Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
People's Republic of China
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
35.6894875
139.69170639999993
Collection information
Japan,Tokyo
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
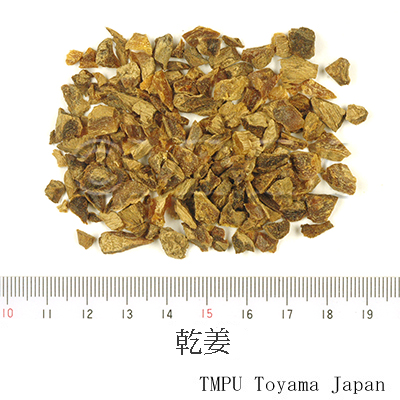
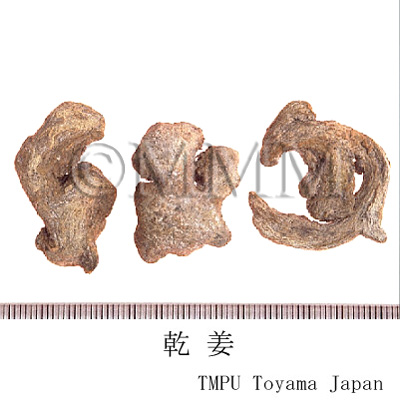
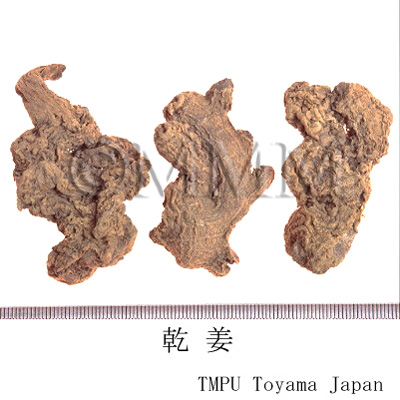
| Common name | 乾姜, Ganjiang, Zingiberis Rhizoma Processum (JP18), Zingiberis Rhizoma (CP2020), Processed Ginger (JP18), Zingiber (Dried Ginger) (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
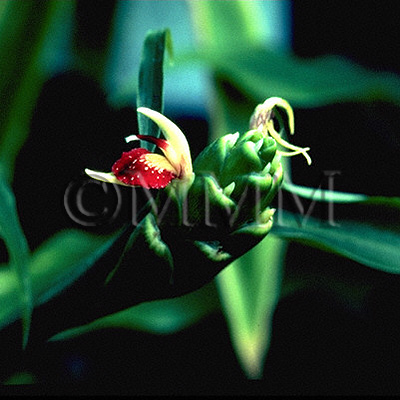
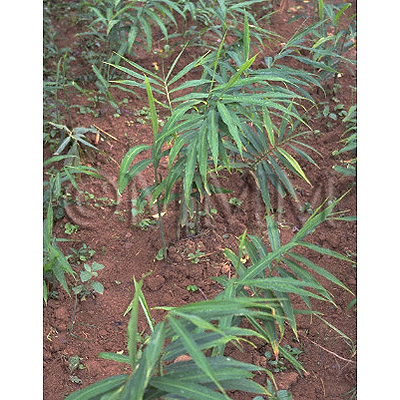
| Original plant name | Zingiber officinale Roscoe, (Shōga) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Zingiberaceae | |||||
| Used part | rhizome (steamed & dried) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | Ganjiang is applied for abdominal pain with cold feeling, lumbago and diarrhea. In chinese medicine, it is applied for cold in the interior synptom-complex. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for dispelling internal cold | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Hot; pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, stomach, kidney, heart and lung. [Actions] To warm the middle energizer, dissipate cold, restore yang, promote blood circulation, warm the lung to resolve fluid retention. [Indications] Cold pain in the epigastrium and abdomen, vomiting, diarrhea, cold limbs and faint pulse, cough and dyspnea caused by cold fluid retention. | |||||
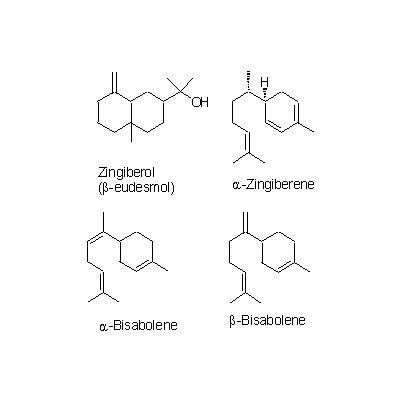
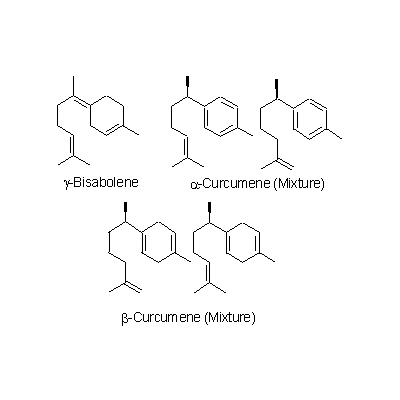
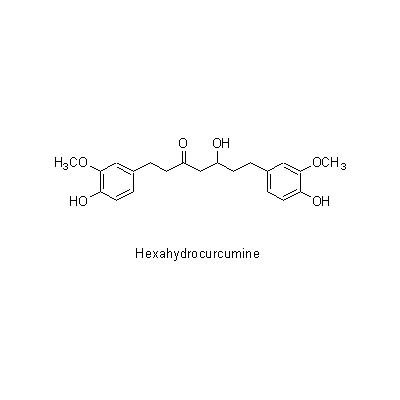
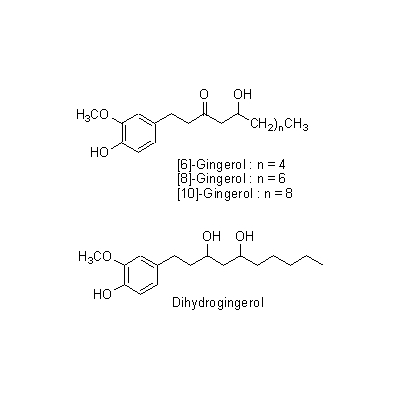
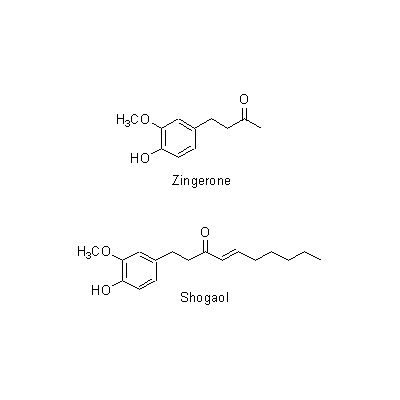
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Methylheptenone, Nonylaldehyde Monoterpenoids (*C1): beta-Phellandrene, Camphene, Citral, Linalool, d-Borneol, Farnesene, alpha-Terpineol, Nerol, Sabinene, 1,8-Cineol, Myrcene Sesquiterpenoids (*C1): Zingiberol, alpha-Zingiberene, alpha-Bisabolene, beta-Bisabolene, gamma-Bisabolene, alpha-Curcumene, beta-Curcumene, Zerumbone Other aromatic derivatives (*C1): Hexahydrocurcumine, Dihydrogingerol, Desmethylhexahydrocurcumine, Zingerone, Shogaol, [6]-Gingerol, [8]-Gingerol, [10]-Gingerol, Dehydrogingerone | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Supression of central nervous system ([6]-gingerol,[6]-shogaol).Analgesic ([6]-shogaol).Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis ([6]-gingerol,[6]-dehydrogingerone).Spasmolytic (essential oil).Conduction anesthesia (water extract).Antitumor (water extract).Antiemetic (ginger juice). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF202418, AF254460, U42081, L05465, AJ388298; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Pain due to abdominal coldness, Diarrhea, Vomitting, Coldness of limbs, Weak pulse, Cough, Dyspnea, A lot of sputum | |||||
| Formulation | Ioto, Ireito, Uzushakusekisigan, Unpito, Orento, Kaikyushokushoto, Kankyooren'ogon'ninjinto, Kankyoninjinhangegan, Kankyobushito, Kangento, Kanzokankyoto, Kanzoshashinto, Kanchuto, Kyukichoketsuin, Kyukihochuto, Keishininjinto, Keishibushito, Keimeisankabukuryo, Kobokumaoto, Kokonrokukenzokumeito, Goshakusan, Saikokeishikankyoto, Shigyakuto, Shigyakukaninjinto, Shishikankyoto, Shokanto, Shokitenkoto, Shokyoshashinto, Shoseiryuto, Shoseiryukasekkoto, Shoseiryugomakyokansekito, Shobaito, Shobaishashinto, Shoyosankato, Seikanto, Seineitsugeutsuto, Senkonto, Sogento, Zokumeito, Daikenchuto, Daisangoshichisan, Daizokumeito, Daitokato, Daibofuto, Danrito, Jizutsuippo, Chukenchuto, Chushaen, Chuseito, Chokobukuryoto, Choburichuto, Tsumyakushigyakuto, Tokito, Ninjinto, Baimoto, Hachimigangoninjinto, Hacchinto, Hangekankyosan, Hangeshashinto, Hangebyakujutsutemmato, Hanbikokantan, Bukuryoshigyakuto, Bushirichuto, Fushinto, Hojinto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Mankeishisan, Richuankaito, Richuto, Ryokankyomishingeto, Ryokankyomishingeninto, Ryokankyomishingeninoto, Ryokangomikyoshinto, Ryokyojutsukanto, Rokumotsuogonto, Fuinto | |||||
| Related drugs | Shengjiang, Paojiang (see "Remarks") | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 116-118. | |||||
| Remarks | Since ancient times, shengjiang, in Chinese Traditiona Medicine, has been representing fresh ginger, and ganjiang means dried one. That is, dried shengjiang (or ganshengjiang) in Chinese drug market indicates ganjiang in Kampo. Then ganjiang in the market means dried, after steamed, shengjiang. It can be called processed one. In China, in contrast, fresh ginger is shengjiang and dried one is ganjiang. In addition, there is Paojiang which is a processed medicine. Paojiang is made as follows.: First of all, the clean sand (gefen, huashifen) should be into a pan and heated at strong fire. The dried unpeeled shengjiang is added in and mixed them until the surface swells and the color turns to brown. Then it is picked up and cooled in air. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||