Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Scientific information data base
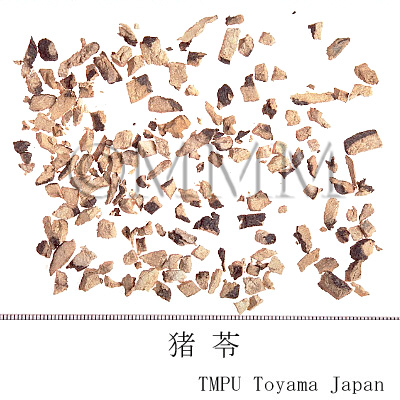
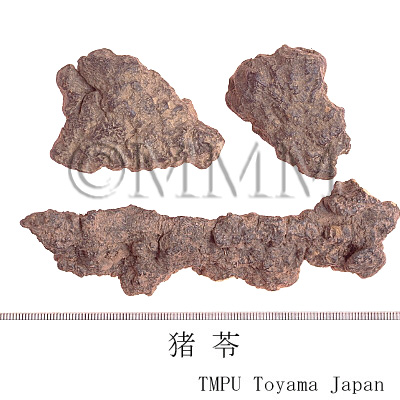
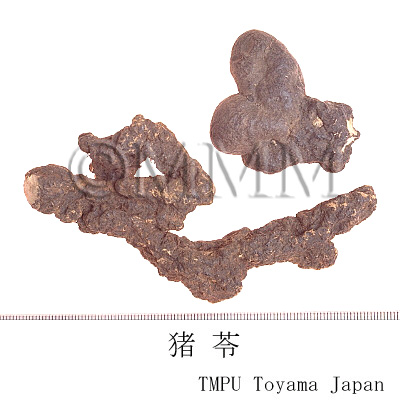
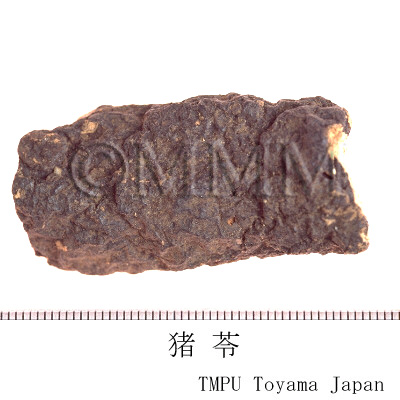
| Common name | 猪苓, Zhuling, Polyporus (JP18), (CP2020), Polyporus Sclerotium (JP18), Chuling (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
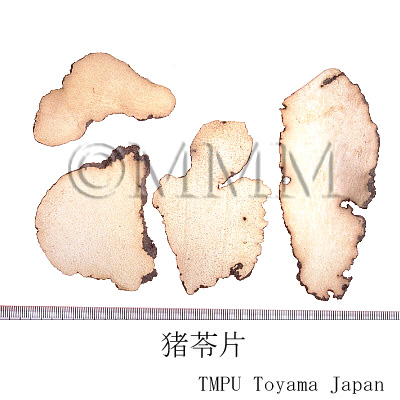
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Polyporus umbellatus Fries, (Choreimaitake) | |||||
| Family name | Polyporaceae | |||||
| Used part | sclerotium | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Zhuling is enlarged and the inside is solid and white. Shrunken one is not good. Neither wine red nor black inside is good. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a diuretic, antifebrile and to relieve thirst, Zhuling is applied for oliguria, thirst and kidney disease. Zhuling is said to remove excessive water and fever, in traditional Chinese medicine. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diuretics removing dampness | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral; sweet and bland. [Meridian Tropism] Kidney and bladder meridians. [Actions] Inhibited urination, edema, diarrhea, turbid stranguria, and abnormal vaginal discharge. | |||||
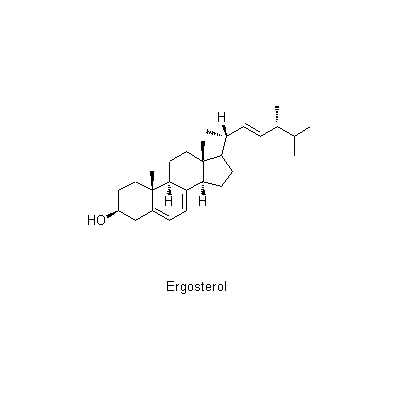
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): 2-Hydroxytetracosanoic acid Polysaccharides (*C1): Glucan Sterols (*C1): Ergosterol, Ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one Sulfur containing alkaloids (*C1): Biotin | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Diuresis (water extract). Antitumor (water-soluble glucan). | |||||
| DNA sequence | D49670, D49671, D49672 | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 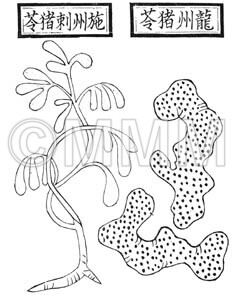 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Oliguria, Edema, Muddy and watery stool, Leukorrhea | |||||
| Formulation | Ireito, Inchingoreisan, Inchinsan, Kagen'ireito, Kamihachimyakusan, Kumihangeto, Goreisan, Saireito, Jippito, Shireito, Jin'en'ippo, Jintanto, Choreito, Choreitogoshimotsuto, Tokinentsuto, Tokibyakujutsuto, Haikanpo, Fushinto, Bunshoto, Kaishun'inchinsan | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, p 239-240. | |||||
| Remarks | Japanese Zhuling is called "Shinchorei" in Japan. It is less heavy and has a lot of constrictions. Chinese Zhuling "Tochorei" is hard and has less irregularity. Both Zhuling and Fuling (Poria) act as diuretc, antitumor, heat clearing and dampness draining. Fuling is effective in invigorating, but Zhuling is not. Zhuling is also applied to treat the symptom accompanied with heat. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2024/02/02 | |||||