Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
36.6512
117.12009499999999
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Shandong Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
29.714699
118.33752099999992
Collection information
People's Republic of China,Huangshan
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
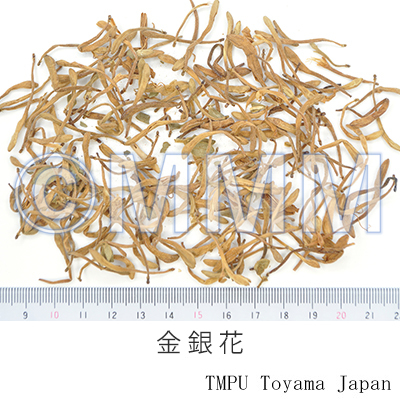
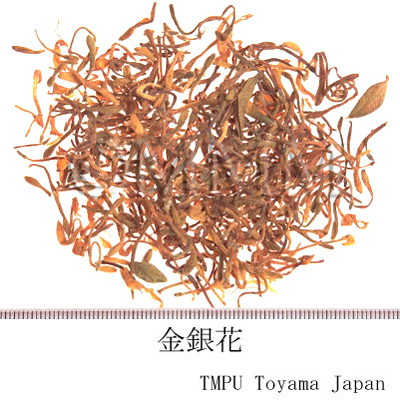
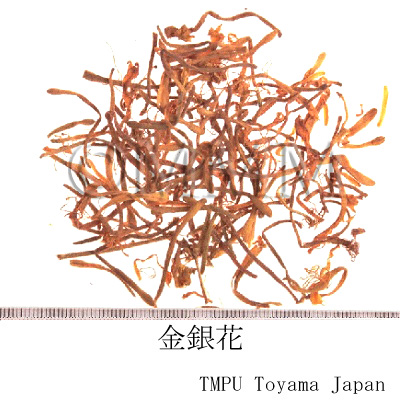
| Common name | 金銀花, Jinyinhua, Lonicerae Flos (Non-JPS2022), Lonicerae Japonicae Flos (CP2020), Lonicera Flower (Non-JPS2022), Japanese Honeysuckle Flower (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 河南産: 南銀花, 密銀花; 山東産: 東銀花, 済銀花 | ||||||
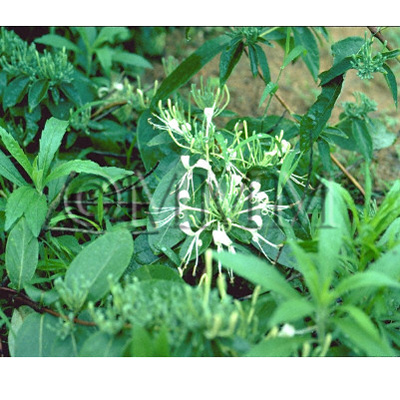
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
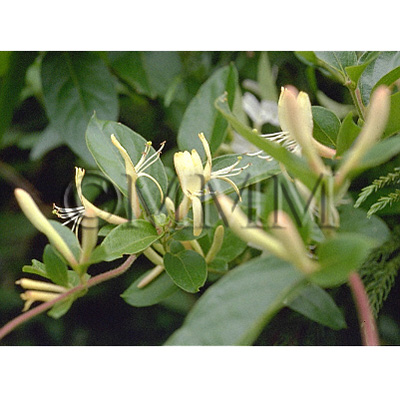
| Original plant name | Lonicera japonica Thunberg (*B1), (Suikazura) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Caprifoliaceae | ||||||
| Used part | flos | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Jinyinhua: The upper part of petal is yellowish-brown and the lower part is reddish-brown. It should be well dried. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | Non-JPS (2022), CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an antifebrile and antidote, it is used to treat festering skin disease, sore throat, diarrhea and onset of wind cold with fever. The baked brown jinyinhua is used as hemostatic. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Febrifugal and detoxicant drugs | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Lung, heart and stomach meridians. [Actions] To clear heat and remove toxin, disperse wind-heat. [Indications] Swelling abscess, deep-rooted boil and sore, throat impediment, erysipelas, heat-toxin blood dysentery, common cold caused by wind-heat, fever in warm disease. | ||||||
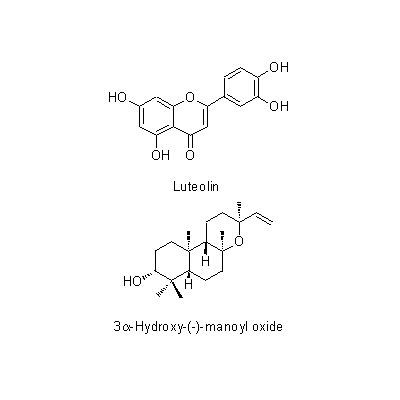
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Ceryl alcohol, Sterin, Arachic acid, Myristic acid, Elaidic acid, Linolenic acid, Linolic acid Monosaccharides (*C1): Inositol Diterpenoids L. japonica var. sempervillosa (*C1): 3alpha-Hydroxy-(-)-manoyl oxide Flavones & Flavonols (*C1): Luteolin, Lonicerin (Luteolin-7-rhamnoglucoside) | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Slight suppression of stress ulcer. Antibacterial (various types of Gram-positive and Gram-negative). Diuresis. Suppression of cholesterol absorption from the intestinal tract. | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AF207727, AF207728, AF207729, AF207730, AF207731, AF207732, AF207733 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Pyogenic dermatosis, Swelling and pain of the throat, Hematochezia, Fever, Rash | ||||||
| Formulation | Seiinrikakuto, Hachimitaikaho | ||||||
| Related drugs | Lonicera leaf and stem. | ||||||
| References | Non-JPS2022: The Japanese standards for non-Pharmacopoeial crude drugs 2022. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1) Shoyakugaku Zasshi,42(1),65-75(1988). C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 109-110. | ||||||
| Remarks | In China, Yinqiao San (銀翹散), the formulation listed in Wen Bing Tiao Bian (温病條辨), is widely used for the initial stages of cold and distemper. Rendong is the stem or stem with leaves of L. japonica. They are used as antipyretic, detoxicant, diuretic and antiinflammatory. Jinyinhua has stronger antipyretic and detoxifying effects. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/20 | ||||||