Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 荊芥, Jingjie, Schizonepetae Herba (JP18), Schizonepetae Spica (CP2020), Schizonepeta Spike (JP18), Fineleef Schizonepeta Spike (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
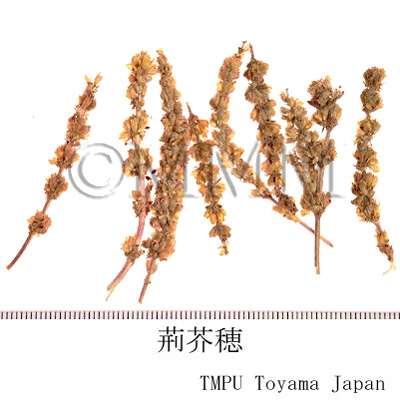
| Synonyms | 荊芥穂 (Jingjiesui) | |||||
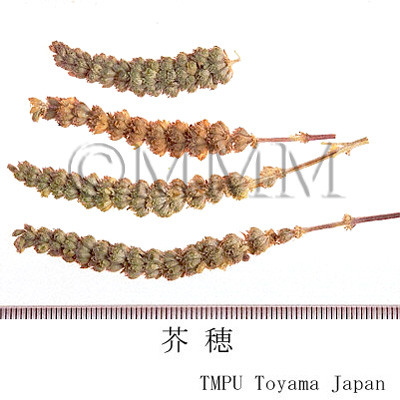
| crude drug image |
| |||||
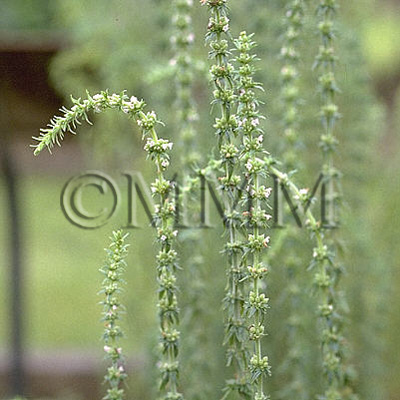
| Original plant name | Schizonepeta tenuifolia Briquet, (Keigai) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Labiatae | |||||
| Used part | aerial part or spike | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Jingjie is fresh and has a strong aroma. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a diaphoretic, antifebrile, carminative, antispasmodic and hemostatic, Jingjie is applied for early stage of cold, headache, sore throat, wound, skin disease, disorder of after childbirth, hematemesis, epistaxis, hematochezia and metrorrhagia and metrostaxis. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diaphoretics with warm property | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild warm; pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and liver meridians. [Actions] To release the exterior and disperse wind, promote eruption, relieve sore. [Indications] Common cold, headache, measles, rubella, early onset of sore and ulcer. | |||||
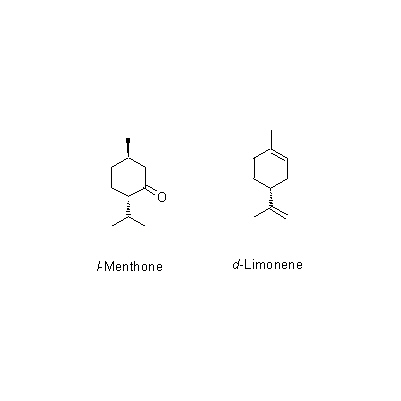
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): 3-Octanone, 3-Octanol, 1-Octen-3-ol Monoterpenoids 精油約/essential oil about 1.8% (*C1): d-Menthone, l-Menthone, d-Limonene, l-Pulegone, l-Isomenthone, Isopulegone, alpha-Pinene, beta-Pinene, Camphene, Piperitone, Piperitenone, Schizo-nepetoside A, Schizo-nepetoside B, Schizo-nepetoside C, Schizo-nepetoside D, Schizo-nepetoside E Sesquiterpenoids (*C1): Caryophyllene, beta-Elemene, beta-Humulene Flavones & Flavonols (*C1): Diosmetin, Hesperetin, Luteolin | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Slight antipyretic, antipruritus, antibacterial (tubercle bacillus). | |||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 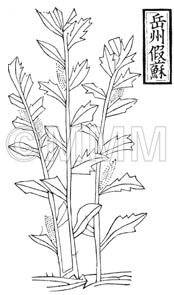 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Common cold, Chill, Fever, Headache, Sore throat, Measles, Rubella, Itching, Pyogenic dermatosis, Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage, Hematochezia | |||||
| Formulation | Kufugedokusan, Keigairengyoto, Jumihaidokuto, Shofusan, Seijobofuto, Senkyuchachosan, Jizusoippo, Tokiinshi, Bofutsushosan, Keigairengyoto, Senkanmeimokuto, Katsuketsugedokuto, Gyokusuito, Kufugedokusan, Shaito, Seiinrikakuto | |||||
| Related drugs | The flower of Ocimum basilicum L. | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 52-53. | |||||
| Remarks | Schizonepete multifida Briq. or Elsholtia ciliata (Thunb.) Hylander (Jap. name: Naginatakōju) are thinly marketed as Jingjie in Northwest China. Salvia plebeia R.Br. and Origanum vulgare L. (Oregano, or Hanahakka in Jap. name) are called Jingjie in Guangdong Prov. Moreover, Ocimum basilicum L. (Basil) in Hubei Prov. and Nepeta cataria L. (Jap. name: Inuhakka) in Yunnan and Shanxi Prov. are called Jingjie. Various species of plants are used as a herbal drug called Tujingjie. In ancient times, Raroku (Jap. name) was used as a species of Jingjie, or Jiasu. These days, Raroku, which is the whole plant of Ocimum basilicum L., is harvested during the flowering period. It is used to improve blood circulation after childbirth and to treat gastric cramp, renal disease, etc. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/02/17 | |||||