Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
30.274084
120.15507000000002
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Zhejiang Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 貝母, Beimu, Fritillariae Bulbus (JP18), Fritillariae Thunbergii Bulbus (CP2020), Fritillaria Bulb (JP18), Thunberg Fritillary Bulb (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 大和貝母, 浙貝母, 浙貝, 大貝, 珠貝, 浙貝片 | |||||
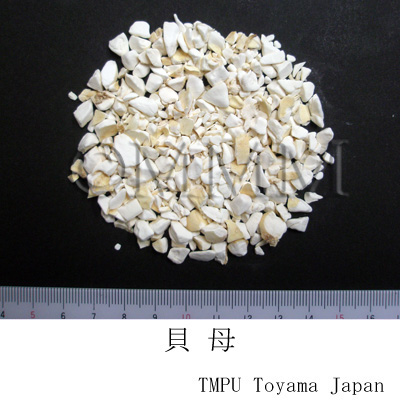
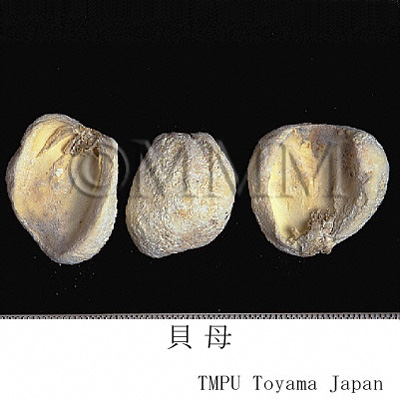
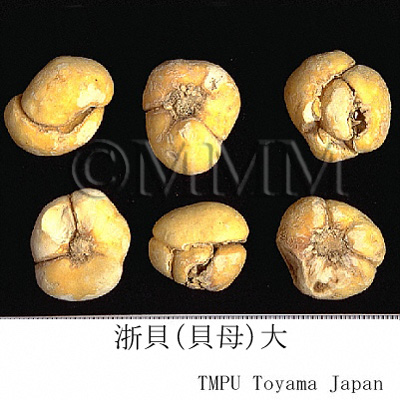
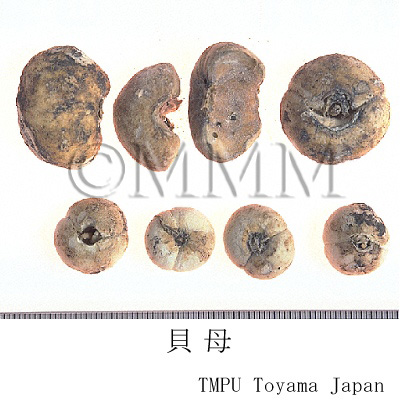
| crude drug image |
| |||||
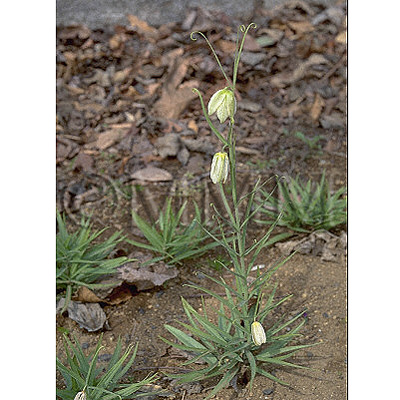
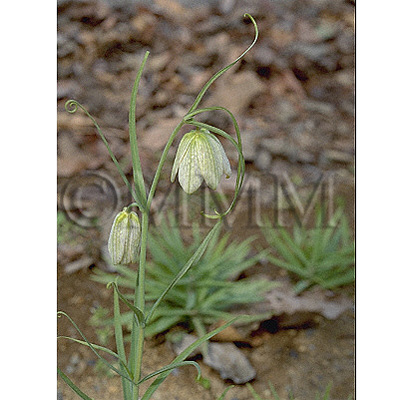
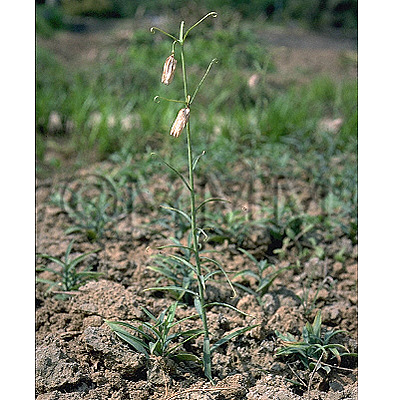
| Original plant name | Fritillaria verticillata Willdenow var. thunbergii Baker (= Fritillaria thunbergii Miquel), (Amigasayuri) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Liliaceae | |||||
| Used part | bulb | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Beimu is small. It has white outside and tannish flesh side. (NI) | |||||
| Official compendium | JHMC (1989), JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.), | |||||
| Clinical application | As antitussive, expectorant and for draining pus, beimu is applied for heat, laryngitis, dazzling, cough and thirst. Zhebeimu has stronger effects in removing heat and resolving phlegm than that of chuanbeimu. Zhebeimu is applied for cough with heat and persisting sputum. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Expectorants | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and heart meridians. [Actions] To clear heat, resolve phlegm, suppress cough, remove toxin, dissipate binds and disperse abscesses. [Indications] Wind-heat cough, phlegm-fire cough, lung abscess, acute mastitis, scrofula, sore and toxin. | |||||
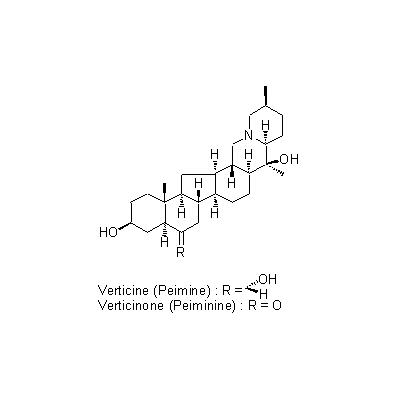
| Chemical constituent | Steroidal alkaloids F. thunbergii (*C1): Fritilline, Fritillarine, Verticine (= Peimine), Verticilline, Apoverticine, Peiminoside, Peimisine, Peimiphine, Peimidine, Peimitidine F. verticillata (*C1,C2): Fritilline A, Fritilline B, Peimisine, Verticilline, Verticine (= Peimine), Peiminoside, Verticinone (= Fritillarine = Peiminine), Isoverticine F. roylei (*C1): Peimidine, Peimiphine, Peimitidine, Peimisine, Verticine (= Peimine) | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Hypotensive (peimine,peiminoside). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF199457 ; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Cough, Sore throat, Few sputum, Expectoration of sputum, Cervical lymphadenopathy, Chest pain, Feeling of pressure in the chest, Lung suppurations, Subcutaneous nodule, Pyogenic dermatosis | |||||
| Formulation | Ikeigoshijunto, Ekkiyoeito, Kikyohakusan, Jiinshihoto, Shionsan, Shijunto, Seihaito, Tokibaimokujingan, Tokiyoketsuto, Ninjin-yoei-to, Baimoto, Haiyoto, Byakugokokinto, Yohaito | |||||
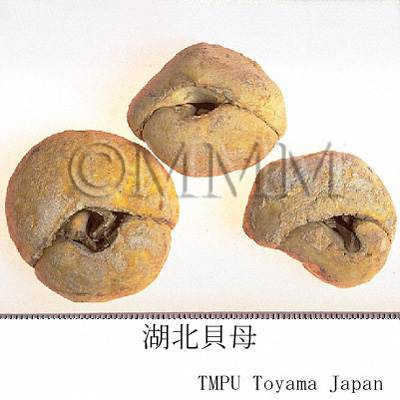
| Related drugs | Hubeibeimu (Hubei Fritillary Bulb), Chuanbeimu (Tendrilleaf Fritillary Bulb), Pingbeimu (Ussuri Fritillary Bulb), Yibeimu (Sinkiang Fritillary Bulb) | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 71-73. C2) CA, 54, 22695 (1960). | |||||
| Remarks | There are many kinds of Beimu. The major kinds are as follows: - Zhebeimu (浙貝母) or Zhebei (浙貝): Fritillaria thunbergii Miq. - Hubeibeimu (湖北貝母): F. hupehensis Hsiao et K.C. Hsia - Chuanbeimu (川貝母) or Chuanbei (川貝): F. cirrhosa D. Don, F. unibracteata Hsiao et K.C.Hsia, F. przewalskii Maxim. - Lubeimu (炉貝): F. delavayi Franch. - Yibeimu (伊貝母) or Yibei (伊貝): F. pallidiflora Schrenk, F. walujewii Regel - Pingbeimu (平貝母) or Pingbei (平貝): F. ussuriensis Maxim. Each of them is listed in the Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China under the different articles [Lubeimu (炉貝) is included in Chuanbeimu (川貝母)]. Beimu is an expectorant drug and is divided into two groups. One of them consists of Zhebeimu (浙貝母) and Hubeibeimu (湖北貝母). The other consists of Chuanbeimu (川貝母), Lubeimu (炉貝), Yibeimu (伊貝母) and Pingbeimu (平貝母). The former is used in the treatment of cough, scrofula, carbuncle and wound poison. The latter is used for cough caused by deficiency of Yin or heat in the lung. Japanese Beimu is the bulb of "Amigasayuri (baimo)" which is the same kind as Zhebeimu (浙貝母). It is cultivated in Nara Prefecture and also called "Yamato-baimo". Beimu must not be used with crude drugs of Aconite root. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||