Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 防已 (日本産/JP production), Bōi, Sinomeni Caulis et Rhizoma (JP18), Sinomenium Stem and Rhizome (JP18) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 漢防已, 青風藤, 青藤 | ||||||
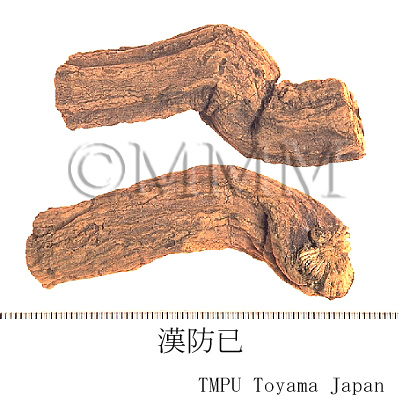
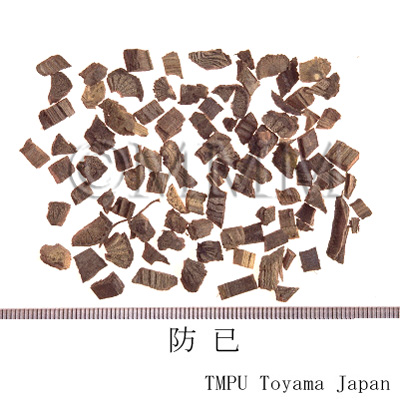
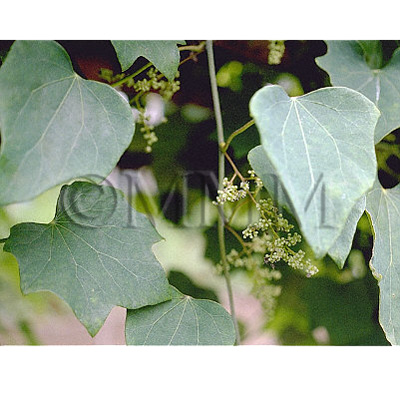
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
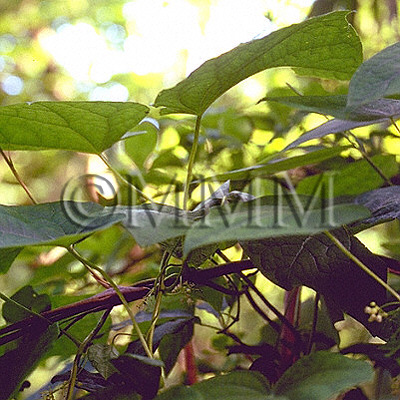
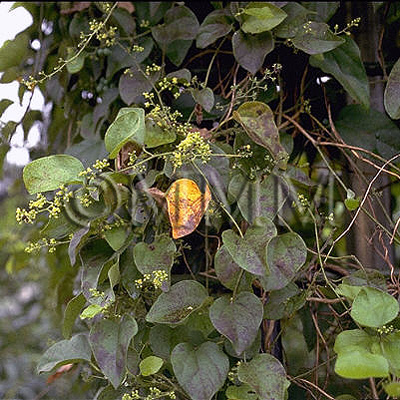
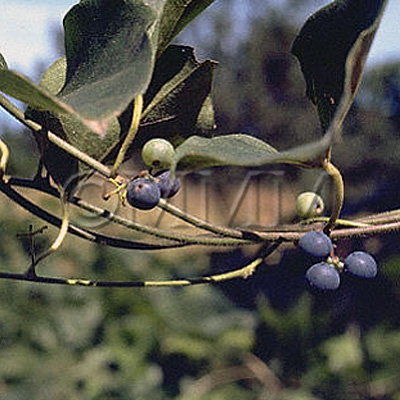
| Original plant name | Sinomenium acutum Rehder et E. H. Wilson, (Ōtsuzurafuji) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Menispermaceae | ||||||
| Used part | vine and rhizome | ||||||
| Quality for selection | The cross section is brown and has a pattern of chrysanthemum. The real one resembles Mutong (木通: Akebia Stem). (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As diuretic and anodyne, it is applied to treat nerve pain, rheumatism, arthritis and edema. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Antirheumatics (dampness-eliminating) | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral; bitter and pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and spleen. [Actions] To dispel wind-dampness, unblock the meridians and collateral vessels, promote urination. [Indications] Painful impediment caused by wind-dampness, joint swelling, numbness and itching. | ||||||
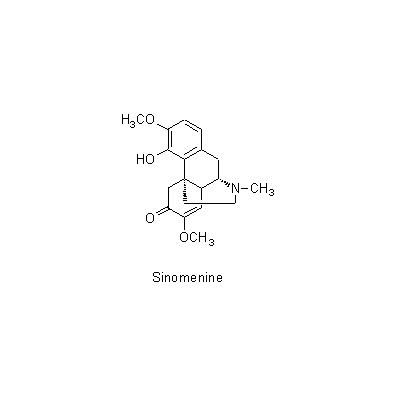
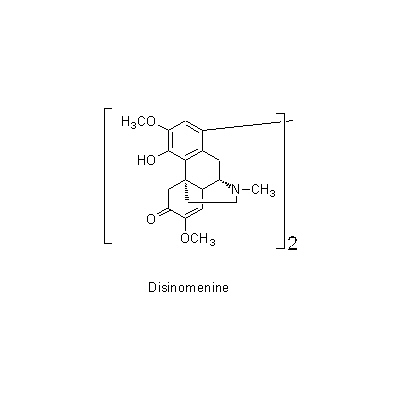
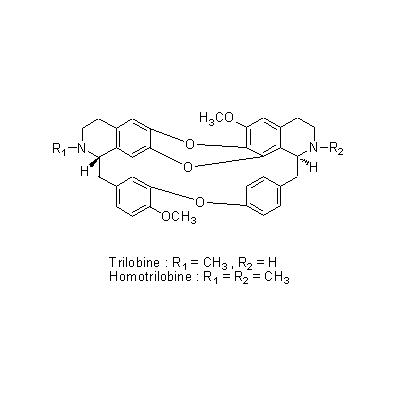
| Chemical constituent | Sterols S. acutum (*C1): beta-Sitosterol, Stigmasterol Isoquinoline alkaloids S. acutum (*C1): Sinomenine, Disinomenine, Isosinomenine, Sinactine, Tuduranine, Acutumine, Acutumidine, Sinoacutine, Magnoflorine C. trilobus (*C1): Trilobine, Isotrilobine, Homotrilobine, Trilobamine, Normenisarine, Cocculolidine, Magnoflorine | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antiinflammatory,antiallergic (hot water extract),antiinflammatory,analgesic,and decreases blood pressure(sinomenine). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Rheumatism, Arthritis, Arthralgia, Numbness, Thirst, Edema, Pulmonary edema, Ascites, Oliguria, Itching | ||||||
| Formulation | Orenshodokuin, Shozokumeito, Jokinritsuansan, Seishitsuto, Zosonmokuboito, Sokeikakketsuto, Haikanpo, Boisan, Boito, Boiogito, Boijioto, Boibukuryoto, Mokuboito, Mokuboikyosekkokabukuryoboshoto, Rokumotsubushito | ||||||
| Related drugs | Mufangji,Fenfangji,Guangfangji (see "Remarks") | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 78-81. | ||||||
| Remarks | "Mokuboi" (Jap. Name) is the stem or roots of Cocculus trilobus (Thunb.) DC. of family Menispermaceae. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia defines "Boi" (Fangji) as the climbing stem and rhizome of Sinomenium acutum Rehder et E.H. Wilson. In China, the climbing stem of S. acutum or S. acutum (Thunb.) Rehder et Wilson var. cinereum Rehder et Wilson is called "Qingfengteng (青風藤)", which is enrolled in the Pharmacopoeia of People's Republic of China(CP). "Fangji", which is also called ”Fenfangji (粉防已)", listed in the CP and it refers the root of Stephania tetrandra S. Moore of family Menispermaceae. "Guangfangji (広防已)" was listed in the CP and it referred the root of Aristolochia fangchi Y.C.Wu ex L.D.Chou ex S.M.Hwang of family Aristolochiaceae. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/03/23 | ||||||