Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
40.842356
111.74999500000001
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
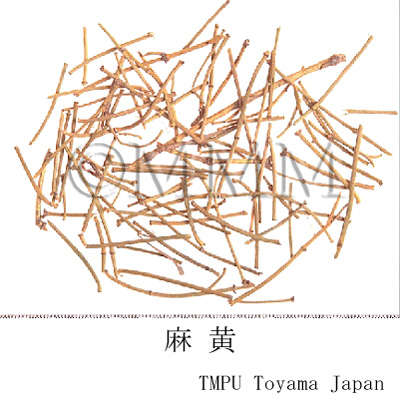
| Common name | 麻黄, Mahuang, Ephedrae Herba (JP18, CP2020), Ephedra Herb (JP18), Ephedra (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
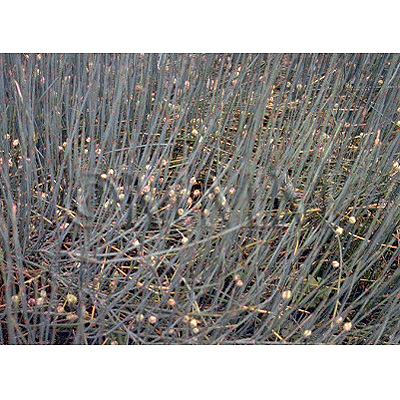
| crude drug image |
| |||||
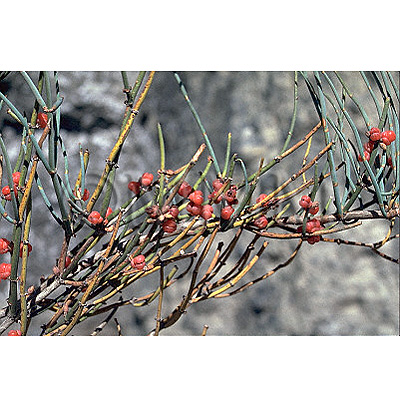
| Original plant name | Ephedra sinica Stapf, Ephedra intermedia Schrenk et C. A. Meyer or Ephedra equisetina Bunge | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Ephedraceae | |||||
| Used part | aerial stem | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Mahuang is fresh and green. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a diaphoretic, antifebrile, antitussive and painkiller, Mahuang is applied for dyspnea due to disorder of skin excretion mechanism, stridor, asthma, chills, general aching and arthritis. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diaphoretics with warm property | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; pungent, mild bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and bladder meridians. [Actions] To induce perspiration for dispelling cold, to relieve asthma and to cause diuresis. [Indications] Common cold with wind-cold syndrome (marked by chilliness and mild fever, headache, stuffy and runny nose, general aching, but no sweating), edema in acute nephritis, bronchial asthma. | |||||
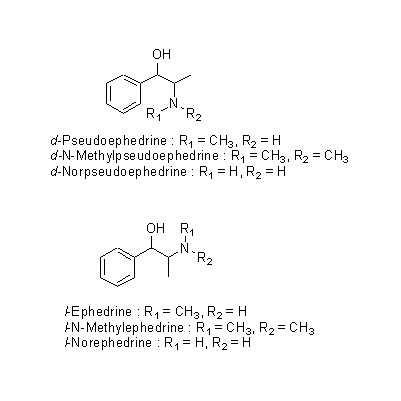
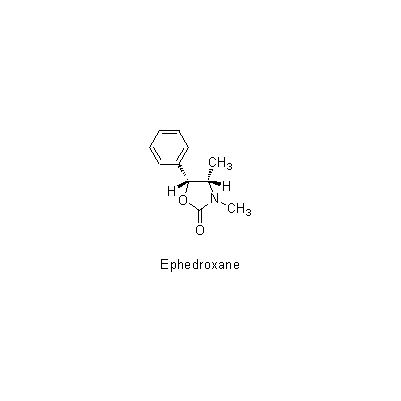
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Nonacosan-10-ol, Nonacosan, Tricosan-1-ol Tannins (*C1): d-Catechin, l-Epicatechin, l-Gallocatechin, l-Epigallocatechin 及びこれらの2量体,3量体 Alkaloids (*C2): Ephedroxane Isoquinoline alkaloids (*C1): l-Ephedrine, d-Pseudoephedrine, l-Norephedrine, l-N-Methylephedrine, d-N-Methylpseudoephedrine, d-Norpseudoephedrine | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antitussive,antiallergy (water,ethanol extract),excitation of sympathetic nerve(increase in blood pressure,bronchodilation,mydriasis,perspiration),central antitussive (ephedrine),antiinflammation(pseudoephedrine). | |||||
| DNA sequence | D38242, D10732, U72821; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Dyspnea, Cough, Chill, Fever, Anhidrosis, Headache, Somatic pain, Arthralgia, Common cold, Influenza, Bronchitis, Pneumonia, Bronchial asthma | |||||
| Formulation | Uzuto, Uyakujunkisan, Eppito, Eppikajutsuto, Eppikahangeto, Kagaisan, Kakkonto, Kakkonkahangeto, Kakkonkaryojutsubuto, Kakkontokashin'isenkyuto, Kankonto, Kanzomaoto, Kyososan, Keikyososooshinbuto, Keishikyoshakuyakukamaobushisaishinto, Keishishakuyakuchimoto, Keishinieppiichito, Keishinieppiittokaryojutsubu, Keishinimaoichito, Keishimaokakuhanto, Kokikososan, Kobokumaoto, Gokoto, Kokonrokukenzokumeito, Goshakusan, Saikatsugekito, San'oto, Sekishozuto, Shoseiryuto, Shoseiryukasekkoto, Shoseiryugomakyokansekito, Shozokumeito, Shimpito, Zokumeito, Daiseiryuto, Daizokumeito, Dokkatsukakkonto, Bofutsushosan, Boreito, Maoto, Maokajutsuto, Maokaryojutsubuto, Maogomito, Maobushikanzoto, Maobushisaishinto, Maorenshosekishozuto, Makyokansekito, Makyoyokukanto, Yakammaoto, Yokuininto, Rengyoto, Rengyoto | |||||
| Related drugs | The root of Ephedrae Herba | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 53-57. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 341. | |||||
| Remarks | - The root of Mahuang is called Mahuanggen and is said to be effective in stopping sweating, as opposed to the aerial part, which is supported by the fact that ephedradines have been isolated from it. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia 17th edition defines Mahuang as the terrestrial stem of E. sinica, E. intermedia or E. equisetina. In addition, it contains not less than 0.7% of total alkaloids (ephedrine and pseudephedrine). - In 1998, the Chinese Government issued "A notice of the export control to the products of ephedrines" (Administration of bureau of external economy and trade No. 573). It says the export of Mahuang is prohibited in order to prevent desertification as well as to preserve the resource. Currently China restricts the export of Mahuang. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/10/04 | |||||