Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
31.820591
117.22721899999999
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Anhui Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
36.3418112
140.4467935
Collection information
Japan,Ibaraki Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
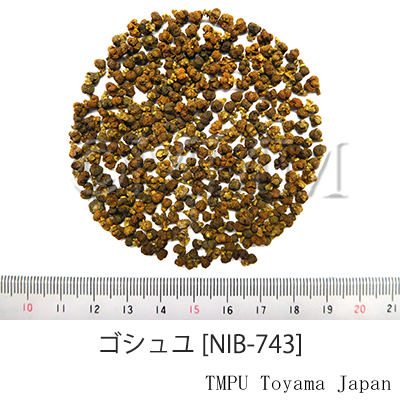
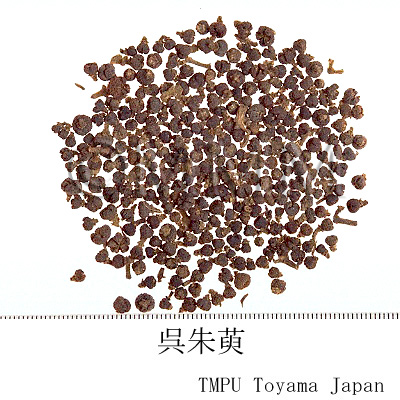
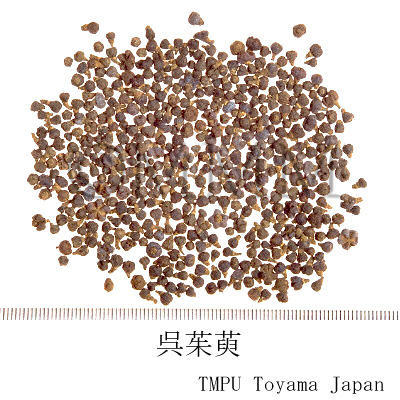
| Common name | 呉茱萸, Wuzhuyu, Euodiae Fructus (JP18, CP2020), Euodia Fruit (JP17), Medicinal Euodia Fruit (CP2015) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
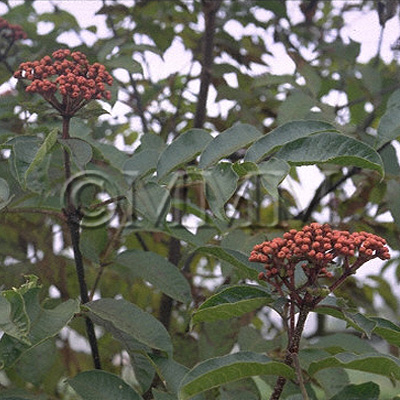
| Original plant name | Euodia officinalis Dode (Evodia officinalis Dode), Euodia bodinieri Dode (Evodia bodinieri Dode) or Euodia ruticarpa Hooker filius et Thomson1 (Evodia rutaecarpa Bentham) , (Goshuyu1) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Rutaceae | |||||
| Used part | fruit | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Wuzhuyu is black and has strong pungency and bitterness. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVII,CP (2015 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a stomachic with warm nature, painkiller, diuretic, for relieving vomiting, Wuzhuyu is applied for headache due to rising of noxious fluid, nausea, a feeling of stuffiness in the chest, abdominal pain due to cold of deficiency type, poor circulation and chilblains. It is used as insecticide and bath agent. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for dispelling internal cold | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Hot; pungent and bitter; slightly toxic. [Meridian Tropism] Liver, spleen, stomach and kidney meridians. [Actions] To dissipate cold and relieve pain, downbear counterflow to check vomiting, assist yang to check diarrhea. [Indications] Reverting yin headache, abdominal pain caused by cold abdominal colic , cold-dampness beriberi, menstruation with abdominal pain, distending pain in the epigastrium and abdomen, vomiting, acid regurgitation, diarrhea before dawn. | |||||
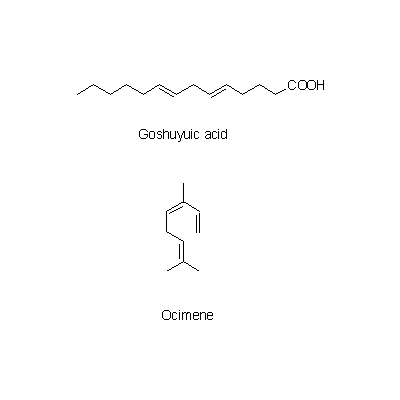
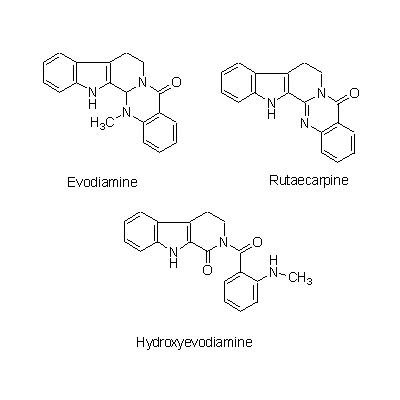
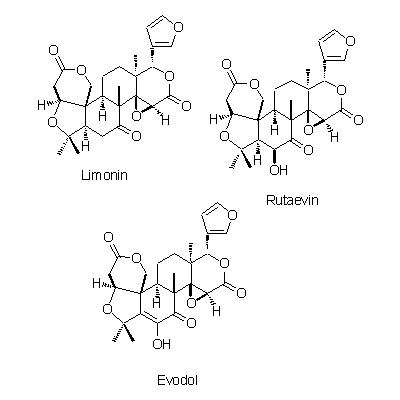
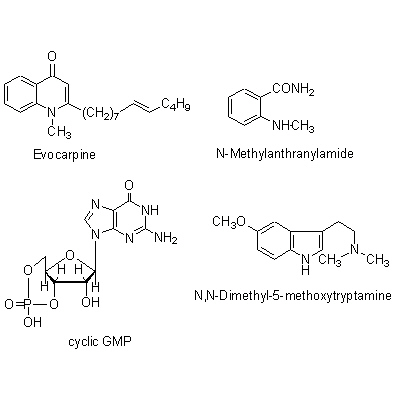
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (*C1): Goshuyic acid Monoterpenoids (*C1): Ocimene Triterpenoids (*C1): Limonin (= Evodin), Rutaevin, Evodol Flavanones & Dihydroflavonols E. rutaecarpa (*C2,C3): Evodioside B(葉/leaves) Alkaloids (*C1): Evodiamine, Rutaecarpine, Hydroxyevodiamine (= Rhetsinine), Evocarpine, N,N-Dimethyl-5-methoxytryptamine, N-Methylanthranylamide, Synephrine, Higenamine Purine derivatives (*C1): Cyclic GMP Others E. rutaecarpa (*C2,C3): 6alpha-Acetoxy-5-epilimonin, 6beta-Acetoxy-5-epilimonin | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Increase in the blood pressure, accelerated respiration, increase in the blood flow(fraction of alcohol extraction), analgesia, rising temperature (evodiamine, rutaecarpine), inducing labor pains, hemostasis, central excitation (beta-indolethyl-amine), hallucination (N,N-dimethyl-5-methoxytryptamine), adrenergic action, cardiotonic action (synephrine, hygenamine). | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 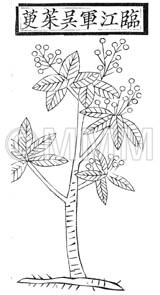 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Headache, Nausea, Vomitting, Upper abdominal pain, Coldness of limbs, Lower abdominal pain, Menorrhalgia, Extension of menstrual cycle, Full stomach, Diarrhea, Cold-natured, Chilblain, Stomatitis | |||||
| Formulation | Unkeito, En'nenhangeto, Keimeisan, Keimeisankabukuryo, Goshuyuto, Jinrento, Jizutsuippo, Tokishigyakukagoshuyushokyoto, Tojichuippo, Henseishinkiin, Hontonto, Hontonto | |||||
| References | (JP18): The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. (CP2020): Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. B1) Nat. Med.,53,275(1999). C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 233-234. C2) Chem.Pharm.Bull.,36,1237(1988). C3) Chem.Pharm.Bull.,41,1472(1993). C4) Nat. Med.,52,322(1998). | |||||
| Remarks | In Japan, the premature fruits of Goshuyu and Hongoshuyu are said to be of high quality. The Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. defines nearly matured fruits of Euoodia rutaecarpa (Juss.) Benth. var. bodinieri (Dode) Huang as well as the above two species as the original plants. These three premature fruits can be distinguished by the length and diameter of style, presence or absence of the hair, and the size of fruit (B1). In addition, they are different in terms of the chemical components (C4). Botanically, the right classification is not genus Evodia, but genus Euodia. Goshuyu is Euodia rutaecarpa (Juss.) Benth. Hongoshuyu is E. rutaecarpa (Juss.) Benth. var. officinalis (Dode) Huang. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/11/16 | |||||