Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
28.682892
115.85819700000002
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Jiangxi Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
36.6952907
137.2113382
Collection information
Japan,Toyama Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 釣藤鈎, Goutenggou, Uncariae Uncis cum Ramulus (JP18), Uncariae Ramulus cum Uncis (CP2020), Uncaria Hook (JP18), Gambir Plant (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 釣藤 Gouteng | |||||
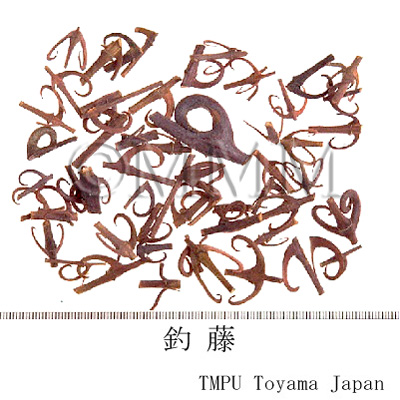
| crude drug image |
| |||||
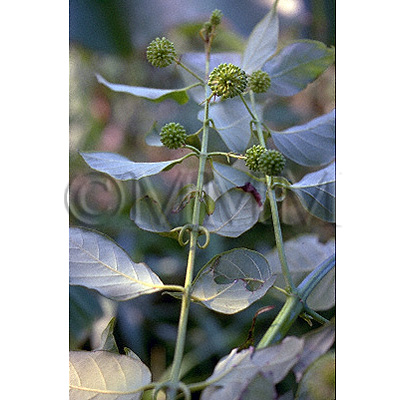
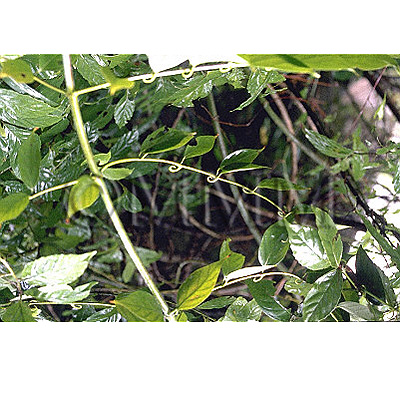
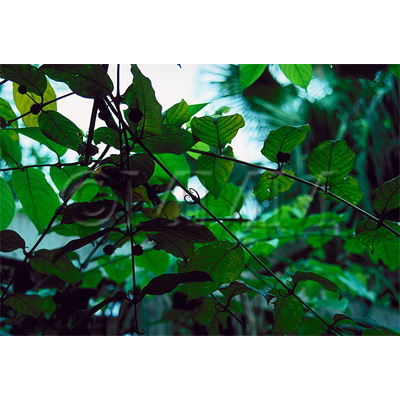
| Original plant name | Uncaria rhynchophylla Miquel1, Uncaria sinensis Haviland2, Uncaria macrophylla Wallich, (Kagikazura1, Tōkagikazura2) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Rubiaceae | |||||
| Used part | hook-bearing stem branch | |||||
| Quality for selection | The best Goutenggou consists of hooks only. Generally, the vine of good Goutenggou is thin and has many soft hooks with a tinge of purple. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antispasmodic and painkiller, Goutenggou is applied for headache and dizziness due to fever or hypertension, sclerosis of cerebral arteries, convulsion, spasm of child, epilepsy, coma with high fever, malaria and rheumatism. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Anticonvulsives | ||||
| Beneficial effect | T[Property and Flavor] Cool; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Liver and pericardium meridians. [Actions] To extinguish wind to settle convulsion, clear heat and pacify the liver. [Indications] Internal stirring of liver wind, fright epilepsy and convulsions, high fever with fright syncope, common cold with fright, infantile terrified crying, pregnant epilepsy, headache, dizziness and hypertension. | |||||
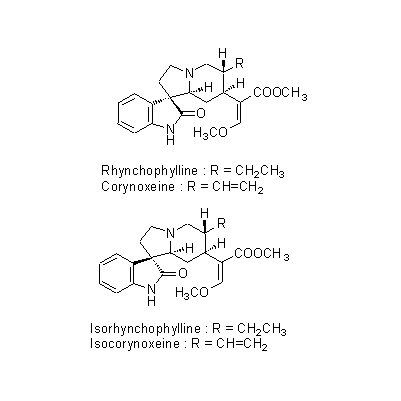
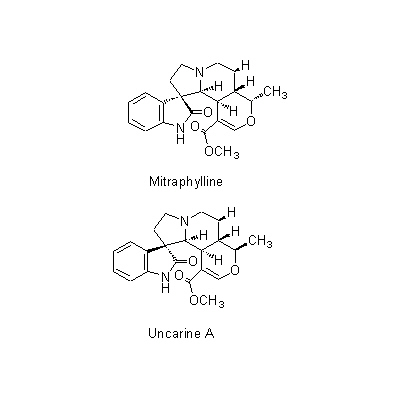
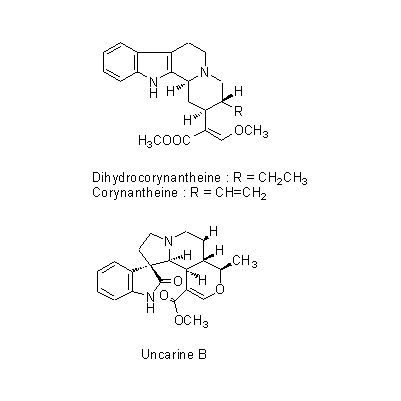
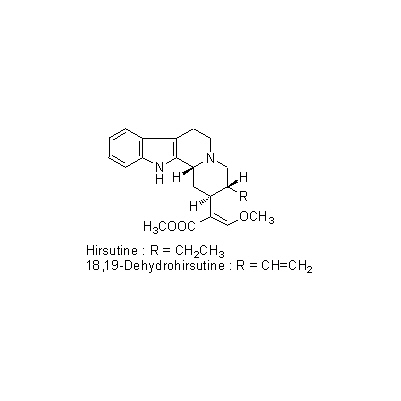
| Chemical constituent | Indole alkaloids U. rhynchophylla (*C1): Rhynchophylline, Corynoxeine, Isorhynchophylline, Isocorynoxeine, Hirsutine, 18,19-Dehydrohirsutine (=Hirsutein), Dihydrocorynantheine, Corynantheine U. sinensis (*C2, C3): Geissoschizine methylether, Hirsuteine, Hirsutine, Rhynchophylline, Corynoxeine, Isorhynchophylline, Isocorynoxeine U. kawakamii (*C1): Uncarine A, Uncarine B, Mitraphylline | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Respiration (low dose: excitation; high dose: inhibition), antispasm, antivirus, vasodilation, alpha-adrenergic blocker, antiarrhythmia, calcium antagonism, inhibition of central serotonin receptor, sedation. Increase in sleep (geissoschizine methylether), decrease in blood pressure (hirsutine, isorhynchophylline)(C2, C4). | |||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 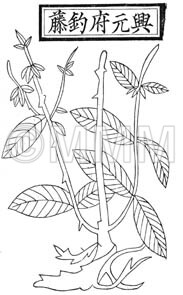 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | High fever, Convulsion, Headache, Vertigo, Stagger, Hypertension, Cerebral arteriosclerosis, Red eye, Convulsion, Tantrum | |||||
| Formulation | Shichimotsukokato, Chotosan, Yokukansan, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Reiyoukakuin | |||||
| Related drugs | CAT'S CLAW, the hook of Uncaria tomentosa (Willd.) DC. | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1) The Journal of Japanese Botany, 74, 42 (1999). C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 186-187. C2) Nat. Med., 51, 79 (1997). C3) Nat. Med., 52, 353 (1998). C4) Nat. Med., 53, 308 (1999). P1) J. Trad. Med., 15, 241 (1998). P2) Am. J. Chin. Med., 29, 173 (2001). P3) J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 51, 715(1999). P4) J. Trad. Med., 19, 28 (2002). Cl1) J. Trad. Med., 11, 246 (1994). Cl2) Phytomed., 4, 15 (1997). | |||||
| Remarks | In Taiwan, Uncaria kawakamii Hayata (Jap. name: Taiwankagikazura) is also used. The Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China defines the hook-bearing branch of U. hirsuta Havil. and U. sessilifructus Roxb. as Goutenggou as well as three species listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. U. rhynchophylla and U. sinensis are mainly distributed in the Japanese market. Reportedly, Goutenggou originated from U. rhynchopylla, produced in Jiangxi and other provinces, contains only oxiindole alkaloids (rhynchophylline, corynoxeine, isorhynchophylline, and isocorynoxeine). Meanwhile, Goutenggou originated from U. sinensis contains mainly indole alkaloids. Additionally, the latter consists of two types depending on its production area. One contains a low amount of oxiindole alkaloids (the type of Guizhou Prov.), the other contains a relatively high amount (the type of Guangxi Prov. Autonomous Region) (C3). Recent results of double blind clinical trials found that Chotosan, which contains Goutenggou, is effective in treating moderate and severe cerebrovascular dementia (C1, C2). Further research in Chotosan is expected. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||