Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
36.6512986
138.18095570000003
Production area information
Japan,Nagano Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 車前草, Chaqiancao, Plantaginis Herba (JP18, CP2020), Plantago Herb (JP18), Plantain Herb (CP2020) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
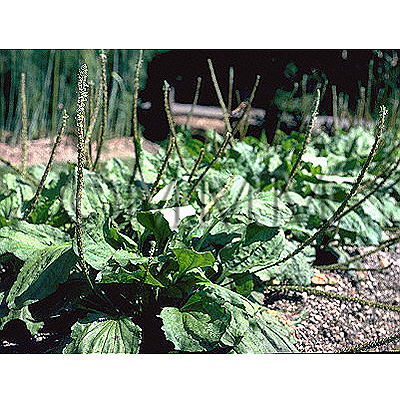
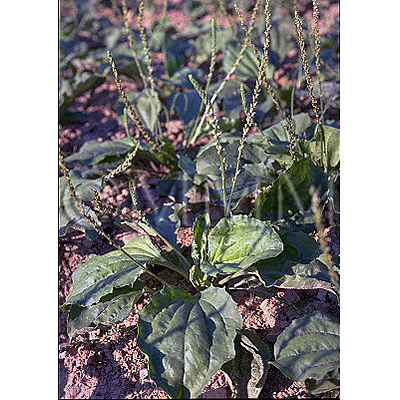
| Original plant name | Plantago asiatica Linn., (Ōbako) | ||||
| original plant image |
| ||||
| Family name | Plantaginaceae | ||||
| Used part | whole plant in flower season | ||||
| Quality for selection | Good chaqiancao is fresh and bluey. (TN) | ||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||
| Clinical application | Diuretic, antibechic and stomachic. | ||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diuretics removing dampness | |||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Liver, kidney, lung and small intestine meridians. [Actions] To clear heat, disinhibit urine and relieve stranguria, dispel phlegm, cool the blood, and remove toxin. [Indications] Heat strangury with slow pain, edema and small quantity of urination, diarrhea, caused by summerheat-dampness, phlegm-heat cough, hematemesis and epixtaxis, swelling abscess, sore and toxin. | ||||
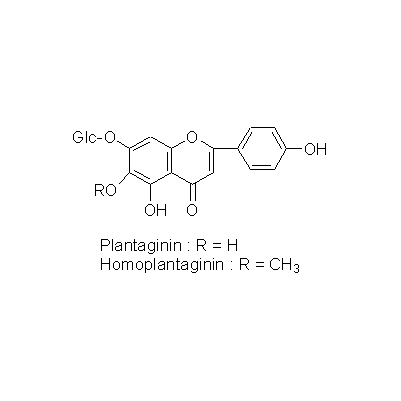
| Chemical constituent | Monoterpenoids (*C1): Aucubin Triterpenoids (*C2): Ursolic acid Sterols (*C2): beta-Sitosterol Phenylpropanoids (*C1): Acteoside Phenylpropanoids (*C1): Syringin Flavones & Flavonols (*C1): Plantaginin, Hispidulin-7-glucoside (= Homoplantaginin) | ||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||
| Pharmacological effect | the water leaching of Plantago Herb inhibit the growth of cutaneous fungi. The other is not exactly known. | ||||
| DNA sequence | L36454, AJ236046; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||
| Disease | Oliguria, Urodynia, Dysuria, Vomitting, Diarrhea, Red eye, Decreaced vision, Muscae valitantes, Corneal opacity, Cough, A lot of sputum, Nasal hemorrhage, Hematuria, Pyogenic dermatosis | ||||
| Formulation | not used in formula | ||||
| Related drugs | Plantagis Semen | ||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 228-229. C2)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p225. | ||||
| Remarks | Chaqiancao (車前草) is derived from the original plant P. depressa Willd. (Jap. Name: Mujinaōbako) and is occasionally found in markets, along with Cheqianzi (車前子). In addition, Commercial samples imported from China may also contain the whole plant of P. hostifolia Nakai et Kitag. (Jap. Name: Enagaōbako). | ||||
| Last renewal date | 2024/01/18 | ||||