Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
24.880095
102.83289100000002
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Yunnan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
36.3418112
140.4467935
Collection information
Japan,Ibaraki Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
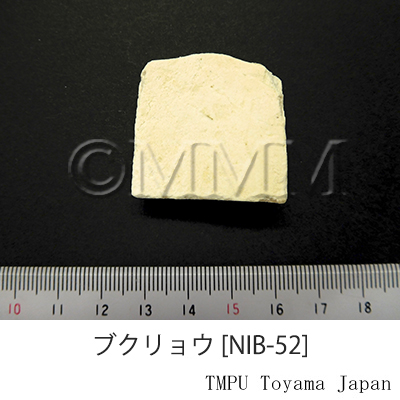
| Common name | 茯苓, Fuling, Poria (JP18, CP2020), Poria Sclerotium (JP18), Indian Bread (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
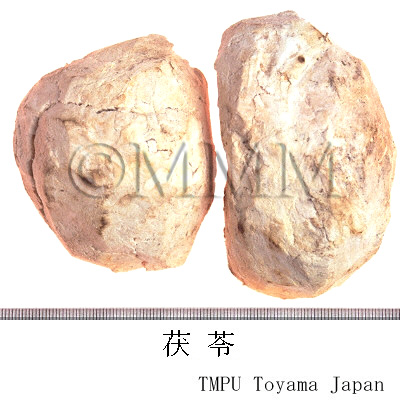
| Original plant name | Wolfiporia cocos Ryvarden et Gilbertson (= Poria cocos Wolf), (Matsuhodo) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Polyporaceae | |||||
| Used part | sclerotium (without outer layer) | |||||
| Quality for selection | The outer surface of good Fuling is black and the inside is pure white. It is solid and stiff. Wild Fuling of Yunnan Prov. is the best one. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a diuretic and tranquilizer, Fuling is applied for edema with urination disorder, oliguria, dizziness, water-retention of the stomach, palpitation, mental instability, insomnia and convulsion. In traditional Chinese medicine, it is said to remove excessive water, invigorating the spleen and tranquilizing the mind. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diuretics removing dampness | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Neutral, sweet and bland. [Meridian Tropism] Heart, lung, spleen and kidney meridians. [Actions] To promote urination to drain dampness, fortify the spleen, and calm the heart. [Indications] Edema, a small amount of urine, dizziness and palpitations caused by phlegm-fluid retention, spleen deficieincy, reduced food intake, sloppy stool, dirrhea, disquieted heart spirit, fright palpitations and insomnia. | |||||
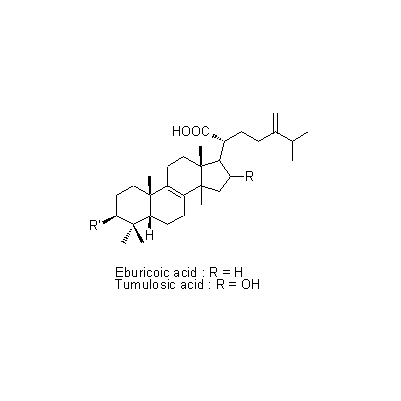
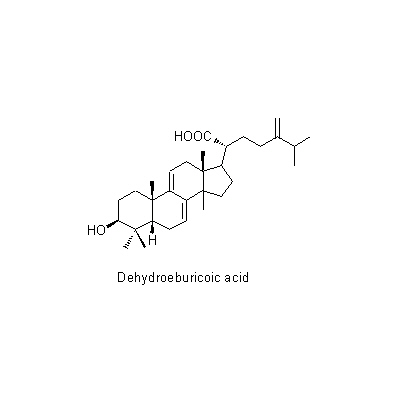
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids related compounds (*C1): Lecithin Polysaccharides (*C1): Pachyman [beta-(1→3)-glucanの多糖体] Triterpenoids (*C1): Eburicoic acid, Dehydroeburicoic acid, Pachymic acid, Tumulosic acid, 3-beta-Hydroxylanosta-7,9,(11),24-trien-21-oic acid (*C2, C3): 3-O-Acetyl-16-alpha-hydroxytrametenolic acid, 3-Epidehydropachymic acid, 3-Epidehydrotumulosic acid, Poricoic acid BM, Poricoic acid E, Poricoic acid F Sterols (*C1): Ergosterol Amino acids (*C1): Histidine Other nitrogen containing compounds (*C1): Adenine Simple nitrogen containing compounds (*C1): Choline | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Reduction in blood sugar(water extract,alcohol extract),immunoenhancement(Pachyman). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AB022187, AB022188; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Oliguria, Edema, Anorexia, Lack of energy, Full stomach, Muddy and watery stool, Nausea, Vomitting, Vertigo, Insomnia, Anxiety, Scary constitution, Palpitation | |||||
| Formulation | Anzanto, Anchusan, Ikosan, Ifuto, Ireito, Inchingoreisan, Inchinsan, Ureitsukito, Ekkiyoeito, Ogibekkoto, Kairosan, Kagaisan, Kagawagedokuzai, Kagen'ireito, Kagenhachimotsuto, Kashokuyohito, Katsuketsugedokuto, Kakkoshokisan, Kakkonkaryojutsubuto, Kamiuntanto, Kamikihito, Kamishoyosan, Kamishoyosangoshimotsuto, Kamihachimyakusan, Kamihassento, Kanchuto, Kippihangeto, Kihito, Gyakubanto, Kyukichoketsuin, Kumihangeto, Keishikaryojutsubuto, Keishikyokeikeikabukuryobyakujutsuto, Keishigomotsuto, Keishinieppiichito, Keishinieppiittokaryojutsubu, Keishibukuryogan, Keihito, Keimeisankabukuryo, Kosharikkunshito, Kochinmuyusan, Goshakusan, Goshajinkigan, Gorinsan, Goreisan, Saikokaryukotsuboreito, Saikokobokuto, Saishakurikkunshito, Saibokuto, Saireito, Sansoninto, Jiinshihoto, Shiinsen, Shionsan, Shikunshito, Shichikensan, Shichimibyakujutsuto, Jippito, Shahito, Shahitokaryukotsuboreito, Juzentaihoto, Jumizasan, Jumihaidokuto, Junkiwachuto, Shogedokuto, Shosaikotokaorenbukuryo, Shosaikogohangekobokuto, Shoshinto, Shohangekabukuryoto, Shohito, Shoyosan, Shoyosankato, Jokinritsuansan, Shireito, Jin'en'ippo, Jinsoin, Jinryobyakujutsusan, Jintanto, Shimbuto, Seishitsuketanto, Seishinrenshiin, Seinetsuhokito, Seihaito, Sekiganryo (keihi), Sekiganryo (hange), Zenshikunshito, Zenshibyakujutsusan, Sogento, Sokeikakketsuto, Daisangoshichisan, Danrito, Jiohanho, Chikujountanto, Jizenippo, Chimobukuryoto, Chokobukuryoto, Chotosan, Choreito, Choreitogoshimotsuto, Tokishakuyakusanmatsu, Tokibyakujutsusan, Tokibyakujutsuto, Tokiyoketsuto, Dotaitsukeito, Dokkatsukiseito, Nijutsuto, Nichinto, Ninjinsan, Ninjin-yoei-to, Ninjin-yoei-to, Haidokuto, Bakumondoinshi, Hachimigangoninjinto, Hachimijiogan, Hachimishoyosan, Hachimitaikaho, Hachimotsuto, Hacchinto, Hangekobokuto, Hangebyakujutsutemmato, Hanbikokantan, Bukuryoin, Bukuryokanzoto, Bukuryokyoninkanzoto, Bukuryokeishikanzodaisoto, Bukuryoshigyakuto, Bukuryotakushato, Bukuryhoshinto, Bushito, Fushinto, Bunshoto, Bunshinkiin, Henseishinkiin, Hointo, Boisan, Boito, Boibukuryoto, Hokikenchuto, Hojinto, Botanpisan, Hochujishitsuto, Hontonto, Hontonbukuryoto, Maokaryojutsubuto, Mankeishisan, Meiroin, Mokuboikyosekkokabukuryoboshoto, Yohaito, Yokukansan, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Yokukansankachinpihangeto, Richuankaito, Rikkunshito, Ryukotsuto, Ryokankyomishingeto, Ryokankyomishingeninto, Ryokankyomishingeninoto, Ryokangomikyoshinto, Ryokito, Ryokyojutsukanto, Ryo-kei-kan-so-to, Ryokeigomikanzoto, Ryokeijutsukanto, Reiyoukakuin, Renjuin, Rogyokuto, Rokuutsuto, Rokumijiogan, Rokumotsubushito, Kaishun'inchinsan, Kogikujiogan, Koshayoito | |||||
| Related drugs | Poria Cum Pinus Radix | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 241-243. C2) Phytochemistry,40,225(1995). C3) Phytochemistry,39,1165(1995). | |||||
| Remarks | The sclerotia is a parasite of the roots of genus Pinus. It forms unstable aggregated sclerotia around the root which stem had been felled 3 to 4 years before. The one which sclerotia is penetrated by a root is called Fushen and highly appreciated. Recently, there are many cultivated Fulings. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||