Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
33.844582
115.77867600000002
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Bozhou
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
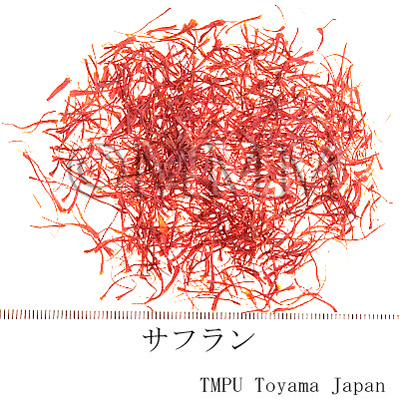
| Common name | サフラン, Xihonghua, Crocus (JP18), Croci Stigma (CP2020), Saffron (JP18), (CP2020) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 番紅花 | ||||
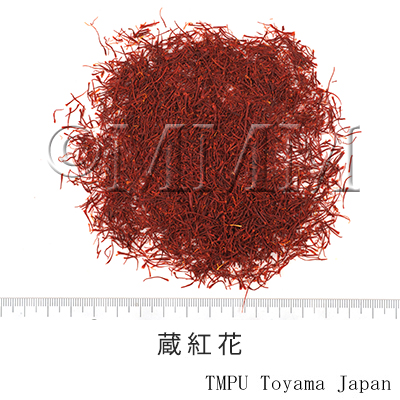
| crude drug image |
| ||||
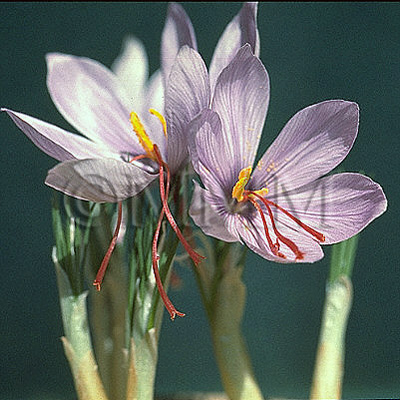
| Original plant name | Crocus sativus Linn., (Safuran) | ||||
| original plant image |
| ||||
| Family name | Iridaceae | ||||
| Used part | stigma | ||||
| Quality for selection | The less pollen or smaller the base of stigma (yellow colored), the better the quality. The aged one is not good. (TN) | ||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||
| Clinical application | As a tranquilizer, painkiller and emmenagogue, Xihonghua is applied for mental disease, dysmenorrhea, menstrual disorder and amenorrhea. | ||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for invigorating blood circulation | |||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Heart and liver meridians. [Actions] To activate blood to resolve stasis, cool the blood to remove toxin, relieve depression and tranquilize the mind. [Indications] Amenorrhea, aggregation and accumulation, postpartum stasis and obstruction, macula and papule caused by warm toxin, doldrums, stuffiness and oppression, fnght palpitations and manic psychosis. | ||||
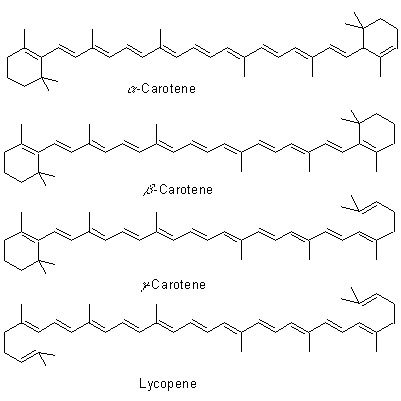
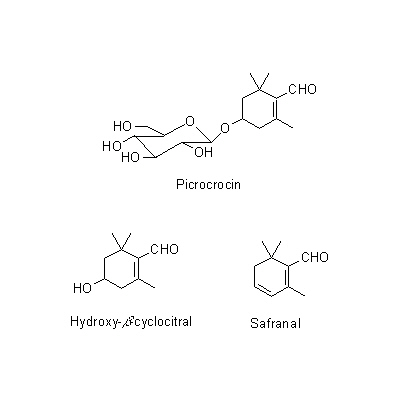
| Chemical constituent | Monoterpenoids (*C1,C2): Picrocrocin, Safranal, Pinene, Cineole Carotenoids (*C1): Crocin (Crocetin digentiobiose ester), Crocetin gentiobiose glucose ester, Crocetin diglucose ester, Crocetin gentiobiose ester, Crocetin glucose ester, alpha-Carotene, beta-Carotene, gamma-Carotene, Lycopene | ||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||
| Pharmacological effect | Uterus excitation. | ||||
| DNA sequence | AB017325; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||
| Disease | Amenorrhea, Menorrhalgia, Intra-abdominal tumor, Dystocia, Dead fetus, Swelling and pain due to contusion, Pyogenic dermatosis, Anginal pain | ||||
| Formulation | |||||
| Related drugs | Safflower | ||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 113-116. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 332. | ||||
| Remarks | In Mediterranean region, Saffron has been used as a spice since before Christ. Dioscorides listed it as Krokos in "De Materia Medica". It was introduced from India to China during the Tang Dynasty (the middle of the 7th century) and listed in "Men Bao Ben Cao" (Sung Dynasty) under the name of Yujinxiang (Jap. name: Ukonkō). | ||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/04/24 | ||||