Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
Japan
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
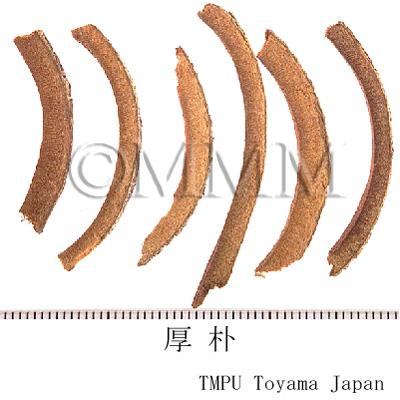
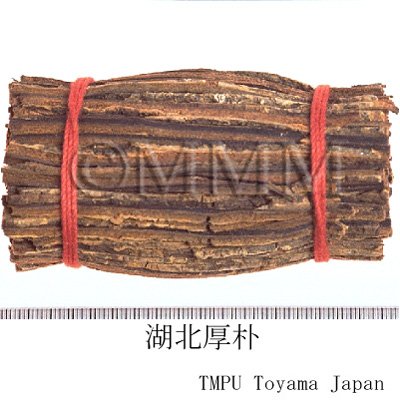
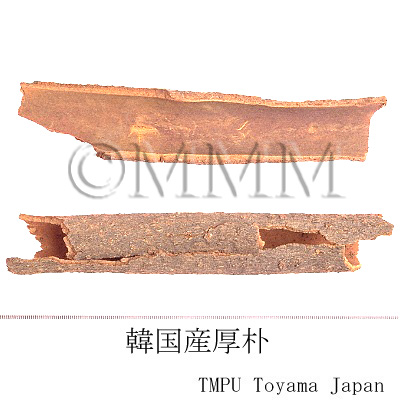
| Common name | 厚朴, Houpo, Magnoliae Cortex (JP18), Magnoliae Officinalis Cortex (CP2020), Magnolia Bark (JP18), Officinal Magnolia Bark (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| |||||
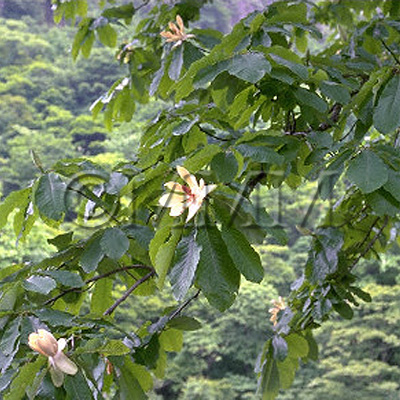
| Original plant name | Magnolia obovata Thunberg1 (= Magnolia hypoleuca Siebold et Zuccarini), Magnolia officinalis Rehder et E. H. Wilson or Magnolia officinalis Rehder et E. H. Wilson var. biloba Rehder et E. H. Wilson, (Hōnoki1) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Magnoliaceae | |||||
| Used part | trunk and blanch bark | |||||
| Quality for selection | The outside of good Houpo is deep violet and the inside has longitudinal crests. The bark is very thick and dense. The fresh one, which tastes a little bitter, is good. (NI) | |||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an antispasmodic, painkiller, stomachic, astringent, expectorant and diuretic, Houpo is applied for abdominal distention and pain, cough and asthma, and abnormal tension of skeletal muscle with anxiety, mental strain and all. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Aromatic drugs for resolving dampness | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; bitter, pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, stomach, lung and large intestine meridians. [Actions] To dry dampness, resolve phlegm, direct qi downward, and disperse fullness. [Indications] Dampness stagnation damaging ,the middle, epigastric stuffiness, vomiting, diarrhea, food retention, qi stagnation, abdominal distension, constipation, and wheezing and cough caused by phlegm-fluid retention. | |||||
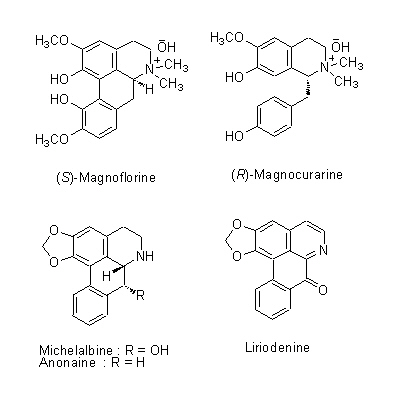
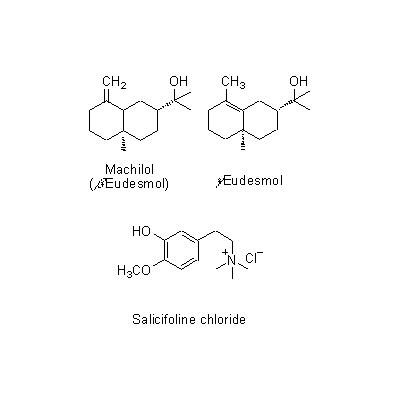
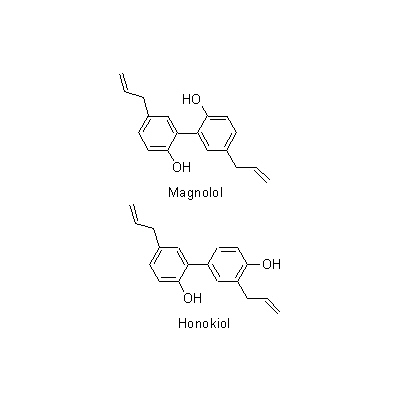
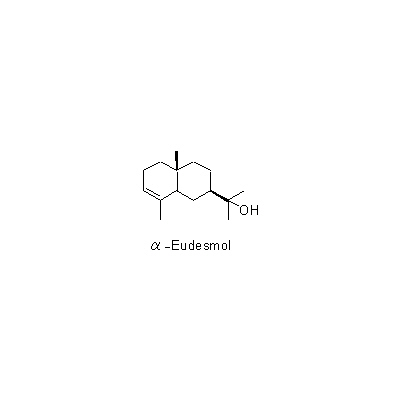
| Chemical constituent | Monoterpenoids M. obovata (*C1): alpha-Pinene, beta-Pinene, Camphene, Limonene, Bornyl acetate Sesquiterpenoids M. obovata (*C1): alpha-Eudesmol, beta-Eudesmol(= Machilol), gamma-Eudesmol, Cryptomeridiol, Eudesobovatol A, Eudesobovatol B, Caryophyllene epoxide M. officinalis (*C1): beta-Eudesmol Phenylpropanoids M. obovata (*C1): Magnolo l(= bis-Chavicol), Honokiol, Magnoloside A, Magnoloside B, Magnoloside C M. officinalis (*C1): Magnolol, Honokiol M. officinalis, M. obovata (*C3,C4,C5): Magnolol, Honokiol, 以下代謝物 / the followings are the metabolites Tetrahydromagnolol, 5-(1-Propen-1(E)-yl)-5'-propyl-2,2'-dihydroxybiphenyl, 5-Allyl-5'-(1-propen-1(E)-yl)-2,2'-dihydroxybiphenyl, Isomagnolol, 5-Allyl-5'-propyl-2,2'-dihydroxybiphenyl (*C6): Magnolol M. obovata 葉/leaf (*C2): Obovatal, Obovatol Isoquinoline alkaloids M. obovata, M. officinalis (*C1): Magnocurarine, Magnoflorine, Michelalbine, Anonaine, Liriodenine, Salicifoline chloride M. officinalis, M. obovata (*C5): Magnocurarine, Magnoflorine | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Relaxation of muscles (water extract).Sedation,suppression of righting reflex,suppression of spinal reflex,antispasm and antitremor (ether extract).Myoneural junction blokade,transient decrease in blood sugar(magnocurarine).Sedation,central relaxation of muscles,dental caries protection (magnolon,honokiol),antibacterial and insecticidal,antiparkinsonism (magnolol). | |||||
| DNA sequence | AB020999, AB021013, AB021000; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Full stomach, Abdominal pain, Constipation, Diarrhea, Cough, Dyspnea | |||||
| Formulation | Anzanto, Ireito, Inchinsan, Unpito, Kagen'ireito, Kakkoshokisan, Kamijokito, Kamiheiisan, Kanchuto, Kumibinroto, Keishikakobokukyoninto, Gohekiin, Kobokusammotsuto, Kobokushichimotsuto, Kobokushokyohangekanzoninjinto, Kobokumaoto, Kobokuto, Goshakusan, Saikokobokuto, Saibokuto, Shisoshito, Jippito, Shakuyakutokadaio, Shahito, Shahitokaryukotsuboreito, Jurokumiryukiin, Junchoto, Shosaikogohangekobokuto, Shojokito, Shobaito, Shohito, Jin'en'ippo, Shimpito, Zenshikunshito, Soshikokito, Daijokito, Jizenippo, Chokoshiteito, Tsudosan, Tokito, Hangekobokuto, Fukankinshokisanryo, Bunshoto, Heiisan, Hokikenchuto, Hochujishitsuto, Chuseito, Tokiyoketsuto, Naitaku-san, Naitaku-san, Hangekobokushichimotsuto, Binrojunkito, Kaishun'inchinsan, Koshayoito | |||||
| Related drugs | Magnolia Flower | |||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 145-147. C2) Chem.Pharm.Bull.,30,3347(1982). C3) Chem.Pharm.Bull.,32,5010(1984). C4) Chem.Pharm.Bull.,34,158(1986). C5) J.Med.Pharm.Soc.WAKAN-YAKU,3,129(1986). C6) Shoyakugaku Zasshi,42,130(1988). | |||||
| Remarks | The Japanese Pharmacopoeia defines three kinds of bark as Houpo and it is required to contain not less than 0.8% of magnolol. The Pharmacopoeia of People's Republic of China defines Houpo, Magnoliae Officinalis Cortex, as the bark of M. officinalis (Chuanpo, Hubeipo, etc) and M. officinalis var. biloba (Wenpo, Wenzhouhoupo). Aside from the bark (trunk bark, branch bark), the root bark is also used. In the Japanese market, Chinese houpo is named generically as Tokoboku. In Korea, as well as the bark of M. officinalis, the bark of Machilus thunbergii Sieb. et Zucc. of family Lauraceae (Jap. name: Tabunoki) is substituted. Though it is called Houpo or Baopo, the properties and flavors are completely different. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2023/12/06 | |||||