Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
43.8899438
125.31683650000002
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Northeast Part
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
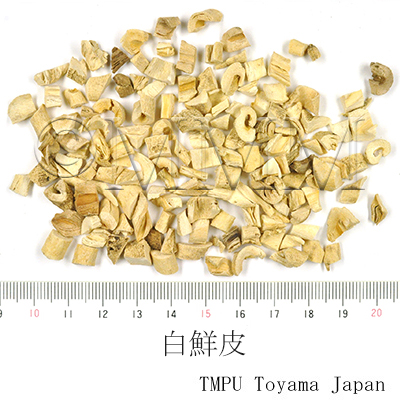
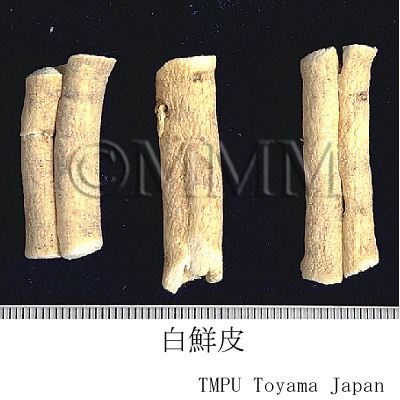
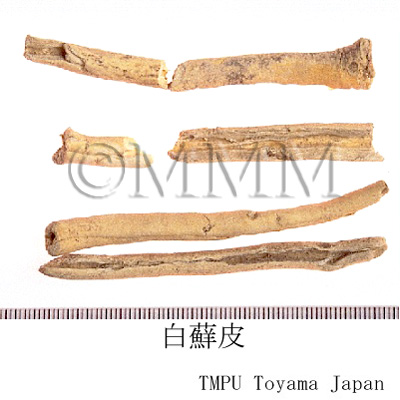
| Common name | 白蘚皮, Baixianpi, Dictamni Cortex (CP2020), Densefruit Pittany Root-bark (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
| Original plant name | Dictamnus dasycarpus Turczanínow , (Hakusen) | |||||
| Family name | Rutaceae | |||||
| Used part | root bark | |||||
| Official compendium | CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antipyretic, antidote, analgesic, cholagogue, it is employed in the treatment of rheumatism, nervous pain, jaundice, and skin disease like an itch. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Febrifugal and detoxicant drugs | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, stomach and bladder meridians. [Actions] To clear heat, dry dampness, dispel wind and remove toxin. [Indications] Dampness-heat sore and skin infections with yellow watery pus, eczema, rubella, scabies and tinea, wind-dampness heat bi disorder, jaundice and deep-colored urine. | |||||
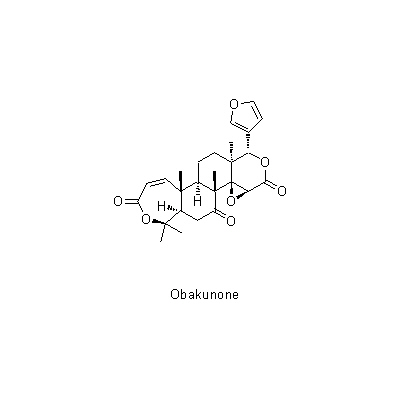
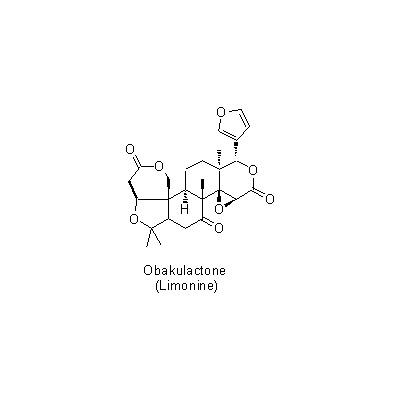
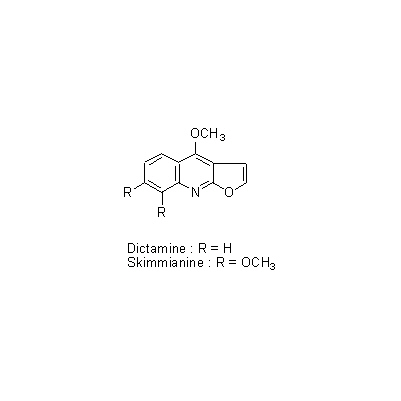
| Chemical constituent | Triterpenoids (*C1): Limonin, Obacunone, Obacunonic acid Sterols (*C1): Campesterol, Sitosterol Other aromatic compounds (*C1): Fraxinellone Alkaloids (*C1): Dictamine (= Dictamnine), Skimmianine (= beta-Fagarine), Trigonelline Simple nitrogen containing compounds (*C1): Choline Others (*C1): Dictamnolide | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antipyretic action (decoction: laboratory rabbit). Inhibitory action (infusion: pathogenic fungus). Stimulant action, contractile action (dictamine). | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Fever, Rheumatism, Neuralgia, Jaundice, Scabies, Eczema, Rubella, Hematuria | |||||
| Formulation | rarely used in formula | |||||
| References | CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. Ⅱ, pp 138-139. | |||||
| Remarks | It is called "Beixianpi" (北蘚皮). The root instead of the root-bark is used for medicinal purposes in Xiangyang and of Jingshan Hubei, Huaiyin of Jiangsu and Chuzhou of Anhui, and called "Guxianpi" (古蘚皮). Baixianpi (白蘚皮) used in Xinjiang is the root-bark of Dictamnus angustifolius G. Don. Baixianpi used in Shaanxi, Shichuan and Hunan are regarded as the root bark of Caragana chamlagu Lam. of Leguminosae (Jap. name: Muresuzume). But the one used in Henan is not botanically identified for now. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/03/08 | |||||