Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
41.420018
128.200789
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Changbai
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
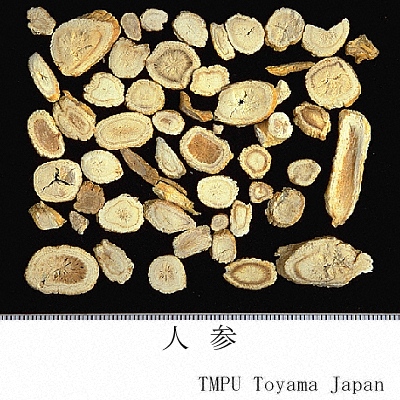
| Common name | 人参, Renshen, Ginseng Radix (JP18), Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma (CP2020), Ginseng (JP18), (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
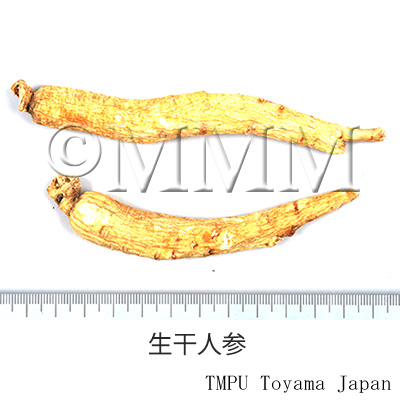
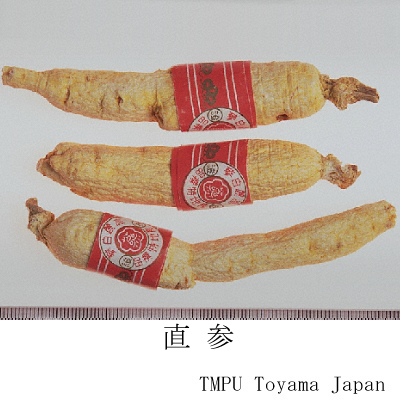
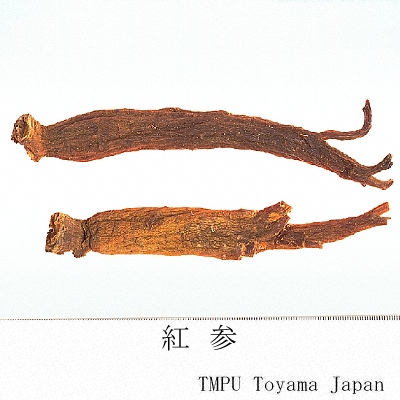
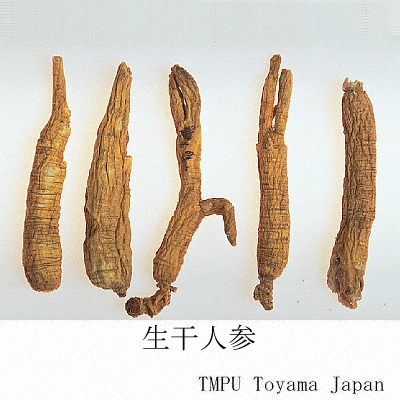
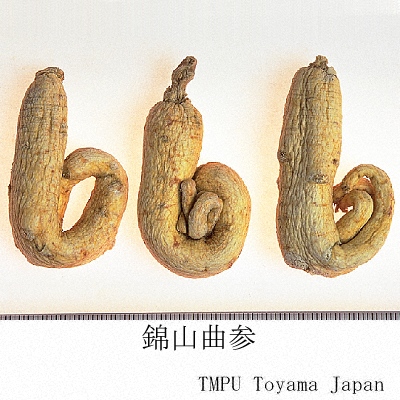
| Synonyms | 白参, 生干人参, 曲参, 半曲参 | ||||||
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
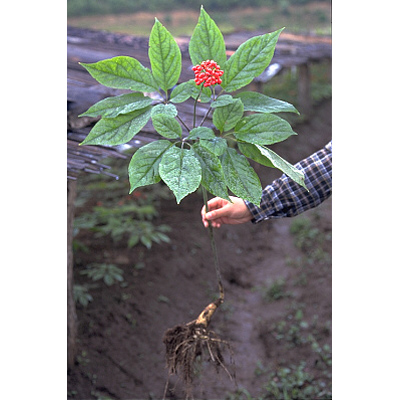
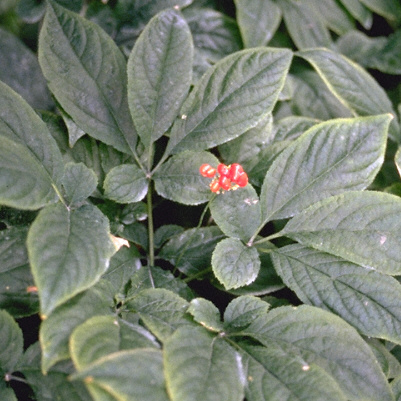
| Original plant name | Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer (Panax schinseng Nees), (Otaneninjin) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Araliaceae | ||||||
| Used part | root | ||||||
| Quality for selection | A high quality Ginseng has long root with big branch and long rhizome. The one of excessive sweetness is lower quality. (NI) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | Widely used as tonic, cardiotonic, replenishing vital essence, tranquilizer, stomachic and anti-fatigue drug. Ginseng cures the decline of metabolism by gastric weakness. It is applied to treat invalid's gastric stagnation, indigestion, nausea, chest pain, relaxant diarrhea and lack of appetite. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for replenishing Qi (vital energy) | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild warm; sweet and mild bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, lung, heart and kidney meridians. [Actions] To tonify qi, relieve collapse-syndrome and indistinct pulse, invigorate spleen and lung. To promote the production of body fluid, calm the mind. [Indications] For general weakness with impending collapse, cold limbs and faint pulse, diminished function of the spleen with loss of appetite, cough due to diminished function of the lung, thirst due to impairment of body fluid, diabetes caused by internal heat, general weakness irritability and insomnia in chronic disease, impotence or frigidity, heart failure, cardiogenic shock. | ||||||
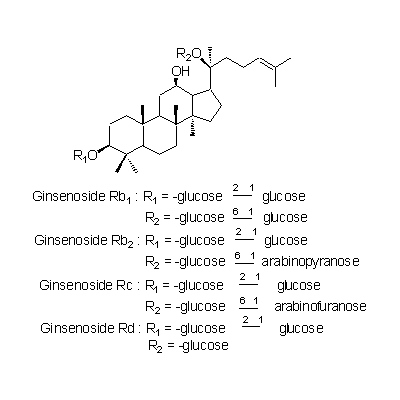
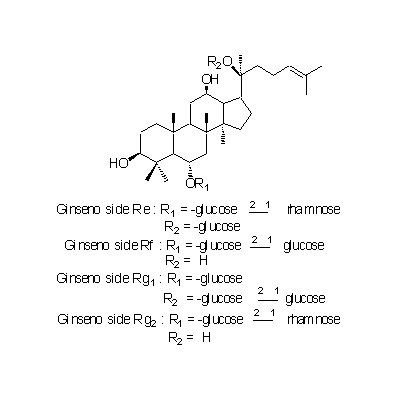
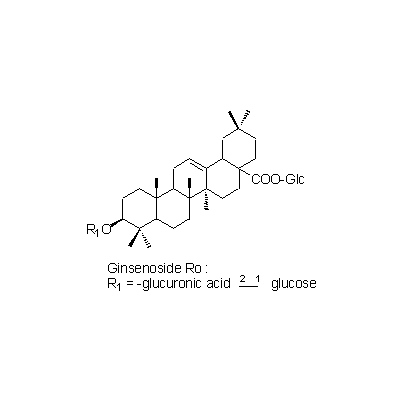
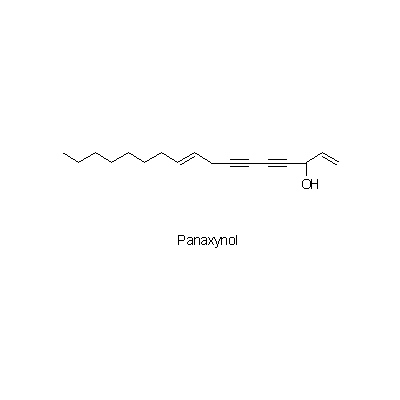
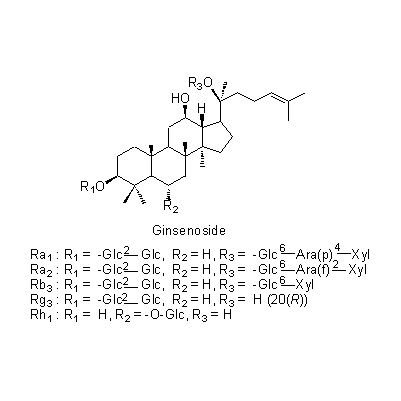
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1,C2): Panaxynol, Panaxydol, Heptadece-1-en-4,6-diyn-3,9-diol Sugar (*C1,C2): D-Glucose, D-Fructose, Sucrose, Maltose, Trisaccharide A, Trisaccharide B, Trisaccharide C Sesquiterpenoids (*C1,C2): Panacene, beta-Elemene Triterpenoids (*C1,C2): Oleanolic acid, (20S)-Protopanaxadiol, (20S)-Protopanaxatriol Triterpenoid saponins (*C1,C2,C3): Ginsenoside Ro, Ginsenoside Ra1, Ginsenoside Ra2, Ginsenoside Rb1, Ginsenoside Rb2, Ginsenoside Rb3, Ginsenoside Rc, Ginsenoside Rd, Ginsenoside Re, Ginsenoside Rf, Ginsenoside Rg1, Ginsenoside Rg2, Ginsenoside Rh, Ginsenoside La(葉/leaves), 24(S)-Pseudoginsenoside F11, Pseudoginsenoside Rc1 Steroids (*C1,C2): beta-Sitosterol, beta-Sitosterylglucoside Simple nitrogen containing compounds (*C1,C2): Choline Others (*C1,C2): Vitamin B | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Water extract:hypoglycemic, decreases blood ketones, enhances RNA synthesis in the liver. Ethanol extract:enhances cholinergic action, antihypertensive, accelerates breathing, hypoglycemic, increases red blood cells, promotes digestive motion, enhances adrenocortical function. Saponin fraction:stimulates central nervous system, reduces stress, effects the central nerve function (Rb group, sedation; Re group, excitation). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | 18SrRNA: D83275(*S1), matK: D89057(*S2), ITS:U41680,U41681,U41682, AB043871, AB043872; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Tiredness, Weak constitution, Decline of strength after illness, General malaise, Dyspnea, Shortness of breath, Thirst, Amnesia, Palpitation, Anxiety | ||||||
| Formulation | Ioto, Ikosan, Ifuto, Unkeito, Untanto, Ekkiyoeito, En'nenhangeto, Ogibekkoto, Orento, Orenshodokuin, Kaikyushokushoto, Kagenhachimotsuto, Kashokuyohito, Kamiuntanto, Kamikihito, Kankyooren'ogon'ninjinto, Kankyoninjinhangegan, Kanzoshashinto, Kippichikujoto, Kihito, Gyakubanto, Kyukihochuto, Kumisaikoto, Keishikashakuyakushokyoninjinto, Keishininjinto, Keihito, Kosharikkunshito, Kochinmuyusan, Kobokushokyohangekanzoninjinto, Kokonrokukenzokumeito, Goshuyuto, Saikanto, Saikokaryukotsuboreito, Saikokyohangekakaroto, Saikokeishito, Saikoshimotsuto, Saishakurikkunshito, Saibokuto, Saireito, Shionsan, Shigyakukaninjinto, Shikunshito, Jijinmeimokuto (Jinkimeimouto), Shisowakiin, Shichikensan, Shichimibyakujutsuto, Shakanzoto, Shahito, Shahitokaryukotsuboreito, Juzentaihoto, Shunrinshakusekishito, Shokyokanzoto, Shokyoshashinto, Shosaikoto, Shosaikotokaorenbukuryo, Shosaikogohangekobokuto, Shoshinto, Shozokumeito, Shobaishashinto, Shohito, Shomyakusan, Jinkimeimokuto, Jinsoin, Jinryobyakujutsusan, Jintanto, Seishoekkito, Seishinto, Seishinrenshiin, Seinetsuhokito, Zenshikunshito, Zenshibyakujutsusan, Sempukukataishasekito, Sogento, Zosonmokuboito, Zokumeito, Daikenchuto, Daitokato, Daihangeto, Daibyakuchuin, Daibofuto, Danrito, Jiohanho, Chikujountanto, Chikuyoto, Chikuyosekkoto, Chimobukuryoto, Chukenchuto, Chotosan, Choburichuto, Teizento, Tokito, Tokinentsuto, Dokkatsukiseito, Naitaku-san, Naitaku-san, Nyoshinsan, Ninjinsan, Ninjinto, Ninjin-yoei-to, Ninjin-yoei-to, Bakumondoto, Bakumondoinshi, Hachimigangoninjinto, Hachimotsuto, Hacchinto, Hangeshashinto, Hangebyakujutsutemmato, Byakkokaninjinto, Bukuryoin, Bukuryoshigyakuto, Bukuryhoshinto, Bushito, Bushirichuto, Fuhishomyakusankabyakukyu, Hointo, Hokikenchuto, Hojinto, Botanpisan, Hochuekkito, Hochujishitsuto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonbukuryoto, Mokuboito, Mokuboikyosekkokabukuryoboshoto, Rikkunshito, Yohaito, Richuankaito, Richuto, Rokumotsuogonto, Koshayoito | ||||||
| Related drugs | "Hongshen" (Ginseng Radix Rubra), "Zhujierensheng" (Panax Japonicus Rhizome ), "Guangdongrenshen" (Panacis Quinquefolii Radix), "Sanqirenshen" (Panacis Notoginseng Radix) | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. S1)Biol.Pharm.Bull.,19,1530(1996). S2)Biol.Pharm.Bull.20,765(1997). C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, p 2. C2)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,37,1966(1989). C3)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,34,730(1986). | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/11/02 | ||||||