Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
34.0657179
134.55936010000005
Production area information
Japan,Tokushima Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
35.6894875
139.69170639999993
Collection information
Japan,Tokyo
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
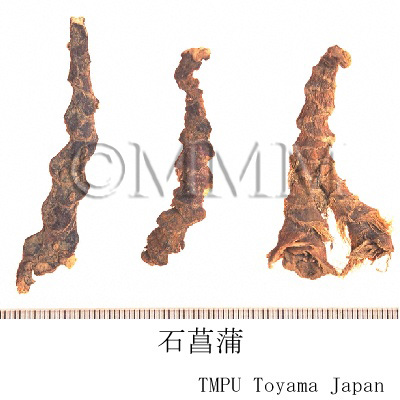
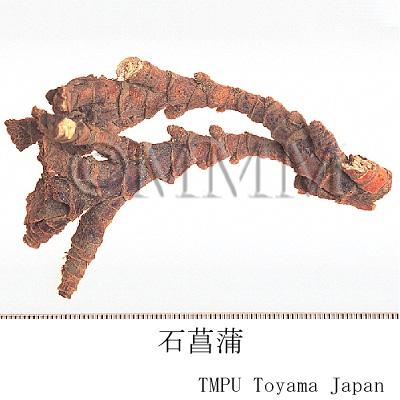
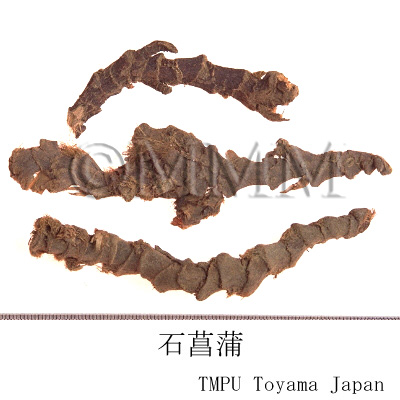
| Common name | 石菖蒲, Shichangpu, Acori Graminei Rhizoma (Non-JPS2022), Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma (CP2020), Acorus Gramineus Rhizome (Non-JPS2022), Grassleaf Sweetflag Rhizome (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 石菖根 (Shichanggen) | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
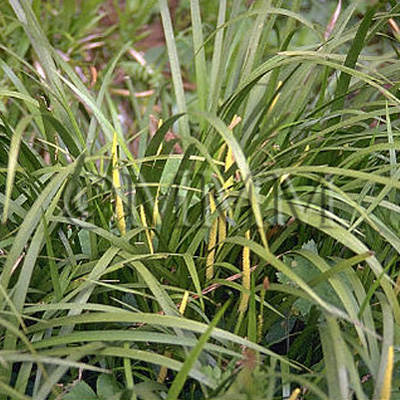
| Original plant name | Acorus gramineus Solander1 or Acorus tatarinowii Shott, (Sekishō1 ) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Araceae | |||||
| Used part | rhizome | |||||
| Official compendium | Non-JPS (2022), CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a tranquilizer, painkiller, stomachic and anthelmintic, it is applied to treat tinnitus, talk in delirium, headache, and carbuncle. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Stimulants | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent and bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Heart and stomach meridians meridians. [Actions] To open the orifices and sweep phlegm, enliven the spirit and replenish wisdom, resolve dampness to increase the appetite. [Indications] Loss of consciousness, epilepsy, forgetfulness and insomnia, tinnitus and deafness, epigastric stuffiness and torpid intake, food-denying dysentery. | |||||
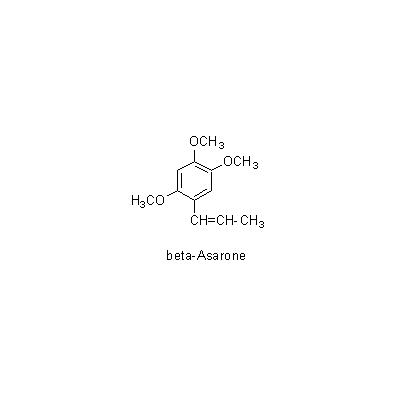
| Chemical constituent | Phenylpropanoids (*C1): beta-Asarone(精油/essential oil 0.5~0.8%の約/about 86%) | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antibacterial (cutaneous fungus), sedation (Asarone). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AB017425, AB040155, D28866, AF197584 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Disturbance of consciousness, Headache, Insomnia, Frenzy, Amnesia, Deafness, Ear buzzing, Epilepsy, Anorexia, Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Diarrhea | |||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||||
| Related drugs | The rhizome of Acorus calamus L. | |||||
| References | Non-JPS2022: The Japanese standards for non-Pharmacopoeial crude drugs 2022. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 145-146. | |||||
| Remarks | Suishōbu (Shōbukon) is the rhizome of Shōbu (Acorus calamus L.). Its rhizome is thicker than the that of Sekishōbu (A. gramineus) or Shichangpu (A. tatarinowii) and has less nodes but stronger odor. Generally, Sekishōbu or Sekishō is used in the Kampo formulation. The leaves of Sekishōbu or Sekishō are narrow, evergreen and have indistinct midribs by which distinguishable from Shōbu. Generally, Japanese Sekishō does not bear fruit, while Chinese or Thai strains bears fruit and grows large. There are various strains in one species like Shōbu. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/20 | |||||