Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
40.842356
111.74999500000001
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 赤芍, Chishao, Paeoniae Radix Rubra (CP2020), Red Peony Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 川芍薬, 川赤芍 | |||||
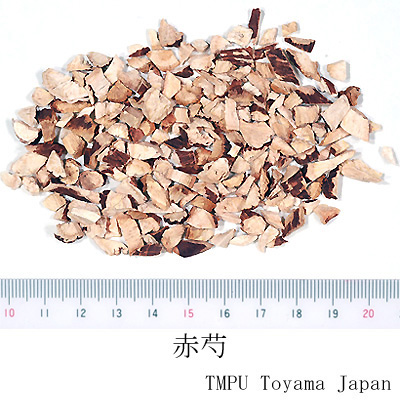
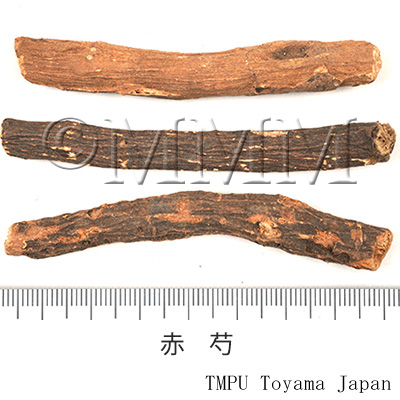
| crude drug image |
| |||||
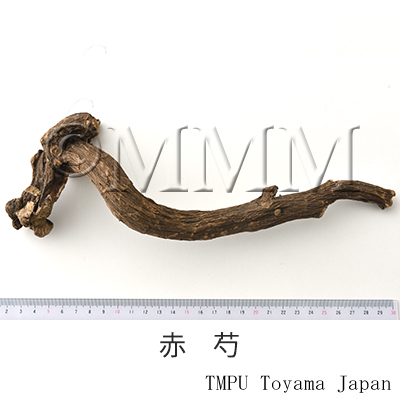
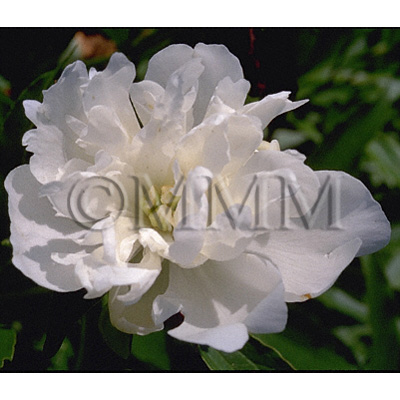
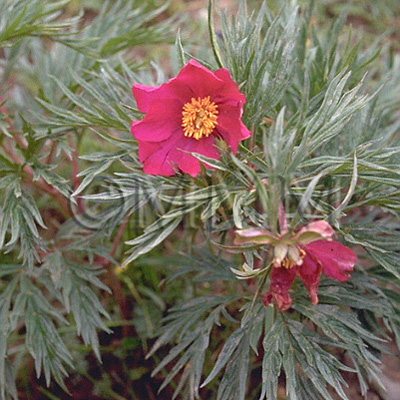
| Original plant name | Paeonia lactiflora Pallas1, Paeonia veitchii Lynch, (Shakuyaku1) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Paeoniaceae | |||||
| Used part | root with periderm | |||||
| Quality for selection | The good one has thicker, longer roots and deep wrinkles on its surface. The outer bark is easily peeled off. The cross-sectioned surface is whitish in color and a powdery state. | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | It activates blood and moves stagnation. It disperses abscesses and swellings. It is used for pain in the lower abdomen and the lower back caused by blood heat stagnation. It is also applied to gynecological disease such as amenorrhea. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for invigorating blood circulation | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Liver meridian. [Actions] To clear heat, cool the blood, dissipate stasis, and relieve pain. [Indications] Heat entering nutrient-blood aspects, macula and papule caused by warm toxin, hernatemesis, epistaxis, red painful swelling eyes, liver depression with hypochondriac pain, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, abdominal pain caused by masses traumatic injures swelling abscess, sore and ulcer. | |||||
| Chemical constituent | Monoterpenoids P. lactiflora Pall. var. trichocarpa Stern. (*C1): Paeoniflorin, Albiflorin, Oxypaeoniflorin, Paeoniflorigenone, Paeonilactones P. albiflora Pall. var. trichocarpa Bunge 代謝物/metabolites (*C2, C3): Paeonilactone-A, Paeonilactone-B, Paeonilactone-C P. albiflora Pall. (*C7-C16): Paeoniflorin, Oxypaeoniflorin, Benzoylpaeoniflorin, Desbenzoylpaeoniflorin, Albiflorin, Paeoniflorigenone, 6-O-Acetylpaeoniflorigenone 以下代謝物/the followings are metabolites; 7S-Paeonimetaboline I, 7R-Paeonimetaboline I, 6-O-Acetylpaeonimetaboline I, Paeonimetaboline II, Paeonimetaboline III, Paeonilactone-A(Metabolite-A1), Paeonilactone-B(Metabolite-A2), Metabolite A1-acetate, 7S-Paeonimetaboline-6-O-3,5-dinitrophenyl carbamate, 7R-Paeonimetaboline-6-O-3,5-dinitrophenyl carbamate, 7S-8-(2-Carboxyethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, 7R-8-(2-Carboxyethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, 7S-8-(2-Hydroxyethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, 7R-8-(2-Hydroxyethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, 7S-8-Benzoylthiopaeonimetabolin I, 7R-8-Benzoylthiopaeonimetabolin I, 7R-8-(Carboxymethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, 7S-8-(Carboxymethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, 7R-8-(2'-Carboxyethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, 7S-8-(2'-Carboxyethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, 7R-8-(5'-Carboxyethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, 7S-8-(5'-Carboxyethylthio)paeonimetabolin I, Pentaacetylpaeoniflorin, Tetraacetylpaeoniflorin, Albimetaboline I, Albimetaboline II P. albiflora 代謝物/metabolites (*C17-C19): 7S-Paeonimetaboline I, 7R-Paeonimetaboline I, Paeonimetaboline II, Paronimetaboline III Triterpenoids P. lactiflora (*C4,C5,C6): Palbinone Tannins P. lactiflora var. trichocarpa (*C1): Tetragalloylglucose, Pentagalloylglucose, Hexagalloylglucose P. albiflora (*C7): Gallotannins (*C20): Tetra - Undecagalloylglucose, d-Catechin, Procyanidin B-1 Other aromatic compounds P. lactiflora var. trichocarpa(*C1): benzoic acid | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antiinflammatory, antihypertensive, sedative (paeoniflorin). Inhibition of stress ulcer. Antispasmodic, improvement of experimental spatial cognitive impairment (water extract, paeoniflorin). Central antispasmodic effect (paeoniflorin, paeonimetabolin I). Antibacterial (Staphylococcus aureus and all). ※Metabolism by human entric bacteria (*C7-C19). Paeoniflorine is metabolized by 7-R-paeonimetaboline I or 7-s-paeonimetaboline I, which have central antispasmodic behavior. Therefore, they seem to be the real medical properteis. | |||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Disease | Lower back pain, Abdominal pain, Swelling and pain due to contusion, Anginal pain, Nasal hemorrhage, Irregular menstruation | |||||
| Related drugs | "Shaoyao", "Baishao", "Shanshaoyao" | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 102-104. C2)Tetrahedron Lett.,26,3699(1985). C3)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,37,843(1989). C4)Tetrahedron Lett.,33,255(1992). C5)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,41,487(1993). C6)Phyto.Res.,9,379(1995). C7)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,33,3838(1985). C8)J.Med.Pharm.Soc.Wakan-Yaku,2,398(1985). C9)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,35,3726(1987). 10)J.Med.Pharm.Soc.Wakan-Yaku,4,82(1987). C11)J.Pharmacobio-Dyn.,10,s-58(1987). C12)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,36,3043(1988). C13)J.Trad.Med.,13,73(1996). C14)J.Trad.Med.,14,15(1997). C15)Biol.Pharm.Bull.,20,517(1997). C16)J.Trad.Med.,14,105(1997). C17)J.Trad.Med.,13,248(1996). C18)J.Pharm.Pharmacol.,49,35(1997). C19)Nat.Med.,52,265(1998). C20)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 297. | |||||
| Remarks | [Origin] The name "Shaoyao" (芍薬) is not used in China, but white-peony and red-peony are used distinctively. The Pharmacopoeia of The People's Republic of China defines red-peony as the roots of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. or P. veitchii Lynch., and white-peony as the boiled roots of P. lactiflora after removal of the skin or as the boiled unbarked roots. In Japan, generally, white-peony and red-peony are not used distinctively but divided into 3 categories according to the following processes: Shin-Shakuyaku (the skin of roots is removed, boiled and dried like Chinese white-peony). "Kiboshi-Shakuyaku" (after being washed in water, the skin is removed and it is dried). "Kawatsuki-Shakuyaku" (washed and dried like Chinese red-peony). The Japanese Pharmacopoeia (1st appendix of 14th edition), adapts the theory which consolidates P. lactiflora Pall. var. trichocarpa Stern (= P. albiflora Pall) into the mother species, and defines it as the roots of P. lactiflora. Chinese red-peony can not adapt to Japanese officinal. In Japan, P. lactiflora has been cultivated as Japanese peony in Nara, Hokkaido and Tottori prefectures. Though European peony of the garden plant is also used now, the quality is said to be lower. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/09/07 | |||||