Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
36.3906675
139.06040610000002
Production area information
Japan,Gunma Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
35.6894875
139.69170639999993
Collection information
Japan,Tokyo
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
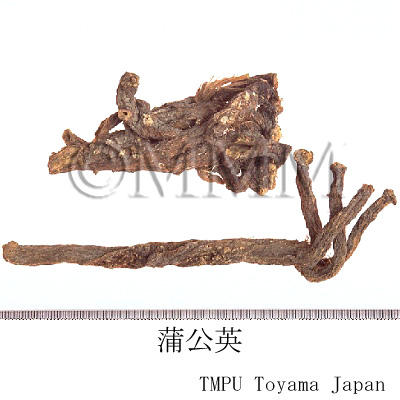
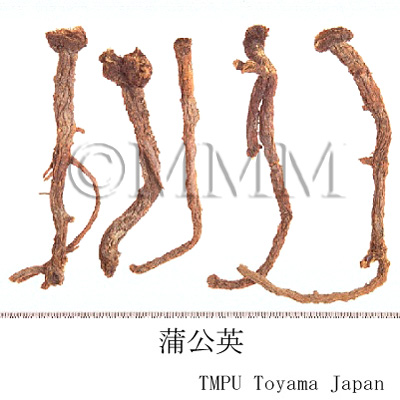
| Common name | 蒲公英, Pugongying, Taraxaci Herba (CP2020), Dandelion (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
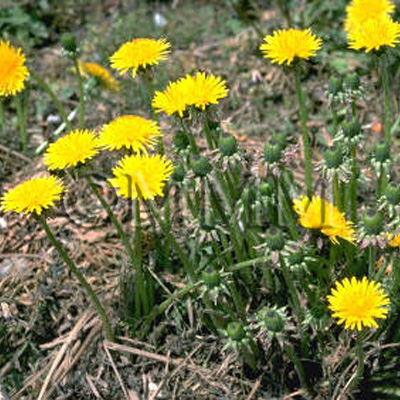
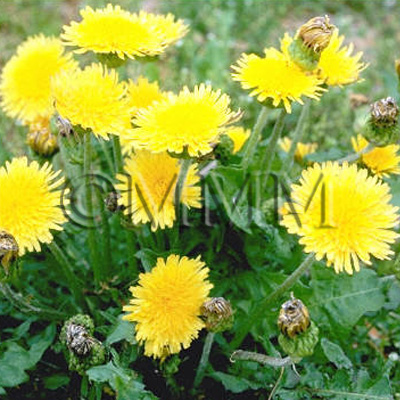
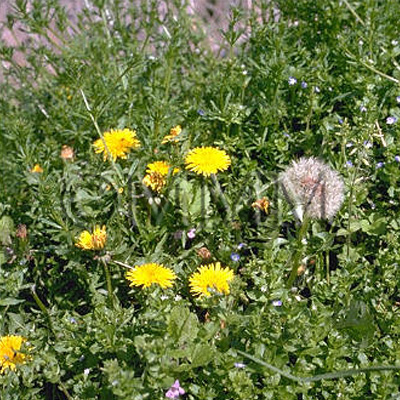
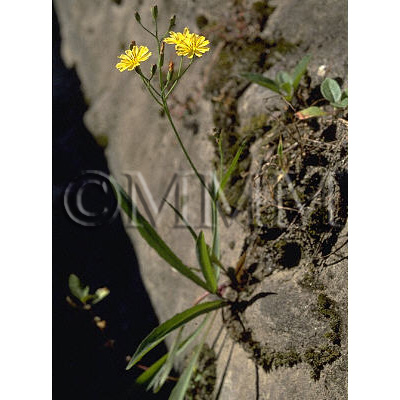
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
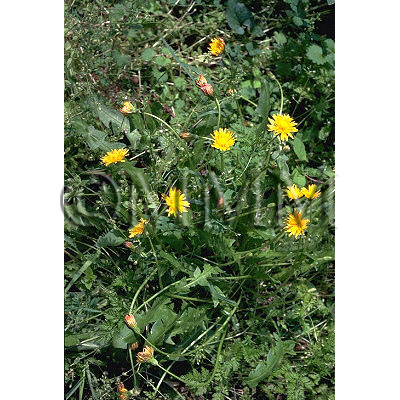
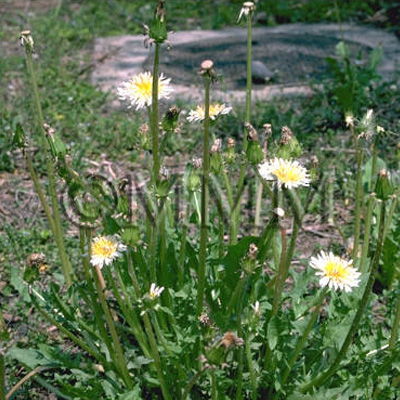
| Original plant name | Taraxacum spp. (B1), (Taraxacum spp.) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Compositae | ||||||
| Used part | whole plant with root (CN); root (JP) | ||||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | It is used as an antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, stomachic, diuretic, galactagogue, for abscesses, skin ulcers, eye tumors, indigestion, constipation, urinary disorders, colds, laryngitis, gonorrhea, and agalactorrhea. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Febrifugal and detoxicant drugs | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter and sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and stomach meridians. [Actions] To clear heat and remove toxin, disperse swelling and dissipate binds, disinhibit urine and relieve stranguria. [Indications] Deep-rooted boil and sore, swelling and toxin, acute mastitis, scrofula, red eyes, sore throat, lung abscess, intestinal abscess, dampness-heat jaundice, heat strangury with slow pain. | ||||||
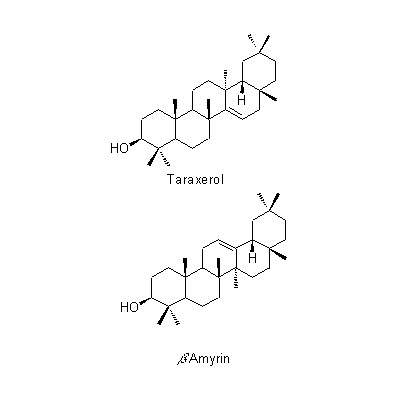
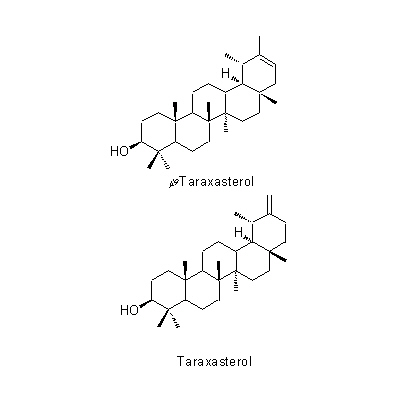
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds T. officinale, 根/ root (*C1): 有機酸 / organic acids Sugar T. officinale (*C1): 根/ root: 糖類/sugar, 葉, 花粉/ leaf, pollen: Vitamine C Polysaccharides Taraxacum属植物 / Genus Taraxacum plant, 全草/ whole plant (*C1): Inulin, Pectin Triterpenoids T. officinale, 根/ root (*C1): Taraxol, Taraxerol, ψ-Taraxasterol, Taraxasterol, beta-Amyrin Carotenoids T. officinale, (*C1): Lutein(葉,花/ leaf, flower), Violaxanthin(葉/ leaf), Flavoxanthin(花/ flower) Sterols Taraxacum属植物 / Genus Taraxacum plant, 全草/ whole plant (*C1): Taraxasterol T. officinale (*C1): Stigmasterol(根/ root), beta-Sitosterol(根,花粉/ root, pollen), 5alpha-Stigmast-7-en-3beta-ol(花粉/ pollen), Vitamin D(葉/ leaf) Phenylpropanoids T. officinale, 根/ root (*C1): Caffeic acid Benzoquinones T. officinale, 葉/ leaf (*C1): Plastoquinone Pteridine derivatives T. officinale, 花粉/ pollen (*C1): Folic acid Simple nitrogen containing compounds Taraxacum属植物 / Genus Taraxacum plant, 全草/ whole plant (*C1): Choline T. officinale, 根/ root (*C1): Choline | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Bactericidal (Bordetella, hemolytic interlocking cocci, S. pneumoniae, Fusobacterium, Jifiteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, P. aeruginosa, Chifis aeruginosa, etc.), antibacterial, choleretic, and diuretic effect. | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AJ228656, AJ228657, L48337, L48338, AF422138 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Mastitis, Breast cancer, Dyspepsia, Habitual constipation, Acute appendicitis, Upper respiratory inflammation, Tonsillitis, Acute conjunctivitis | ||||||
| Formulation | Hokoeito | ||||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1)Shoyakugaku Zasshi,41(4),289-300,301-307,318-325,326-332(1987). C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. Ⅱ, pp 68-71. | ||||||
| Remarks | The Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China defines (2020 edi.) defines the whole plant of Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz. (Jap. name: Mōko-tampopo), T. borealisinense Kitam. (Jap. name: Shina-tampopo) as "Pugongying" (蒲公英). Others are T. erythropodium Kitag., T. ceratophorum DC., T. pseudo-albidum Kitag., T. pseudo-albidum Kitag. var. lutescens Kitag., T. ohwianum Kitam., T. dissectum Ledeb., T. asiaticum Dahlst., T. cuspidatum Dahlst., T. officinale Weber (Jap. name: Seiyō-tampopo) etc. The above plants are mainly used in northeastern and northern China. TMany commercial products are found to be contaminated. In southern China, the whole plant of Emilia sonchifolia (L.) DC. of family Compositae (Jap. name: Usubeninigana) or Elephantopus scaber L. is known as "Pugongying" or "Tugongying" (土公英) and used. In Yunnan Province, Picris divaricata Vent. is referred to as "Pugongying". In Taiwan, the whole plant of Ixeris chinensis (Thunb.) Nakai (Jap. name: Usagiso) is called "Pugongying". The whole plant of I. laevigata (Blume) Sch.-Bip. ex Maxim. var. oldhami (Maxim.) Kitam. (Jap. name: Atsubanigana) is also used in the same way. The Korean "Pugongying" is mainly the whole plant of T. mongolicum Hand.-Mazz. var. corniculatum Nakai (JP name: Keirin-tampopo), or T. asiaticum Dahlst. etc. In rare cases, the roots are also sold as "Pugongying-gen". In Japan, it is mainly the roots of T. japonicum Koidz. (Jap. name: Kansai-tampopo) and T. officinale, and is called "Hokōeikon" (Pugongying-gen). | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/08/26 | ||||||