Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
37.87059
112.54887899999994
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Shanxi Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
36.3418112
140.4467935
Collection information
Japan,Ibaraki Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 地黄, Dihuang, Rehmanniae Radix (JP18), (CP2020), Rehmannia Root (JP18), (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 乾地黄, 懐慶地黄, 生地黄, 生地 | ||||||
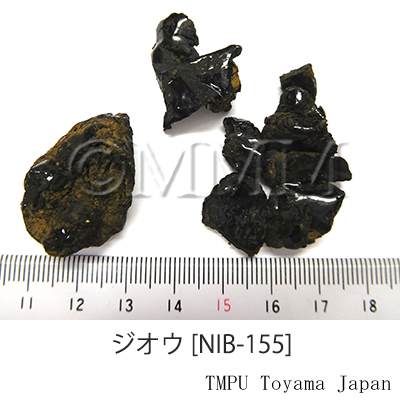
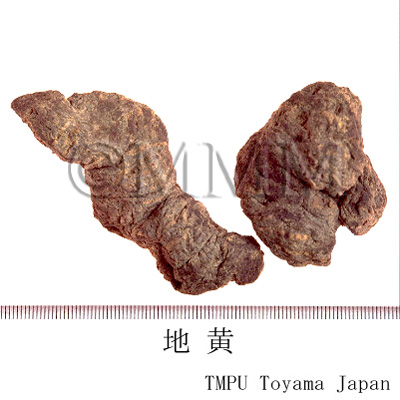
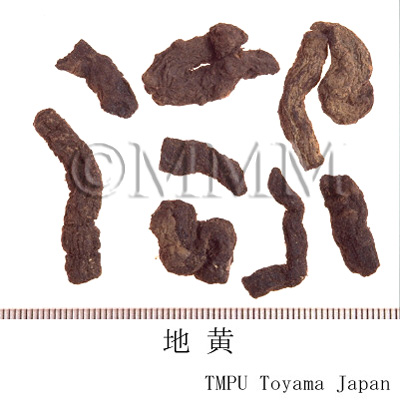
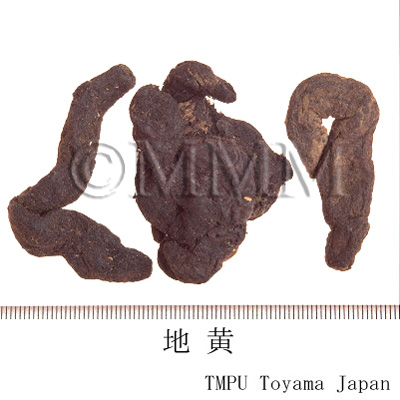
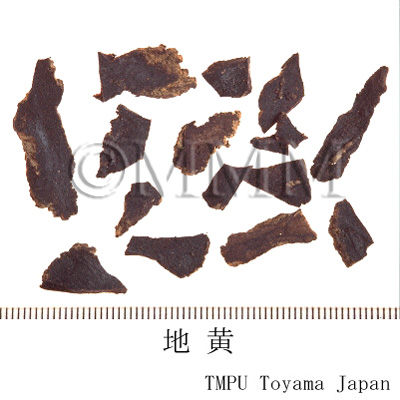
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
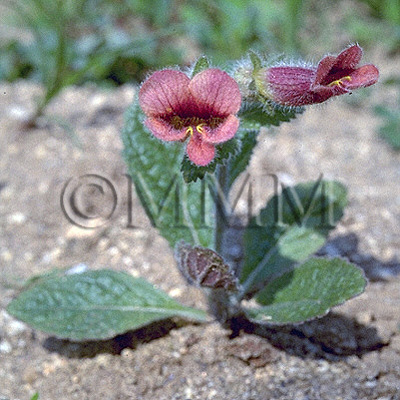
| Original plant name | Rehmannia glutinosa Liboschitz var. purpurea Makino1 or Rehmannia glutinosa Liboschitz, (Akayajiō1) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Scrophulariaceae | ||||||
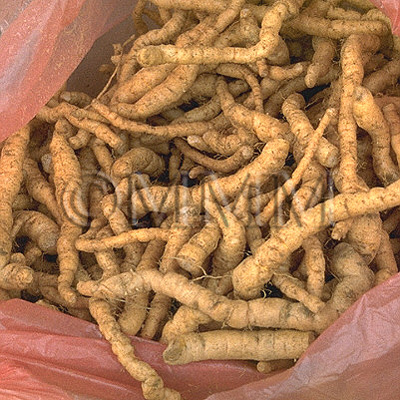
| Used part | thickening root | ||||||
| Quality for selection | The cortex of good Dihuang is grey and the inside is deep violet. It is enlarged. The taste is sweet with a faint bitterness. (NI) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a tonifying and heat-clearing drug, for reducing heat in blood, nourishing blood, dihuang is applied for hematemesis, thirst and mental instability. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for eliminating heat from blood | |||||
| Beneficial effect | Unprocessed Rehmannia Root: [Property and Flavor] Cold; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, liver and kidney. [Actions] To clear heat, cool the blood, nourish yin and engender fluids. [Indications] Heat entering nutrient-blood aspects, macula and papule caused by warm toxin; hematemesis damaging yin, crimson tongue, vexation and thirst, fluid comsumption, yin deficiency fever, steaming bone, consumptive fever, interior heat, and wasting-thirst. | ||||||
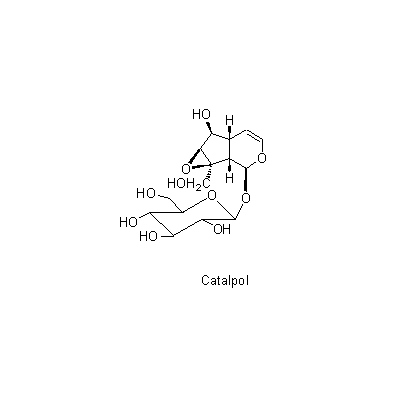
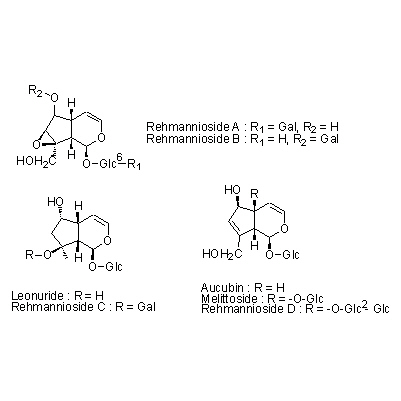
| Chemical constituent | Lipids (*C1): Cerebroside, Jio-cerebroside Sugar (*C1): Manninotriose, Verbascose Monosaccharides (*C1): D-Mannitol, D-Glucose, D-Fructose, D-Galactose Oligosaccharides (*C1): Raffinose, Stachyose, Sucrose Monoterpenoids Iridoids: (*C1): Catalpol, Aucubin, Rehmannioside A, Rehmannioside B, Rehmannioside C, Rehmannioside D, Rehmaionoside A, Rehmaionoside B, Rehmaionoside C, Rehmaionoside D, Melittoside, Leonuride Carotenoids & Vitamin A (*C2): Vitamin A Sterols (*C1): Sitosterol Phenol derivatives (*C1): Acteoside Amino acids (*C2): Arginine Others (*C2): 鉄 [Fe] | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Hypoglycemic,cardiotonic,hypertensive,diuretic (extract). Cathartic and diuretic(catalpol). | ||||||
| DNA sequence | Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Fever, Thirst, Constipation, Sore throat, Hematemesis, Nasal hemorrhage, Hematuria, Hematochezia, Irregular vaginal bleeding, Bleeding, Internal bleeding, Polyposia | ||||||
| Formulation | Ishoho, Unseiin, Ekigento, Ekkiyoeito, Ogibekkoto, Odoto, Orenshodokuin, Kagenryokakusan, Kakkonkokato, Kamiuntanto, Kamisaikakujioto, Kamishimotsuto, Kamishoyosangoshimotsuto, Kamihachimyakusan, Kamihassento, Kanroin, Kikyoto, Kibanto, Kyukikyogaito, Kyukichoketsuin, Keigairengyoto, Keishigomotsuto, Keishitoninto, Goshajinkigan, Gomotsudaioto, Gorinsan, Saikakujioto, Saikoseikansan, Saikosokanto, Saikoyoeito, Sammotsuogonto, Jiinkokato, Shiinsen, Jijintsujito, Jijinmeimokuto (Jinkimeimouto), Shichikensan, Shichimotsukokato, Shimotsuto, Shaito, Shaito, Juzentaihoto, Jumizasan, Junchoto, Shojioto, Shoshinto, Shofusan, Jokinritsuansan, Jinkimeimokuto, Seiishakato, Seishinto, Seisoyoeito, Seinetsuhoketsuto, Seiryoin, Senkanmeimokuto, Sokeikakketsuto, Daibofuto, Jishusabiho, Choreitogoshimotsuto, Tokiinshi, Tokirokuoto, Dokkatsukakkonto, Dokkatsukiseito, Ninjin-yoei-to, Bakumondoinshi, Hachimigangoninjinto, Hachimijiogan, Hacchinto, Byakugokokinto, Bukuryhoshinto, Hointo, Boijioto, Hontonto, Mankeishisan, Ryutan-shakan-to, Ryutan-shakan-to, Renjuin, Rokumijiogan | ||||||
| Related drugs | Shudihuang, Xiandihuang (see "Remarks") | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 63-64. C2) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p229. | ||||||
| Remarks | Dihuang which originates from Akayajiō (Jap. name) hardly has market value in Japan. In Nara Prefecture, only a few is cultivated in order to keep the lineage. Fukuchiyama No.1 has been developed by hybridization between "Kaiekeijiō" (Rehmannia glutinosa) and "Akayajiō" (Rehmannia glutinosa var. purpurea). In China, the fresh root of "Kaikeijiō" is called "Xiandihuang" and the dried root is called "Shengdihuang" (Jap. name: "Kanjiō"). "Shudihuang" is dried after steaming. "Shudihuang" is steamed with "Huangjiu", a kind of rice wine such as "Shaoxingjiu", or simply steamed. Then it is dried by daylight. This process, steaming and drying, is repeated 9 times. "Kanjiō" and "Shengdihuang" are applied for heat symptom complex as a drug to dispel pathogenic heat from blood. "Shudihuang" is applied for deficiency of vital energy as a drug for enriching the blood. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/10/12 | ||||||