Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Crude drug name | Market name | 牛黄 |
|---|---|---|
| Formal name | 牛黄 | |
| Japanese name | ごおう, Goō | |
| Vernacular name | Oriental Bezoar | |
| Latin name | Bezoar Bovis (JP), Bovis Calculus (CP) | |
| English name | Oriental Bezoar (JP), Cow-bezoar (CP) | |
| Original plant name | Bos taurus L. var. domesticus Gmelin, (Ushi) | |
| Family name | Bovidae | |
| Used part | Classification | Animal origin |
| Production area information | South America | |
| TMPW No. | 2904 | |
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 牛黄, Niuhuang, Bezoar Bovis (JP18), Bovis Calculus (CP2020), Oriental Bezoar (JP18), Cow-bezoar (CP2020) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original plant name | Bos taurus Linn. var. domesticus Gmelin, (Ushi) | |||
| original plant image |
| |||
| Family name | Bovidae | |||
| Used part | a stone formed in the gall sac | |||
| Quality for selection | Both the inside and outside of good Niuhuang are deep yellow. It is light, cracks by layer and tastes sweet. Australian niuhuang is the best. Indian niuhuang is not good. (TN) | |||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||
| Clinical application | As a tonic, antispasmodic, tranquilizer, antifebrile, antidote and for normalizing the function of gallbladder, Niuhuang is applied for delirium due to fever, convulsion and palpitation of the heart. It is also applied for sore throat, carbuncles and boils externally. | |||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Febrifugal and detoxicant drugs | ||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cool; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Heart and liver meridians. [Actions] To clear the heart, sweep phlegm, open the orifices, cool the liver, extinguish wind, and remove toxin. [Indications] Loss of consciousness in febrile disease, wind-stroke and phlegm clouding the heart, seizures, convulsions, epilepsy, manic psychosis, swelling and sore throat, mouth and tongue sores, swelling abscess, deep-rooted boil and sore. | |||
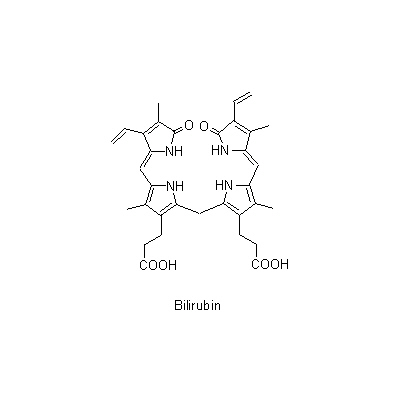
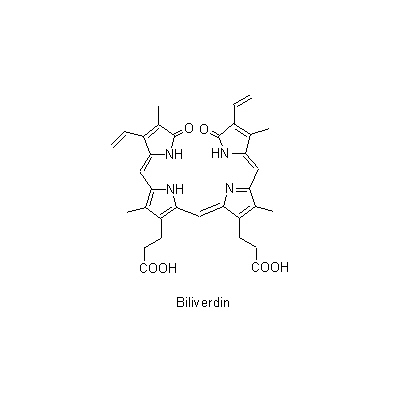
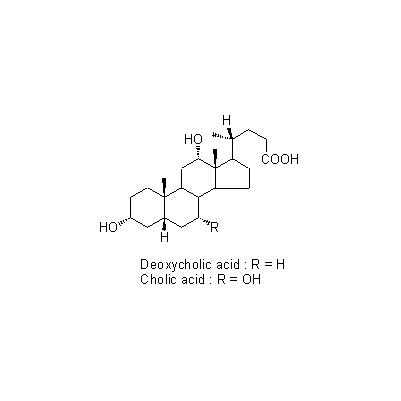
| Chemical constituent | Bile acid, Bile alcohol (*C1): Cholic acid, Deoxycholic acid, Chenodeoxycholic acidからなる胆汁酸/bile acid, 抱合型胆汁酸/conjugated bile acid Amino acids (*C1): Alanine, Glycine, Taurine, Aspartic acid, Arginine, Leucine, Methionine Porphyrin derivatives (*C1): Bilirubin, Biliverdin | |||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||
| Pharmacological effect | Hemopoiesis.hypercholeresis.sedation.Contraction of smooth muscles,antiinflammation(peptides),cardiotonic. | |||
| DNA sequence | U52355, AB016657, AF176811; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||
| Disease | Disturbance of consciousness, High fever, Convulsion, Cervical lymphadenopathy, Lung suppurations, Appendicitis, Cancer, Pyogenic dermatosis, Swelling and pain of the throat, Stomatitis, Diphtheritic pharyngitis, Chronic hepatitis | |||
| Formulation | Rokushingan | |||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 270-273. | |||
| Remarks | The Chinese formation which contains Niuhuang are Liushen Pills, Niuhuang Qingxin Pills, Angong Niuhuang Pills, Zhibao Dan and Zixue Dan. When one takes Niuhuang, 0.1~0.5g is adequate for one dose. Though Niuhuang has a lesser effect of inducing resuscitation than Shexiang, it tends to remove toxic heat. Recently China has been substituting artificial one, which is made from the bile of cows or pigs, for Niuhuang. | |||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||