Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
31.2303904
121.47370209999997
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Shanghai
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
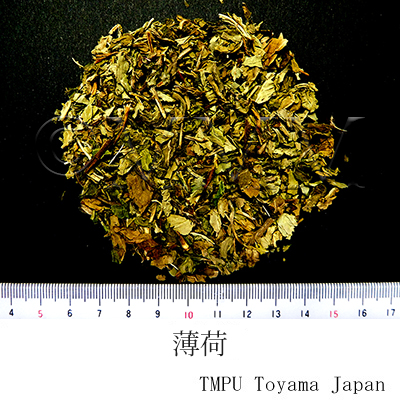
| Common name | 薄荷, Bohe, Menthae Herba (JP18), Menthae Haplocalycis Herba (CP2020), Mentha Herb (JP18), Peppermint (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 蘇薄荷 (Subohe) | ||||||
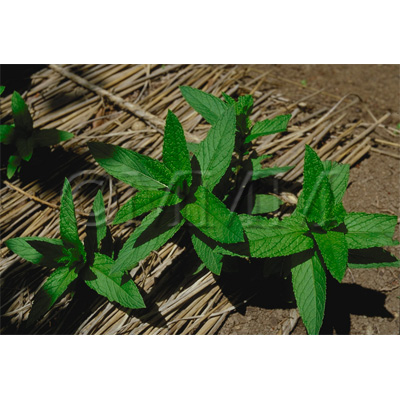
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
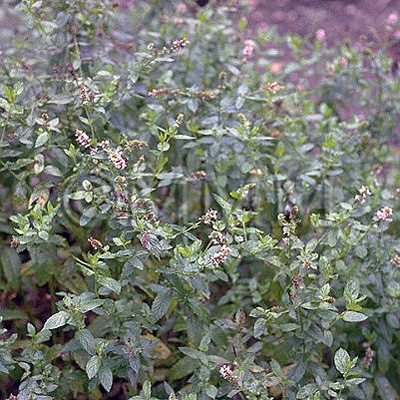
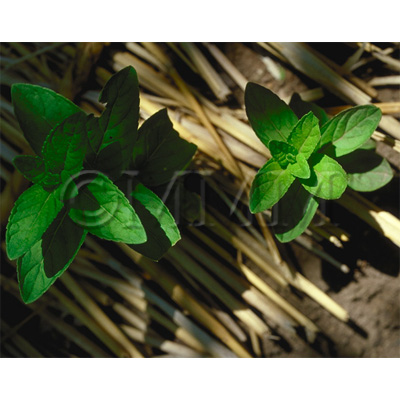
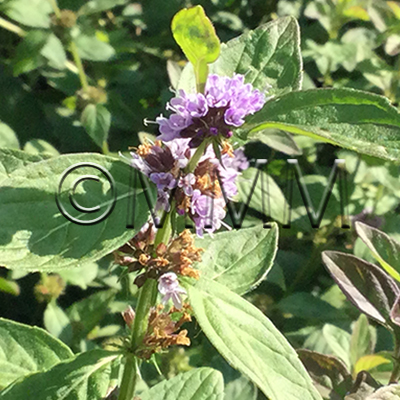
| Original plant name | Mentha arvensis Linn. var. piperascens Malinvaud1, Mentha haplocalyx Briquet2, (JP products: Hakka1, CN products: Kōnminto2) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Labiatae | ||||||
| Used part | terrestrial part | ||||||
| Quality for selection | The leaf of good Bohe is dark-green and has a strong odor. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an aromatic stomachic and carminative, Bohe is applied for headache, dizziness, sore throat, scrofula and a discomfort feeling of distension in the chest and abdomen. Mostly, it is used as raw material for l-menthol (antiseptic, local anesthesia), peppermint oil and peppermint water. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diaphoretics with cold property | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cool; pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and liver meridians. [Actions] To disperse wind-heat, clear and sooth head and eyes, soothe the throat, promote eruption, soothe the liver to move qi. [Indications] Common cold caused by wind-heat, early onset of wind-warmth disease, headache, red eyes, throat impediment, mouth sore, rubella, measles, distention and oppression in the chest and the hypochondriurn. | ||||||
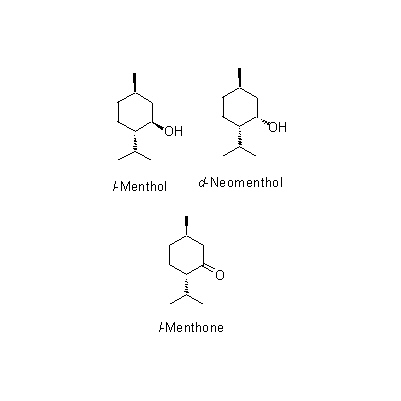
| Chemical constituent | Monoterpenoids (*C1): l-Menthol(精油約1%の70~90%), l-Menthone, 1,8-Cineole, Isomenthone, d-Neomenthol, alpha-Pinene, Camphene, Menthenone, l-Limonene, Piperitone, Piperitenone, Pulegone Sesquiterpenoids (*C1): beta-Caryophyllene, Germacrene-D | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Central inhibition, vasodilation, skin stimulation, spasmolysis (essential oil), local stimulation, local anesthesia, spasmolysis, carminative, cholagogue, and anthelmin (menthol). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | Z37420, U28876; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Fever, Chill, Headache, Anhidrosis, Swelling and pain of the throat, Red eye, Measles, Itching, Pain due to flatulence of hypochondrium, Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Vomitting, Diarrhea | ||||||
| Formulation | Kagenryokakusan, Kagenryokakusan'ippo, Kamishoyosan, Kamishoyosangoshimotsuto, Kyoseihatekigan, Keigairengyoto, Kokyuto, Saikoseikansan, Jiinshihoto, Shaito, Shoyosan, Seiishakato, Seiinrikakuto, Seijobofuto, Seiryoin, Senkanmeimokuto, Senkyuchachosan, Chimobukuryoto, Naisoorento, Hachimishoyosan, Bofutsushosan, Ryutan-shakan-to, Ryokakusan | ||||||
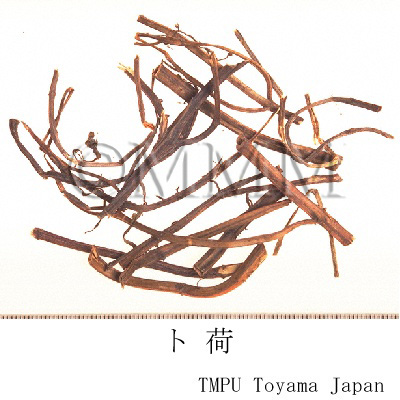
| Related drugs | Sōiyōhakkayō (Peppermint leaf), Midorihakkayō (Spearmint leaf) | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 42-43. | ||||||
| Remarks | - Mentha piperita L. (Jap. name: Seiyōhakka) is a natural hybrid between Mentha spicata L. (Jap. name: Midorihakka) and Mentha aquatica L. (Watermint). It is cultivated for gardening and commercial use all over the world. It is a major European crude drug and called Menthae Piperitae Folium (Jap. name: Seiyohakkayō) or Peppermint. Being antispasmodic, carminative and cholagogue, it is used to treat gastrointestinal colic pain, flatulence and chronic gallbladder disease. The essential oil (peppermint oil: 0.5-4%) contains less menthol than that of Chinese Mentha Herb, "Bohe" (Jap. name: Hakka), but has a stronger odor and taste. Peppermint leaf contains menthofuran, however, "Bohe" contains only traces of it. These two can be distinguished by this component. - The leaf of M. spicata (Jap. name: Midorihakkayō) is the medicine for stomachic and carminative. The essential oil (spearmint oil: 0.8-2.5%) is, as well as peppermint oil, widely used for mouth wash and various sweets. The essential oil contains 50% of carvone and no menthol. - It is said that the usage of Peppermint leaves in Europe was introduced to China and the eastward, and Japanese Mentha Herb, "Hakka" was utilized. In Japan, "Hakka" is widely cultivated in Hokkaido in order to extract mentha oil (Oleum Menthae Japonicae). | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/10/28 | ||||||