Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
28.682892
115.85819700000002
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Jiangxi Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
35.6894875
139.69170639999993
Collection information
Japan,Tokyo
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
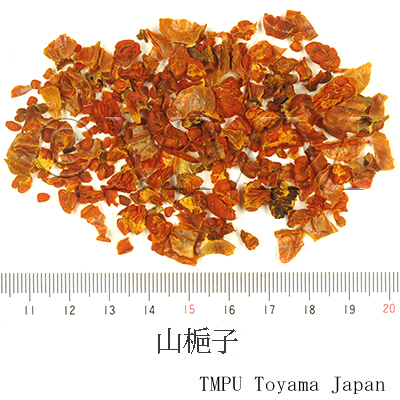
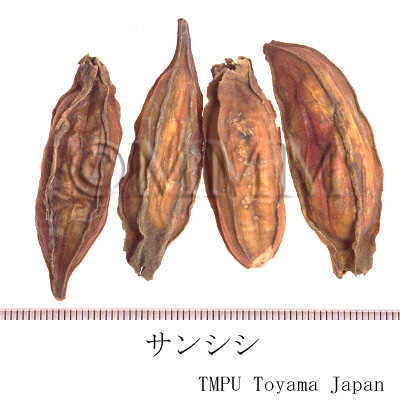
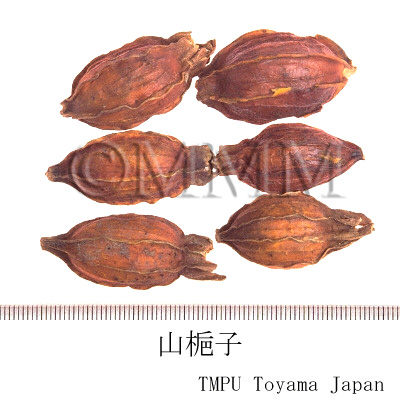
| Common name | 山梔子, Shanzhizi, Zhizi, Gardeniae Fructus (JP18), (CP2020), Gardenia Fruit (JP18), Cape Jasmine Fruit (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 水梔子, 梔子 | |||||
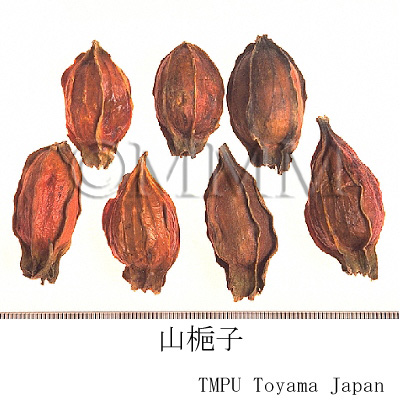
| crude drug image |
| |||||
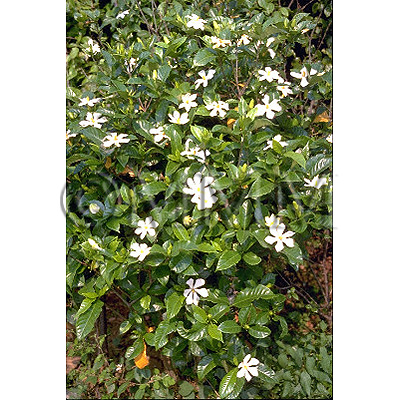
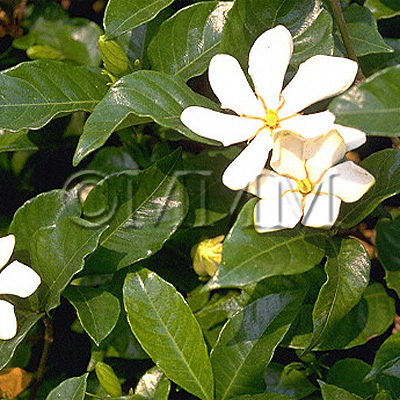
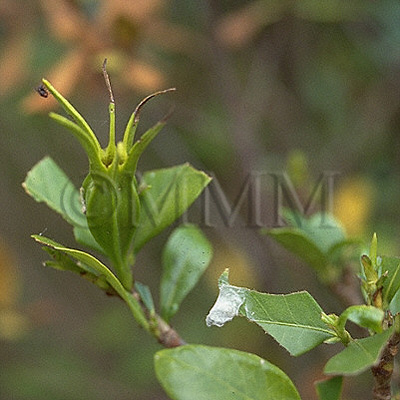
| Original plant name | Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis1, Gardenia jasminoides f. grandiflora Makino, Gardenia jasminoides var. radicans Makino, (Kuchinashi1, Korinkuchinashi, Kokuchinashi) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Rubiaceae | |||||
| Used part | fruit | |||||
| Quality for selection | The shape of Shanzhizi is round and that of Shuizhizi is slender. In general, the round type, which is massive and ponceau, is higher in quality. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antiinflammatory drug, hemostatic, sedative, for normalizing the function of gallbladder, shanzhizi is applied for fidgetiness (mental instability) due to congestion or inflammation, hematemesis, hematuria, congestion and jaundice. For external use, the powder of shanzhizi should be blended with the powder of huangbo and other materials, then kneaded with vinegar. It is applied to bruise externally. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for reducing intense internal heat | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, lung meridians and triple energizers. [Actions] To purge fire to relieve vexation, clear heat and drain dampness, cool the blood, remove toxin; topically disperse swelling and relieve pain. [Indications] Febrile disease with vexation, dampness-heat jaundice, stranguria with slow pain, blood heat with hematemesis, red painful swelling eye, fire-toxin sore and ulcer; topically for sprain and contusions. | |||||
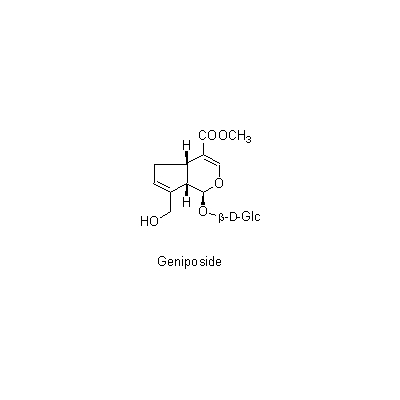
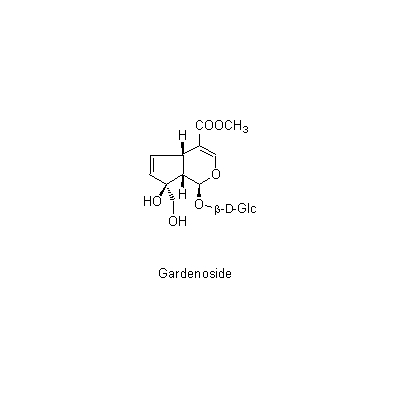
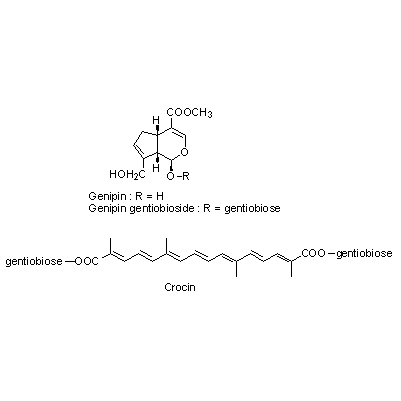
| Chemical constituent | Monoterpenoids Iridoids: (*C1): Gardenoside, Geniposide, Genipin, Genipin 1-beta-gentiobioside, Shanzhiside, Methyl decacetylasperuloside, Geniposidic acid, 10-Acetylgeniposide, Gardoside, Scandoside methyl ester (*C2): Geniposide, Gardenoside, 以下代謝物 [The following compounds are the metabolites] Genipinine, Genipinine monoacetate, Gardenogenin A, Gardenogenin B, Gardenine Carotenoids (*C1): Crocin (Crocetin + Gentiobiose) Other aromatic derivatives (*C1): p-オキシケイヒ酸誘導体 | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Aperient,stimulation of bile secretion,suppression of gastric juice secretion,analgesic (geniposide).Stimulation of bile secretion,suppression of increase in bilirubin and cholesterol in blood (crocin,crocetin,extract).Hypotensive (extract). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF201044, AJ286697, AF102426, AJ224833; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 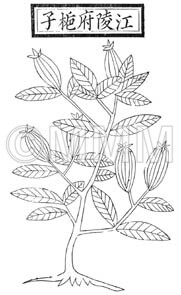 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | , High fever, Disturbance of consciousness, Red eye, Feeling of bitter in the mouth, Thirst, Jaundice, Urodynia, Dysuria, Cloudy urine, Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage, Hematochezia, Hematuria, Internal bleeding, Pyogenic dermatosis, Swelling and pain due to contusion, Burn | |||||
| Formulation | Inchinkoto, Inchinsan, Unseiin, Ogesan, Orengedokuto, Orengedokuto, Orenshodokuin, Kagenshosaikoto, Kagenryokakusan, Kagenryokakusan'ippo, Kakkonkokato, Kamikihito, Kamishokankyoto, Kamishoyosan, Kamishoyosangoshimotsuto, Kamihachimyakusan, Kijitsushishishito, Kijitsushishidaioshito, Kumisaikoto, Keigairengyoto, Keigairengyoto, Gorinsan, Saikoseikansan, Shishikankyoto, Shishikanzoshito, Shishikobokuto, Shishishito, Shishishokyoshito, Shishidaioto, Shishihakuhito, Shijunseiryoin, Jijinmeimokuto (Jinkimeimouto), Shaito, Junkiwachuto, Shin'iseihaito, Jinkimeimokuto, Seiishakato, Seiinrikakuto, Seijobofuto, Seineitsugeutsuto, Seihaito, Seiryoin, Senkanmeimokuto, Jiohanho, Jishusabiho, Tonsonto, Naisoorento, Bofutsushosan, Rikakuto, Ryutan-shakan-to, Ryutan-shakan-to, Ryokakusan, Rokuutsuto, Kaishun'inchinsan, Compound Phellodendron Powder for Cataplasm | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 187-188. C2) Planta Med.,57,536(1991). | |||||
| Remarks | G. jasminoides has a lot of variants. They are called "Shanzhizi", "Shuizhizi", "Hongzhizi" and "Huangzhizi" according to the color or shape. "Shanzhizi" is the round hand type and "Shuizhizi" is the long hand type. Kuchinashi (Jap. name), a kind of Korinkuchinashi, is G. jasminoides Ellis forma grandiflora (Lour.) Makino. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia does not define Kuchinashi as a variant, but as a breed of G. jasminoides. The original plant of "Shuizhizi" is G. jasminoides Ellis forma longicarpa Z.W. Xie et Okada. "Shanzhizi" has been frequently used as a natural yellow dye since ancient times. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/03/23 | |||||