Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | アロエ・蘆薈, Luhui, Aloe (JP18, CP2020), Aloe (JP18), Aloes (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | ケープ・アロエ (Cape Aloes), 透明アロエ (Aloe Lucida) | ||||||
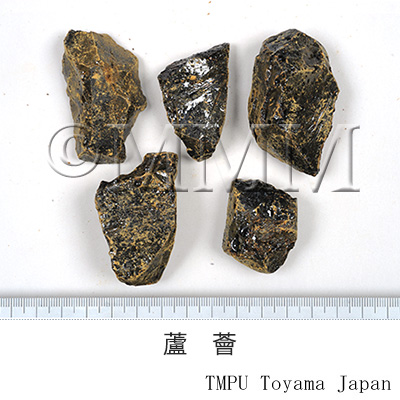
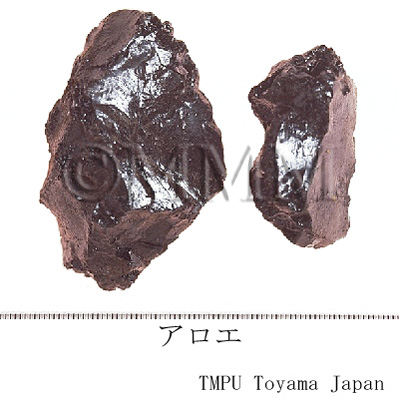
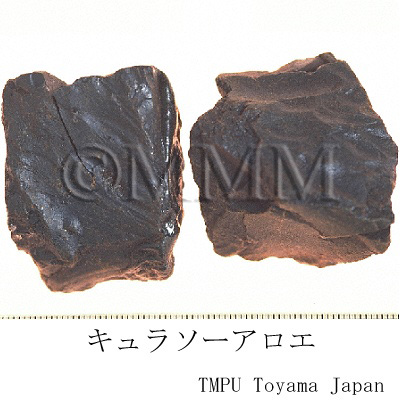
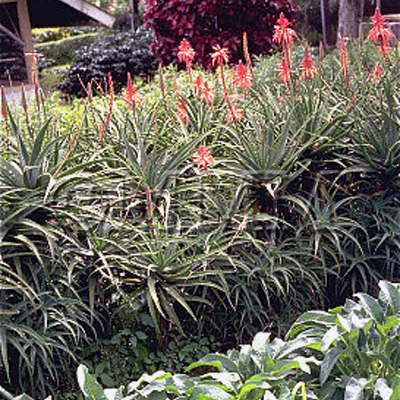
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
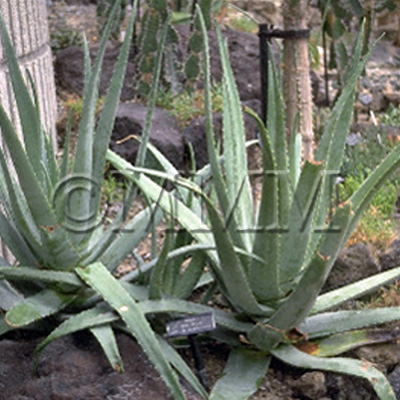
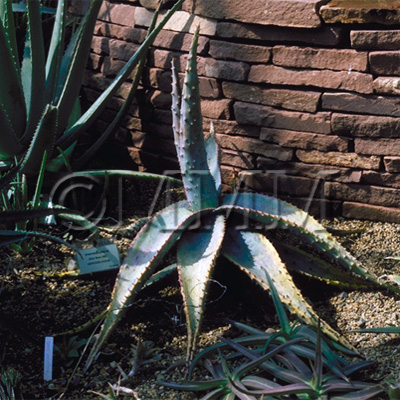
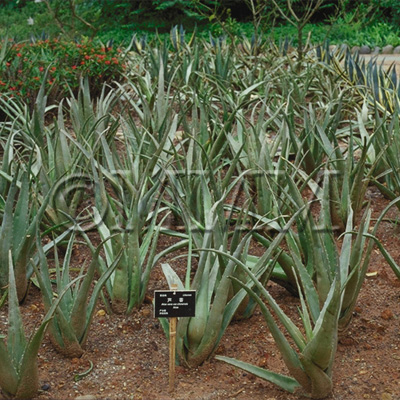
| Original plant name | Aloe ferox Miller, mainly or of interspecific hybrids of the species with Aloe africana Miller or Aloe spicata Baker | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Liliaceae | ||||||
| Used part | leaf juice | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Luhui is solid and dark brown. The cross- section is smooth and has glassy luster. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | Luhui is widely used for chronic constipation as a laxative. It is applied for apepsia and chronic gastric catarrh as a stomachic in small doses. Since luhui doesn't contain tannin, it doesn't cause constipation after laxation. In large doses, it congests intestinal wall and pelvic lumen. Therefore, it must be used carefully during menstrual or pregnancy period and hemorrhoid. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Purgatives | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter [Meridian Tropism] Liver, stomach and large intestine meridians. [Actions] To purge the intestines, open the bowels, clear the liver, purge fire, kill worms and relieve malnutrition. [Indications] Heat bind constipation, seizures and convulsions, infantile malnutrition with food retention; topically for tinea and sore. | ||||||
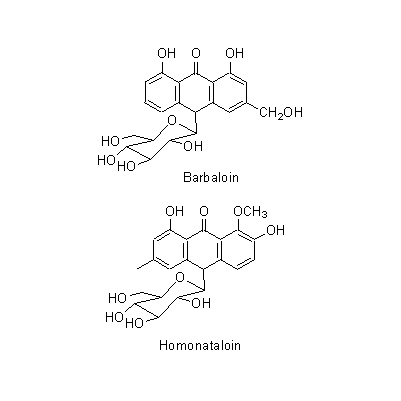
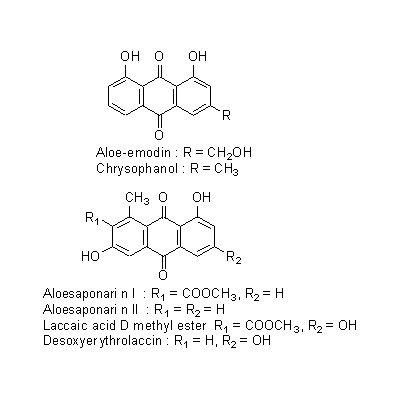
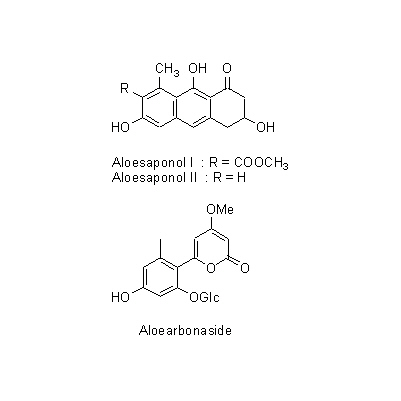
| Chemical constituent | Polysaccharides 糖タンパク / glycoprotein Cape Aloes, Socotrine Aloes, Curacao Aloes (*C1): Loctin A Anthraquinones Cape Aloes, Socotrine Aloes, Curacao Aloes (*C1,C2): Barbaloin, Aloinoside A, Aloinoside B, Aloe-emodin, Chrysophanol, Aloe-emodin rhamnoside, Rhabarberon Curacao Aloes (*C1): Isobarbaloin Natal Aloes (*C1): Homonataloin Aloe saponaria (*C1): Aloesaponarin I, Aloesaponarin II, Laccaic acid D methyl ester, Desoxyerythrolaccin Chromones Cape Aloes, Socotrine Aloes, Curacao Aloes (*C1): Aloesin, 2''-O-p-Coumaroylaloesin, 2''-O-Feruloylaloesin (*C3,C4,C5): Aloesin (Aloeresin B), Aloeresin A, Aloesone(2-Acetonyl-7-hydroxy-5-methylchromone), Aloesol, (2'R)-Aloesol, (2'S)-Aloesol, (2'R)-8-C-Glucosylaloesol, (2'S)-8-C-Glucosylaloesol, (2'R)-8-C-Glucosyl-7-O-metylaloesol, (2'S)-8-C-Glucosyl-7-O-metylaloesol, 7-O-Methylaloesin, Aloesin 2",3",4",6"-tetra-O-acetate αーPyrones Aloe arborescens var. natalensis (*C1): Aloearbonaside Other aromatic compounds p-Coumaric acid Naphthalenes Aloe saponaria (*C1): Aloesaponol I, Aloesaponol II | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Barbaloin:hypercholeresis in small dose,enhanced bowel movement.Barbaloin is C-glycoside of aloe-emodin anthrone. It is metabolized into aloe-emodin anthrone by Eubacterium sp. BAR, enteric bacteria in human intestine. This component stimulates peristalsis and has cathartic effect. (C3,C6). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AF234338, AJ290255, AJ290289 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Constipation, Lightheadedness, Red eye, Insomnia, Ear buzzing, Restlessness, Abdominal pain, Malnutrition, Dental caries | ||||||
| Formulation | |||||||
| Related drugs | Socotrine Aloes, Curacao Aloes, Natal Aloes, Bombay Aloes (see "Remarks") | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 218-221. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p334. C3)Planta Med.,57,15(1991). C4)Natural Drugs and the Digestive Tract,299(1992). C5)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,39,704(1991). C6)Biol.Pharm.Bull.,19,136(1996). | ||||||
| Remarks | Luhui has the following species as well as Cape Aloes: 1) Socotrine Aloes:Aloe perryi Baker (produced in Socotra Island Northeast Africa) 2) Curacao Aloes:Aloe vera L. and A. vera L. var. chinensis (Haw.) Berger (produced in Curacao Island in Caribbean Barbados) 3) Natal Aloes:Aloe bainesii Th. Dyer. is common (produced in Natal South Africa, Rhodesia region) 4) Bombay Aloes:Aloe perryi Baker (produced in East Africa). Socotrine Aloes and Curacao Aloes are also called Aloe Hepatica. The Aloes which is called "keeping the doctor away" in folklore is Aloe arborescens Miller (produced in South-east Africa, Jap. Name: Kidachiaroe) or its variant, A. arborescens Miller var. natalensis Berg. They are different from the original plant of medicinal Aloes. The fresh liquid of Aloe arborescens Miller is taken orally as a folk medicine for gastrointestinal disease or constipation. It is also applied externally for burns, wounds and scratches. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2025/12/17 | ||||||