Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
40.842356
111.74999500000001
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
36.3418112
140.4467935
Collection information
Japan,Ibaraki Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 防風, Fangfeng, Saposhnikoviae Radix (JP18, CP2020), Saposhnikovia Root and Rhizome (JP18), Divaricate Saposhnikovia Root (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 真防風, 関防風, 東防風, 山防風 | |||||
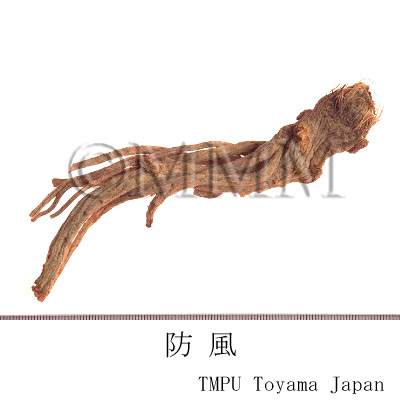
| crude drug image |
| |||||
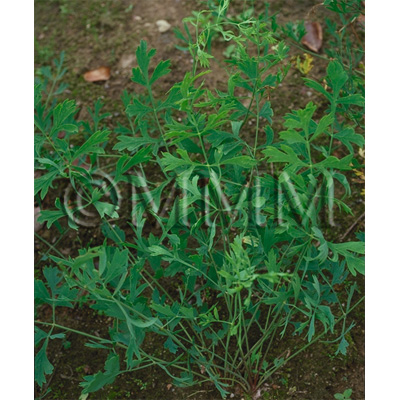
| Original plant name | Saposhnikovia divaricata Schischkin [Saposhnikovia divaricata (Turcz.) Schischkin (= Ledebouriella seseloides auct. non H. Wolff)] | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Umbelliferae | |||||
| Used part | root (and rhizome) | |||||
| Quality for selection | Good Fangfeng is thick and long. The exterior is light yellow and the interior is dense. Generally, there are dark brown fibrous remains of leaf bases at the top of the root. (TN) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As a diaphoretic, carminative, antifebrile and painkiller, fangfeng is applied for cold, headache, fever without sweat, arthralgia, convulsion of limbs and tetanus. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Diaphoretics with warm property | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild warm; pungent and sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Bladder, liver and spleen meridians. [Actions] To dispel wind to release the exterior pattern, dispel dampness and relieve pain, arrest convulsions. [Indications] Common cold, headache, painful impediment caused by wind-dampness, itching caused by rubella, tetanus. | |||||
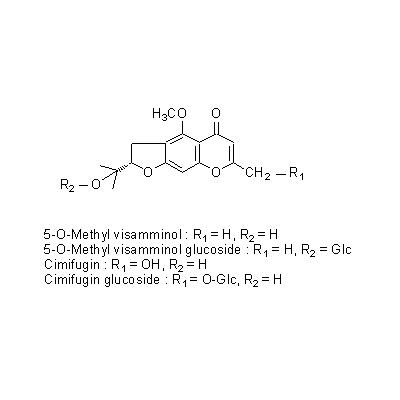
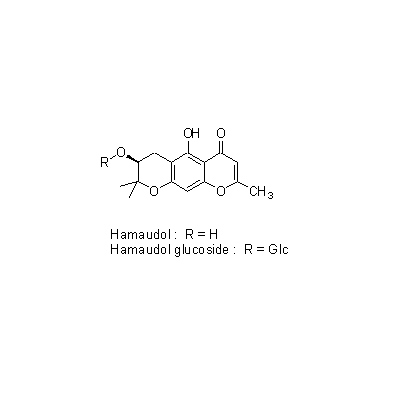
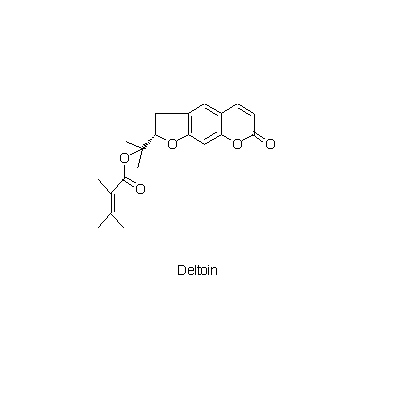
| Chemical constituent | Monosaccharides (*C2): D-Mannitol Terpenoids (Essential oils) (*C2): 精油 Chromones (*C1): 5-O-Methyl visamminol, Cimifugin, Hamaudol,それらの glucoside Coumarins (*C1): Deltoin | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Antipyretic (decoction). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AF077878, U58553, U78377, U78437, AF164833, AF169280, AF169281, AF169282, AF169283; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Common cold, Fever, Chill, Headache, Somatic pain, Swelling and pain of joint, Twitch of the muscles, Convulsion, Itching, Tetanus | |||||
| Formulation | Orenshodokuin, Kamihassento, Gyokuheifusan, Kufugedokusan, Kufushokutsuto, Keigairengyoto, Keigairengyoto, Keishishakuyakuchimoto, Shijunseiryoin, Shaito, Jumizasan, Jumihaidokuto, Shozokumeito, Shofusan, Jokinritsuansan, Joyowaketsuto, Shin'isan, Jingyobofuto, Jintanto, Seiinrikakuto, Seishitsuto, Seijokentsuto, Seijobofuto, Seiryoin, Senkanmeimokuto, Senkyuchachosan, Sokeikakketsuto, Daisangoshichisan, Daibofuto, Chikuyoto, Jizusoippo, Chotosan, Tokiinshi, Tokinentsuto, Naitaku-san, Naitaku-san, Boijioto, Bofutsushosan, Rikkosan, Ryutan-shakan-to, Meiganippo | |||||
| Related drugs | Glehuniae Radix cum Rhizoma | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 82-83. C2) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, p 258. | |||||
| Remarks | The roots of Ligusticum brachylobum Franch.(Jap. name: Senbohū), Seseli mairei Franch. or Seseli yunnanense Franch. (Jap. name: Unbohū) are used in substitution for "Fangfeng". In Japan the root or rhizome of Glehnia littoralis F. Schmidt et Miquel is occasionally used for its substitute. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2021/09/27 | |||||