Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
30.572815
104.06680099999994
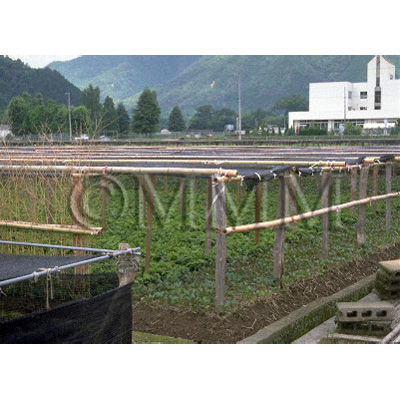
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Sichuan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
36.3418112
140.4467935
Collection information
Japan,Ibaraki Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
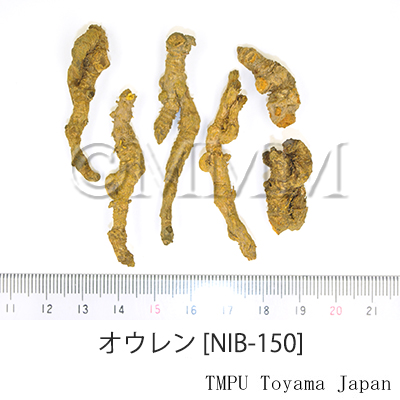
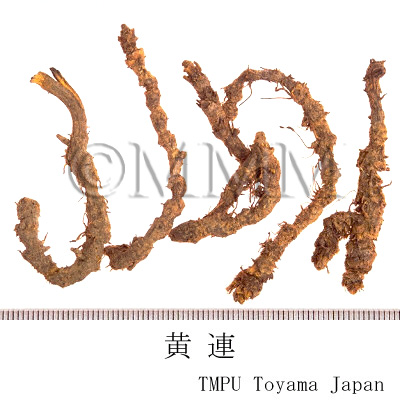
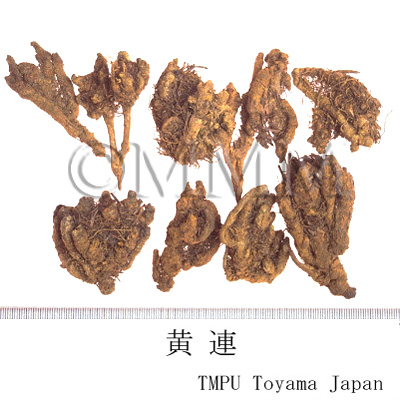
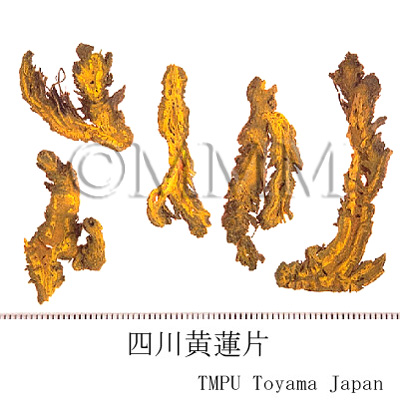
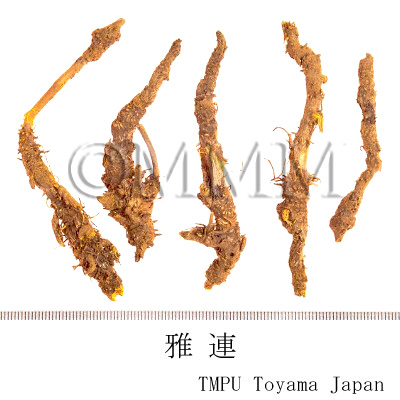
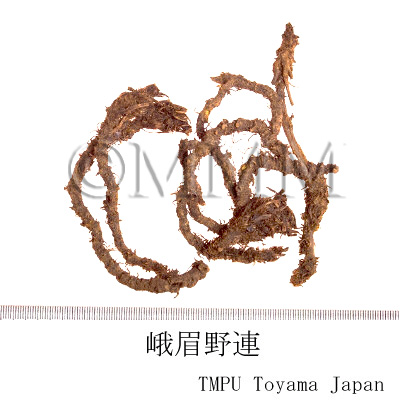
| Common name | 黄連, Huanglian, Coptidis Rhizoma (JP18, CP2020), Coptis Rhizome (JP18), Golden Thread (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 丹波黄連, 越前黄連, 因州黄連, 味連, 雅連 | ||||||
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
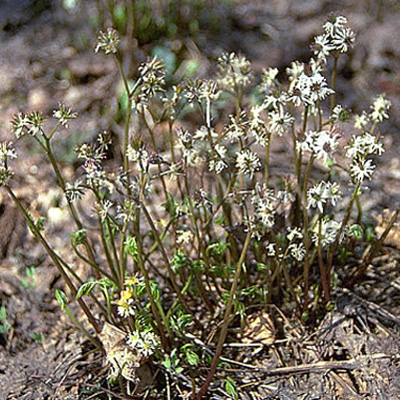
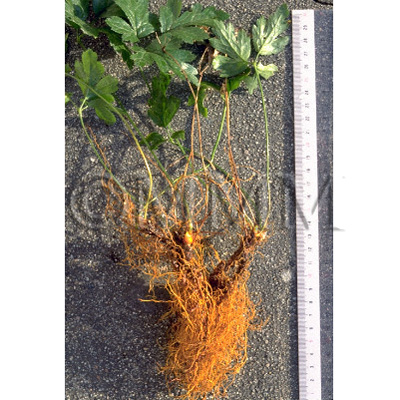
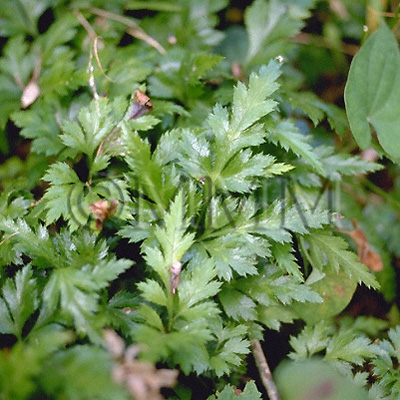
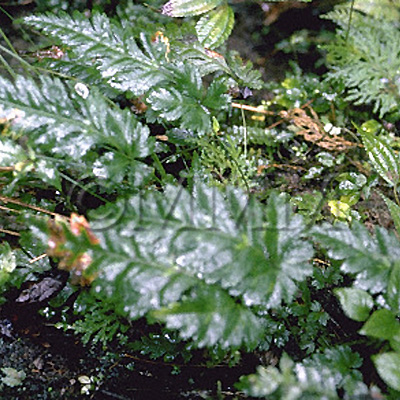
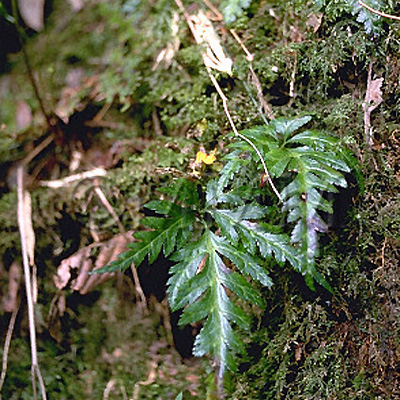
| Original plant name | Coptis japonica Makino1, Coptis chinensis Franchet, Coptis deltoidea C.Y. Cheng et Hsiao or Coptis teeta Wallich, (Oren1) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Ranunculaceae | ||||||
| Used part | rhizome without root | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Huanglian, which is deep yellow inside, is thick, firm and has a strong bitter taste. "Maohuanglian" has fibrous roots and less bitterness. It is lower quality. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As an antiphlogistic amaroid stomachic and tranquilizer, huanglian is applied for palpitation, mental instability, stuffiness of epigastrium, vomiting, diarrhea, stomachache and bleeding, accompanied with congestion or inflammation. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for elimination heat and dampness | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, spleen, stomach, liver, gallbladder and large intestine meridians. [Actions] To clear heat, dry dampness, purge fire and remove toxin. [Indications] Dampness-heat stuffiness and fullness, vomiting, acid reflux, diarrhea and dysentery, jaundice, high fever with loss of consciousness, intense heart fire, insomnia caused by vexation, palpitations, blood heat with hematemesis, red eyes, toothache, wasting-thirst, swelling abscess, deep-rooted boil and sore; topically for eczema, dampness sore, purulent discharge from the ear. | ||||||
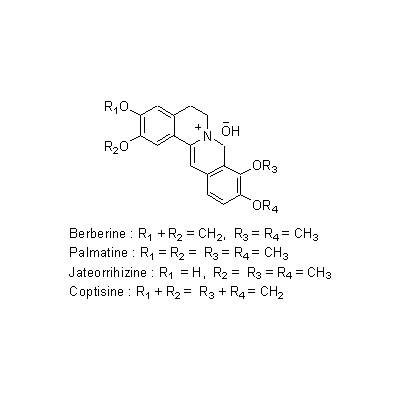
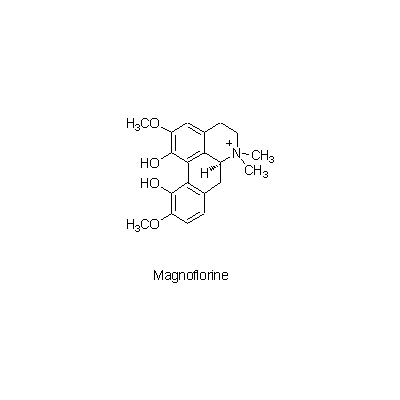
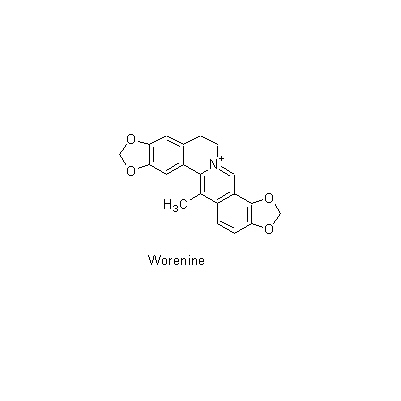
| Chemical constituent | Phenylpropanoids (*C1): Ferulic acid Isoquinoline alkaloids (*C1): Berberine, Palmatine, Jateorrhizine, Coptisine, Magnoflorine, Tetrahydropalmatine, Tetrahydroberberine, Worenine | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antibacterial (broad antibacterial spectrum of berberine),constipation (berberine). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | L75838, AF093730; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Diarrhea, Full stomach, Vomitting, Feeling of pressure in the chest, Thirst, Oliguria, High fever, Disturbance of consciousness, Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage, Fret, Insomnia, Stomatitis, Toothache, Bleeding from root of tooth, Stomachache, Red eye, Swelling and pain of the throat, Pyogenic dermatosis, Tympanitis, Eye pain | ||||||
| Formulation | Anzanto, Ireito, Inchinsan, Unseiin, Ogesan, Orento, Oren'akyoto, Orengedokuto, Orengedokuto, Orenshodokuin, Kagenryokakusan, Kakkon'oren'ogonto, Kakkonkokato, Kamisaikakujioto, Kamishimotsuto, Kamishokankyoto, Kankyoto, Kankyooren'ogon'ninjinto, Kanzoshashinto, Kanrento, Kanrendaioto, Kanrendaiokasekkoto, Keigairengyoto, Keigairengyoto, Kowashakuyakuto, Saikanto, Saikoseikansan, San'oshashinto, San'oshashinto (brewing), Jijinmeimokuto (Jinkimeimouto), Shaito, Shakuyakuto, Junkiwachuto, Shokankyoto, Shokanto, Shokyoshashinto, Shosaikotokaorenbukuryo, Shobaishashinto, Shohito, Jinkimeimokuto, Jinrento, Seiishakato, Seiinrikakuto, Seikanto, Seijobofuto, Seishinto, Seichuankaito, Seineitsugeutsuto, Seiryoin, Senkanmeimokuto, Daibyakuchuin, Danrito, Chikujountanto, Jishusabiho, Jizutsuippo, Chushaen, Chuseito, Tokiyoketsuto, Tokirokuoto, Naisoorento, Nyoshinsan, Hakutooto, Hakutookakanzoakyoto, Hangeshashinto, Bukuryhoshinto, Fushinto, Honposhakuyakuto, Meiroin, Ryutan-shakan-to, Rogyokuto, Kaishun'inchinsan | ||||||
| Related drugs | Maweilian (see "Remarks") | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 154-158. | ||||||
| Remarks | Chinese "Weilian" is the rhizome of C. chinensis, "Yalian" is that of C. deltoidea C.Y.Cheng et Hsiao, "Emeiyelian" is that of C. omeiensis (Cheng) C.Y.Cheng, "Yunlian" is that of C. teeta Wall. Chinese "Mawielian" is the subterranean part of Thalictrum species of family Ranunculaceae. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/07/21 | ||||||