/Asteraceae/Compositae>3, [Otokoeshi1, Genbainazuna2, Hachijōna3] | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Used part | root1, whole plant with fruit2, whole plant with root3 | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | P. villosa: Removing inflammation or blood stasis, and draining pus. It is applied in the treatment of tumor, edema, leukorrhea and abdominal pain after childbirth and all. T. arvense: Applied to eye disease as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Febrifugal and detoxicant drugs | ||||
| Beneficial effect | P. villosa: [Property and Flavor] Cool; pungent, bitter [Meridian Tropism] Stomach, large intestine and liver meridians. [Actions] To clear away heat and toxic material, to clear abscess and to drain pus, to eliminate blood stasis and relieve pain. [Indications] Carbuncle of bowel and lung, abscess and sores, blood stasis, chest and abdominal pain, hyperemesis and stomach ache of after childbirth | |||||
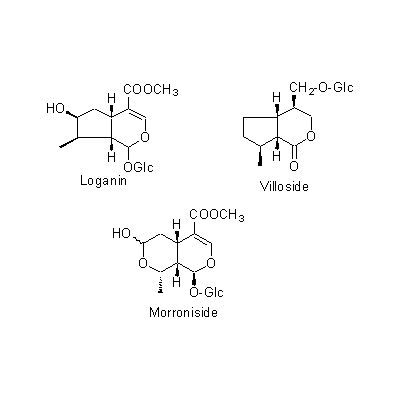
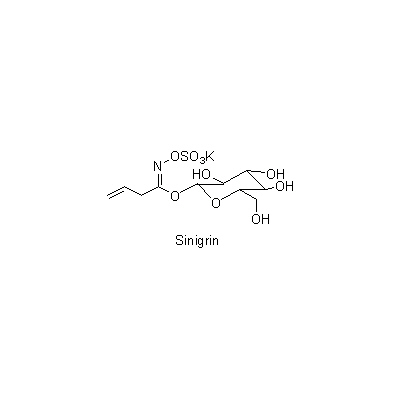
| Chemical constituent | Monoterpenoids P. villosa (根および根茎/root & rhizome) (*C1): Loganin, Villoside, Villoside tetraacetate, Morroniside Glucosinolate T. arvense (全草および種子/whole plant & seeds) (*C1): Sinigrin Others T. arvense (全草および種子/whole plant & seeds) (*C1): Myrosin(酵素/enzyme) | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antibacterial (Staphylococcus aureus)and sedative. | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF144360, AF016841; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Lung suppurations, Pyogenic dermatosis, Chest pain, Abdominal pain, Appendicitis | |||||
| Formulation | Kikyoto, Yokuibushihaishosan | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 64-66. | |||||
| Remarks | The genuine "Baijiangcao (敗醤草)" is P. villosa of family Valerianaceae (Jap. name: Otokoeshi). At present, there are two kinds of "Baijiangcao (敗醤草)" in China. In northern district, S. brachyotus of family Compositae (Jap. name: Hachijōna) is used. Instead, T. arvense of family Cruciferae (Jap. name: Gumbainazuna) is used in southern district. Japanese Baijiangcao is the root of P. villosa of family Valerianaceae (Jap. name: Otokoeshi). Note that each beneficial effect is different. It depends on the original plant. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||