Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
24.880095
102.83289100000002
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Yunnan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
24.880095
102.83289100000002
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Yunnan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
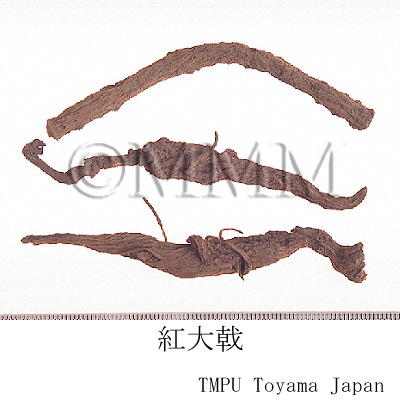
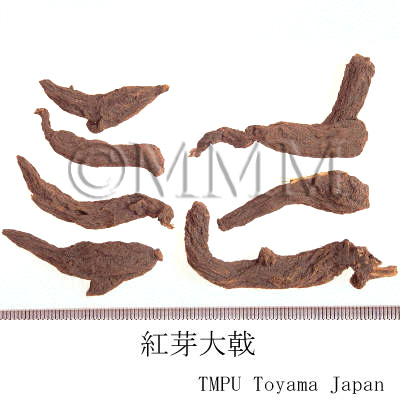
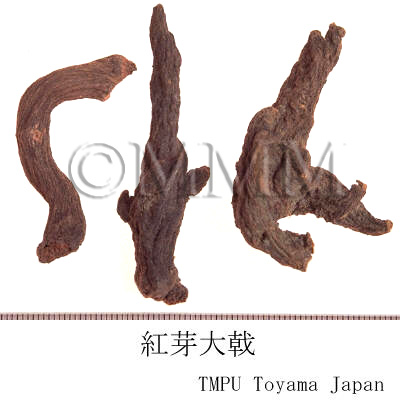
| Common name | 紅芽大戟, Hongyadaji, Knoxiae Radix (CP2020), Knoxia Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 紅大戟, 大戟 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Knoxia valerianoides Thorel ex Pitard | |||||
| Family name | Rubiaceae | |||||
| Used part | root | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antidote, laxative and for curing sores, Hongyadaji is applied for dropsy, a feeling of fullness in the chest, retention of phlegm, carbuncles and sores. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Purgatives for removing water retention | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter; slightly toxic. [Meridian Tropism] Lung, spleen and kidney meridians. [Actions] To expel retained fluid by purgation, disperse swelling and dissipate binds. [Indications] Edema distention and fullness, hydrothorax and ascites, phlegm-fluid retention, aggregation and accumulation, cough and panting caused by qi counterflow, inhibited of defecation and urination, swelling abscess, sore and toxin, scrofula and phlegm nodule. | |||||
| Chemical constituent | Anthraquinones (*C1): アントラキノン誘導体/Anthraquinone derivatives | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Not exactly known. | |||||
| DNA sequence | AJ288631 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 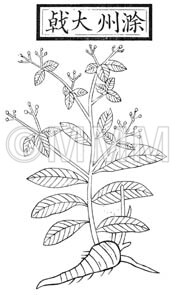 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Ascites, Edema, Oliguria, Constipation, Pleural effusion, Pain due to flatulence of hypochondrium, Pyogenic dermatosis, Cervical lymphadenopathy, Subcutaneous nodule | |||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||||
| Related drugs | Jingdaji: the root of Euphorbia pekinensis Rupr. of family Euphorbiaceae, Caodaji: the root of Lespedeza sp. of family Leguminosae | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, p 14-15. | |||||
| Remarks | At present, three species of Daji (大戟) are distributed in China, Hongyadaji (紅芽大戟) of family Rubiaceae, Caodaji (草大戟) of family Leguminosae and Jingdaji (京大戟) of family Euphorbiaceae. Though each plant belongs to a different family, they are all called Daji. By nature, the real Daji described in materia medicas is Jingdaji. However, only Hongyadaji is imported to Japan at present. Jingdaji: the root of Euphorbia pekinensis Rupr. of family Euphorbiaceae. Once, it was used in Jiangsu Prov., Shanghai city and a part of Anwhei Province. In an area of Jiangsu Prov., the root of Indigofera sp. of family Leguminosae is used as Caodaji. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||





