Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
31.9110956
131.4238934
Production area information
Japan,Miyazaki Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
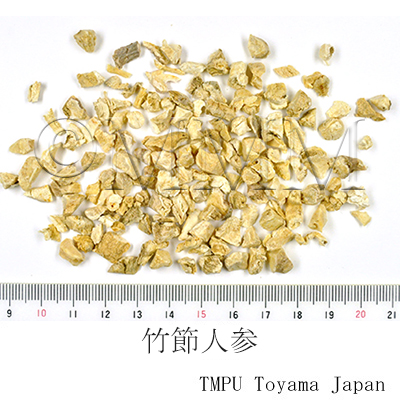
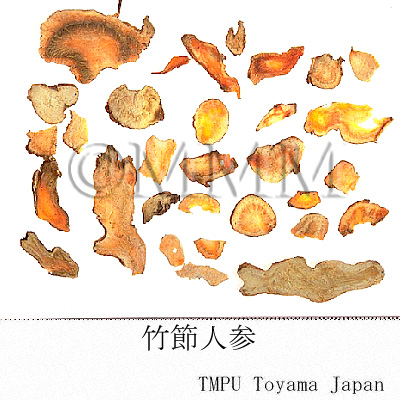
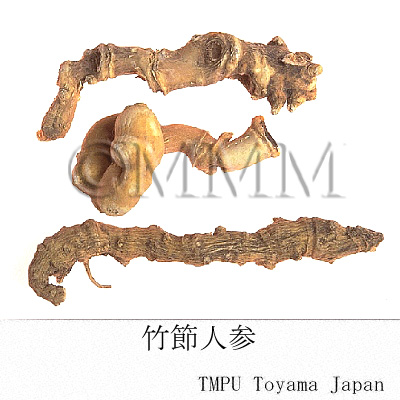
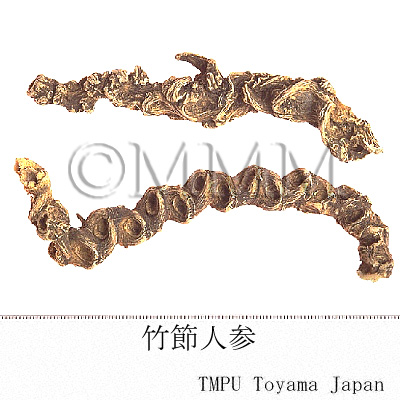
| Common name | 竹節人参, Zhujieshen, Panacis Japonici Rhizoma (JP18, CP2020), Panax Japonicus Rhizome (JP18), Japanese Ginseng (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 竹参, 竹節参 | |||||
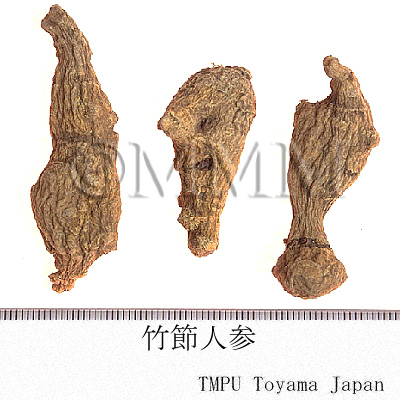
| crude drug image |
| |||||
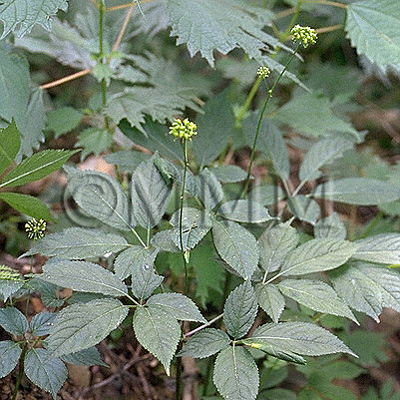
| Original plant name | Panax japonicus C.A. Meyer, (Tochibaninjin) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Araliaceae | |||||
| Used part | rhizome | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Zhujieshen is enlarged. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | Zhujieshen is used as stomachic, antifebrile and expectorant. Though the invigoration of metabolism is weaker than that of ginseng, it has stronger effects in stomachic, antifebrile and expectorant. | |||||
| Medical system | Kampo med., TCM | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; sweet and mild bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Liver, spleen and lung. [Actions] To dissipate stasis and stanch bleeding, disperse swelling, relieve pain, dispel phlegm to suppress cough, replenish and strengthen the body after diseases. [Indications] Cough caused by consumptive disease, hemoptysis, traumatic injuries, cough, profuse sputum, and convalescent weakness after illness. | ||||
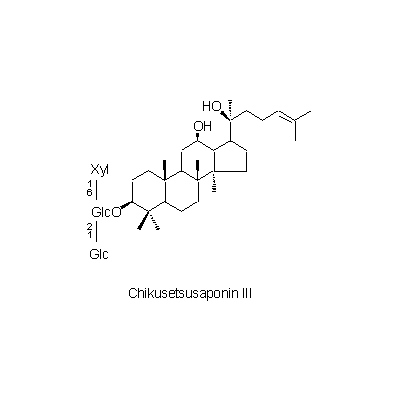
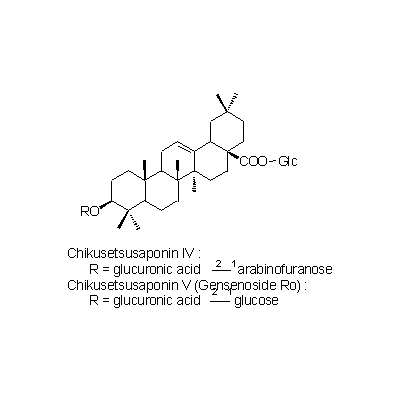
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoid saponins (*C1): サポニン配糖体約5% [saponin glycosides approx.5%[ : Chikusetsusaponin I, Chikusetsusaponin Ia, Chikusetsusaponin Ib, Chikusetsusaponin III, Chikusetsusaponin IV, Chikusetsusaponin IV a, Chikusetsusaponin V | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Sedative,spasmolytic,antifebrile,antitussive,expectorant,enhanced automovement of intestinal motility,suppression of stress ulcer (chikusetsusaponinⅡ).Cholinominetic,histamine release action,and suppression of peptic ulcer (non-saponin fraction,chikusetsusaponin Ⅴ). | |||||
| DNA sequence | 18SrRNA:D84100(*S1), matK:D89058(*S2), ITS:U41701, U41702; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Disease | Dyspepsia, Anorexia, Chronic gastritis, Common cold, Acute Bronchitis, Chronic bronchitis, Cough, Expectoration of sputum | |||||
| Formulation | Jinrento | |||||
| Related drugs | Renshen (Ginseng), Hongshen (Red Ginseng), Sanqirenshen (Panax Notoginseng Root), Guangdongrenshen (American Ginseng) | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 3-4. S1) Biol.Pharm.Bull.,19,1530(1996). S2) Biol.Pharm.Bull.,20,765(1997). | |||||
| Remarks | It was developed as the substitute for Ginseng at an early stage of Edo period (1624-1643). It is blended into "Shosaikoto" and "Hangeshashinto" as a substitute for Ginseng. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||