Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
45.80377499999999
126.53496700000005
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Heilongjiang Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
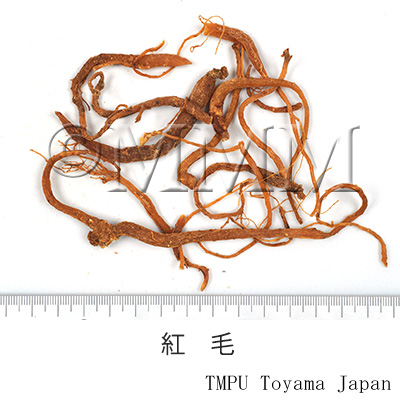
| Common name | 紅参, Hongshen, Ginseng Radix Rubra (JP18), Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma Rubra (CP2020), Red Ginseng (JP18, CP2020) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||
| Original plant name | Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer, (Otaneninjin) | |||
| original plant image |
| |||
| Family name | Araliaceae | |||
| Used part | root | |||
| Quality for selection | Good hongshen is fat and dense. The one which has liner soft parts in its internal is lower quality. (TN) | |||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for replenishing Qi (vital energy) | ||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; sweet and mild bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, lung, heart and kidney meridians. [Actions] To greatly tonify the original qi, regain pulse and secure collapse, tonify qi and control the blood. [Indications] Tending to collapse caused by body deficiency, coldness of limbs and faint pulse, qi failing to control the blood, flooding and spotting. | |||
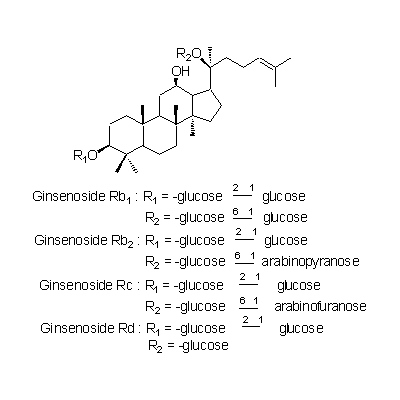
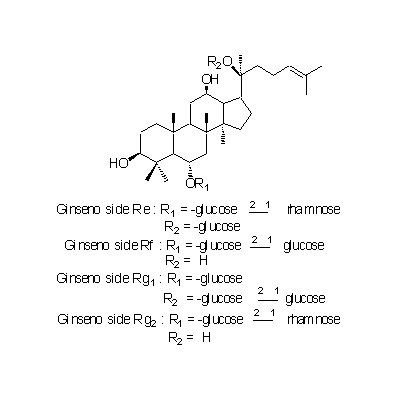
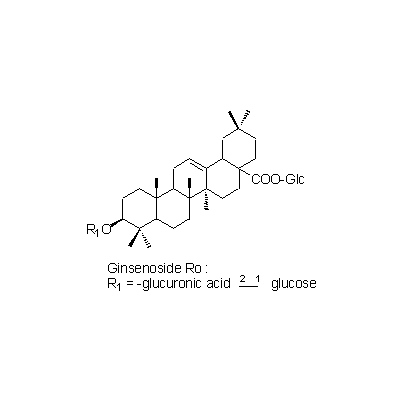
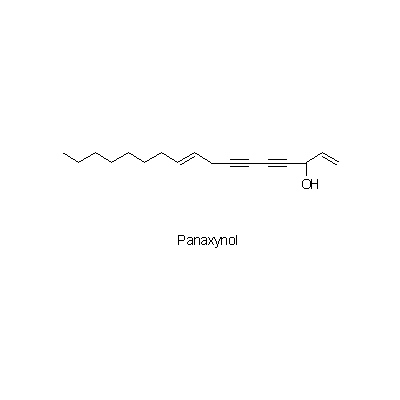
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Panaxynol, Panaxydol, Heptadece-1-en-4,6-diyn-3,9-diol Monosaccharides (*C1): D-Glucose, D-Fructose Oligosaccharides (*C1): Trisaccharide A, Trisaccharide B, Trisaccharide C Sesquiterpenoids (*C1): Panacene, beta-Elemene Triterpenoid saponins (*C1): Ginsenoside R0, Ginsenoside Ra1, Ginsenoside Ra2, Ginsenoside Rb1, Ginsenoside Rb2, Ginsenoside Rb3, Ginsenoside Rc, Ginsenoside Rd, Ginsenoside Re, Ginsenoside Rf, Ginsenoside Rg1, Ginsenoside Rg2, Ginsenoside Rh, Oleanolic acid, (20S)-Protopanaxadiol, (20S)-Protopanaxatriol Sterols (*C1): beta-Sitosterol, beta-Sitosteryl-glucoside Simple nitrogen containing compounds (*C1): Choline Others (*C1): Vitamin Bs群 | |||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||
| DNA sequence | 18SrRNA: D83275, matK: D89057, ITS: U41680, U41681, U41682, AB043871, AB043872 ; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 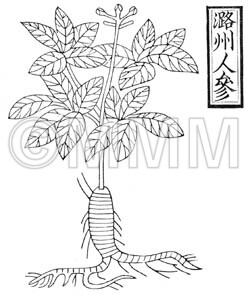 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||
| Disease | Lack of energy, Coldness of limbs, Fatigable, Anorexia, Muddy and watery stool, Visceroptosis, Descent of the uterus, Proctoptosis, Diarrhea, Dyspnea, Cough, Shortness of breath, High fever, Thirst, Spontaneous sweating, Hyperhidrosis, Polyuria, Anxiety, Insomnia, Palpitation, Amnesia | |||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 1-3. | |||
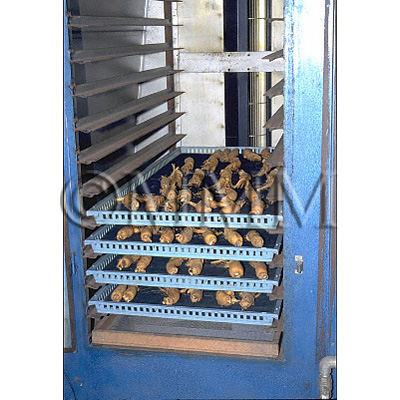
| Remarks | There are two kinds of Hongshen. One is steamed and dried Hongshen which fine roots have not been removed (Japanese Hongshen). The other is dried and pressed Hongshen without fine roots (North Korean and Korean Hongshen). In China, the processed Hongshen with relatively long branching roots is called "Biantiao Hongshen" and the one without fine roots is called "Hongshenxu". | |||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||