Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
24.880095
102.83289100000002
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Yunnan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
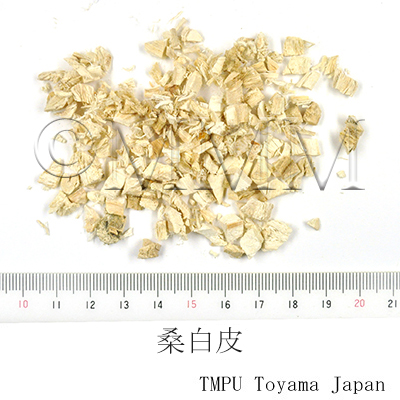
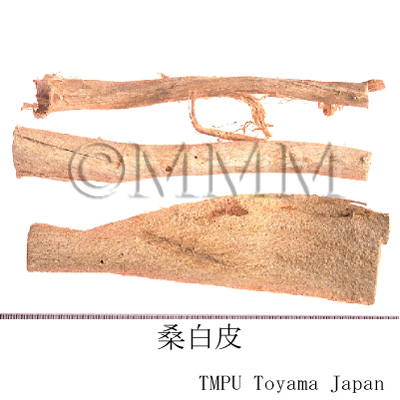
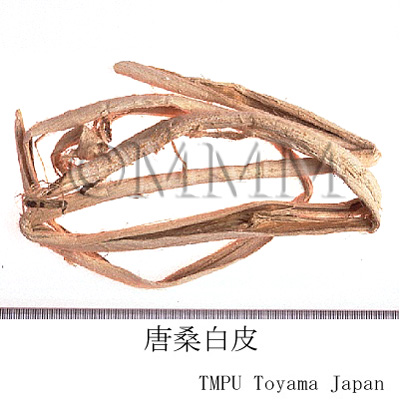
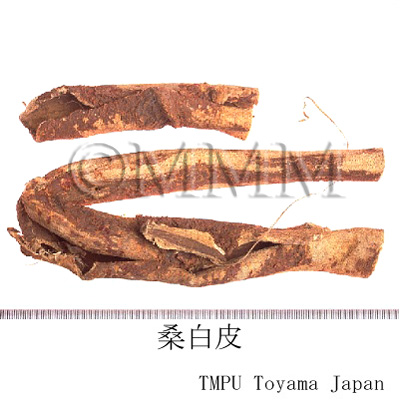
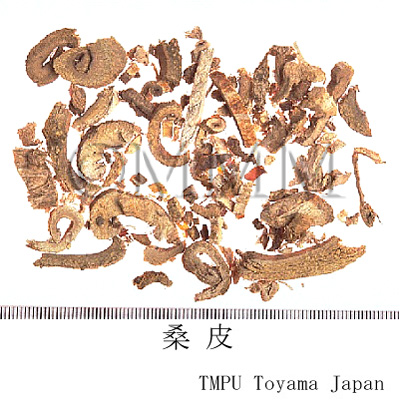
| Common name | 桑白皮, Sangbaipi, Mori Cortex (JP18, CP2020), Mulberry Bark (JP18), White Mulberry Root-bark (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 亳桑皮: 河南,安徽/麗桑皮: 浙江/北桑皮: 江蘇 | |||||
| crude drug image |
| |||||
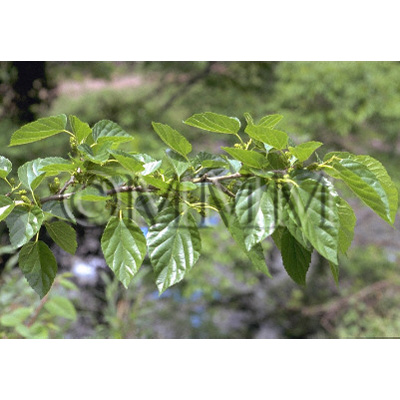
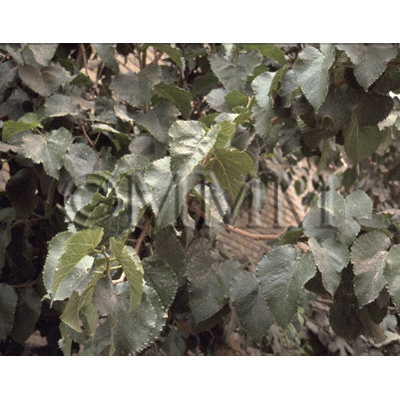
| Original plant name | Morus alba Linn., Morus mongolica (Bureau) Schneider, etc., (Maguwa (Tōguwa, Shiroguwa, Karayamaguwa), Mōkoguwa etc.) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Moraceae | |||||
| Used part | root bark | |||||
| Quality for selection | The outer surface of good Sangbaipi is thin and yellowish-red. Also, there are bleached white Sangbaipis. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antitussive, expectorant, antiphlogistic diuretic, Sangbaipi is applied for bronchitis, cough, oliguria and edema. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Antitussives and antiasthmatics | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Lung meridian. [Actions] To purge the lung and relieve panting, and promote urination to alleviate edema. [Indications] Panting and cough caused by lung-heat, edema, distention and fullness and small quantity of urination, puffiness. | |||||
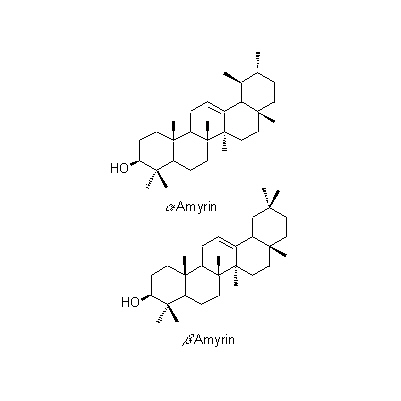
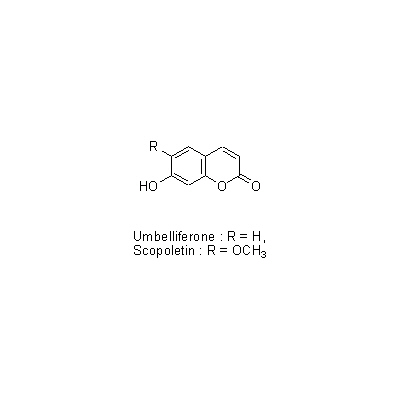
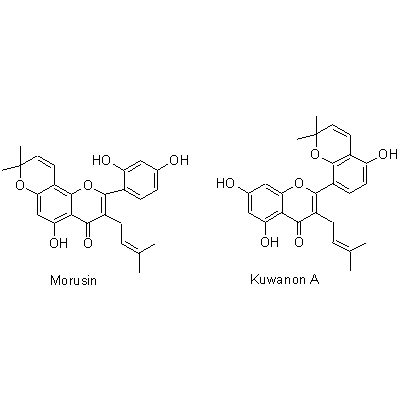
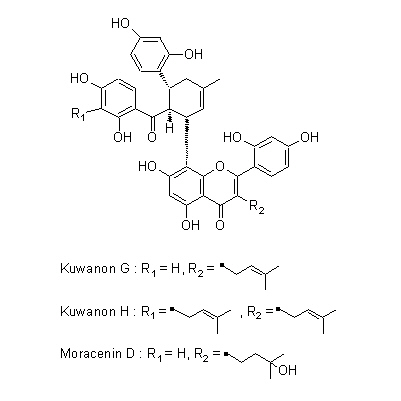
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids (*C1,C2): Palmitic acid, Stearic acid Triterpenoids (*C1,C2): alpha-Amyrin, alpha-Amyrin acetate, beta-Amylin, Betulinic acid Sterols (*C1,C2): Sitosterol, Sitosterol-d-glucoside Flavonoids (*C1,C2): Morusin, Cyclomorusin, Kuwanon A, Kuwanon B, Kuwanon C, Kuwanon D, Kuwanon E, Kuwanon F, Kuwanon G (Moracenin B, Albanin F), Kuwanon H (Moracenin A, Albanin G), Moracenin類, Oxydihydromorusin (=morusinol) (*C3): Kuwanon C, Kuwanon G, Kuwanon E, Kuwanon H, Kuwanon L, Morusin, Sanggenon D, Sanggenon C Coumarins (*C1,C2): Umbelliferone, Scopoletin Amino acids (*C1): Betaine Other nitrogen compounds (*C1): Adenine | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Analgesia, cathartic, antiinflammatory (water soluble fraction), mild anti-tumor (hot water extractable fraction). Decrease in blood sugar (decoction, ethanol extract). | |||||
| DNA sequence | D86319, L01933, L24398; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 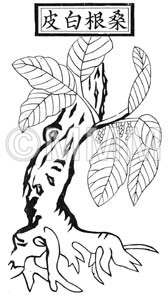 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Bronchitis, Cough, Dyspnea, Rapid breathing, Edema, Oliguria | |||||
| Formulation | Ogibekkoto, Kagaisan, Kagenshahakusan, Kikyoto, Kippihangeto, Kyososan, Gokoto, Shisoshito, Shahakusan, Seihaito, Zenshikunshito, Zosonmokuboito, Teizento, Dosuibukuryoto, Dotaitsukeito, Tonsonto, Ninjin-yoei-to, Baimoto, Hakanto, Bunshinkiin, Henseishinkiin, Boisan, Boito, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonto, Hontonbukuryoto, Mankeishisan, Yohaito | |||||
| Related drugs | Mori Fructus, Mori Folium | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 153-154. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 319. C3)Nat. Med., 48, 75-81(1994). | |||||
| Remarks | - Sōjin (桑椹, the fruit of M. alba, Jap. name: Maguwa): Invigorates liver and kidney and restores the blood of Yin nature. It is applied for irritability and restlessness and insomnia, buzzing, lumbago and weakness in knee as a tonifying or analgesic drug. - Sōyō (桑葉, the leaf of Maguwa): Reduces fever, antitussive, removes heat from the blood and improves vision. It is used to treat common cold, cough, headache, eye problem, beriberi, edema, abdominal pain and diarrhea. The name Kuwa is a generic name. About ten species are known as Kuwa, though some researchers claim more than twenty. There are many kinds of cultivated Kuwa which includes hybrid origin. M. alba (Jap. name: Maguwa) is native of China and widely cultivated as feed for silkworm. M. australis Poir. (Jap. name: Yamaguwa) is widely distributed from Himalaya region through Japan. There is a view that classifies Yamaguwa into the following two species.: One is M. australis Poir. has a large leaf, which is distributed in Japan and Korean Peninsula, and the other is M. bombycis Koidz. (Jap. name: Shimaguwa) has a small lustrous leaf, which is distributed from southern Kyusyu (Japan) through eastern India. Japanese Sangbaipi is the root bark of Yamaguwa or hybrid between Yamaguwa and Maguwa. At present, they have low marketability. The superior one is collected in spring, before germination, and processed. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||