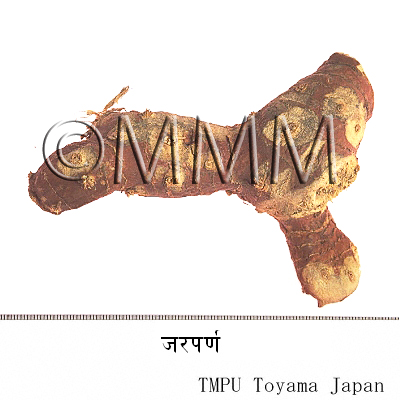
Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Crude drug name_17396a.jpg/20000) | Market name | Kulinjan |
|---|---|---|
| Formal name | Rasna | |
Other names Tips! | Bara kulanjana (T), Sugandha bacha (B), Kulanjana (H), Dumparasmi, Doddarasagadde (K), Peraratta (M), Pedaduma rakshtrakam (Te), Perarattai (Ta), Aratta, Kaluwala (Sin) | |
| English name | Greater Galangal | |
| Original plant name | Alpinia galanga Willd., Greater Galangal | |
| Family name | Zingiberaceae | |
| Used part | Classification | Plant origin | Sub classification | rhizome |
| Collection information | India, New Delhi | |
| Collection date | 1997/05/06 | |
| Collector | Katsuko Komatsu | |
| TMPW No. | 17396 | |
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
28.6139391
77.20902120000005
Collection information
India,New Delhi
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Crude drug name | Ayurvedic name or Sanskrit name, English name | Rasna (Alpinia galanga), Greater Galangal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude drug image |
| ||||
| Original plant name | Alpinia galanga Willd. | ||||
| Family name | Zingiberaceae | ||||
| Used part | Rhizome | ||||
| Distribution area | Throughout India and cultivated for rhizomes. Common in the sub-Himalayan region of Bihar, West Bengal, Assam, Western ghats. | ||||
| Remarks | Common, cultivated. | ||||
| Common uses | Rhizome is considered a tonic, stomachic, carminative, expectorant and stimulant. They are used in the treatment of bronchial catarrh, rheumatism, palpitation of heart, respiratory diseases, especially in the case of children. Dried rhizome provides the drug greater Galangal. Its chief use is for clearing the voice. It has an antispasmodic effect which alleviates asthma and also exhibits antiamphetamine and diuretic properties. In affections of gastrointestinal tract, the drug may be useful like other volatile oils. | ||||
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds (1R,2R,4S) -trans-2-Hydroxy-1,8-cineole beta-D-glucopyranoside (*C4), (1S,2S,4R)-trans-2-Hydroxy-1,8-cineole beta-D-glucopyranoside (*C4), (1R,3S,4S)-trans-3-Hydroxy-1,8-cineole beta-D-glucopyranoside (*C4),. Monoterpenoids alpha-Pinene (*C3), Sabinene (*C3), Limonene (*C3), beta-Phyllandrene (*C3), 1,8-Cineole (*C3, *C5, *C10, *C13), Linalool (*C3, *C5, *C10), Terpinen-4-ol (*C3), alpha-Terpineol (*C3, *C13), alpha-Bergamotene (*C3), (E),(E)-alpha-Fernesena (*C3), Nerolidol (*C3), Geranyl acetate (*C5, *C10), trans-2-Acetoxy-1,8-cineole (*C6), Bornyl acetate (*C10. *C13), Aitonellyl acetate (*C10), 2-Acetoxy-1,8-cineol (*C10), beta-Pinene (*C13), Camphor (*C13), (E)-Methyl cinnamate (*C13), Guaiol (*C13), Borneol (*C13), alpha-Fencyl acetate (*C13) Sesquiterpenoids beta-Caryophyllene (*C3), beta-Patchoulene (*C3), Carotol (*C3), alpha-Bisabolol (*C3), Elemol (*C13) Other aromatic compounds Benzyl benzoate (*C3), Eugenol (*C5, *C10),Benzenemethanol, 4-(acetyloxy)-alpha-ethynyl-,acetate (*C8), Benzenemethanol 4-(acetyloxy)-alpha-ethynyl-3-methoxy-,acetate (*C8), Phenol derivatives p-Hydroxycinnamaldehyde (*C1), [di-(p-hydroxy-cis-styryl)] Methane (*C1)1’-Acetoxychavicol acetate (*C2, *C7, *C9, *C11, *C12) , Eugenol (*C5, *C10),p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (*C12), 1’S-1’-Acetoxyeugenol (*C12), Me eugenol (*C3, *C10), Chavicol (*C5), 1’-Acetoxy chavicol acetate (*C10), | ||||
| Pharmacological effect | Plant is a constituent of a herbal formulation used against rheumatoid arthritis. It also exerted antiinflammatory activity in both acute and chronic inflammation. The ethanolic extract of the herb showed significant antiulcer activity in rats. The oil from rhizome is carminative and in moderate doses has an antispasmodic action on involuntary muscle tissue inhibiting excessive peristaltic movement of the intestines. It is CNS depressant, LD 50 for guinea pig being 0.068ml/100g. The ethanolic extract of the rhizome showed no spermatotoxic activity in mice under acute dosages of 0.5, 1.0 and 3.0 g/kg body wt. (for 24hours) and chronic dose of 100 mg/kg/day for 90 days. There was significant gain in the weight of sexual organs and increased sperm motility and sperm count. The acetone extract of the rhizome possesses anti-oxidant activity where as the hot water extract showed potent nematocidal activity. The compounds Ethyl-trans-cinnamte and Ethyl-4-methoxy-trans-cinnamate significantly induced the activity of the detoxyfying enzyme glutathione S-transferase in several tissues of the female A/J mice liver and intestine and are reported to be potential anti-carcinogenic compounds. The powdered drug mixed with Orchis latifolia and Mucuna pruriens on oral administration to male albino rats in a dose of 300mg/100g body wt. for 5 days showed significant improvement in male sexual function. | ||||
| Medical system | Ayurveda (Traditional Indian medicine) | ||||
| Formulation | Kulinjanadya avaleha, Rasnadi curna, Rasandi kasaya. | ||||
| Related drugs | 1. Alpinia officinarum Hance 2. Alpinia spp. 3. Acorus calamus L. | ||||
| Comments | This is used as a candidate for Rasna in Kerala. But other authors correlate Alpinia galanga to Kulanjana. According to Bhavaprakasa, Raja nighantu and Nighantu ratnakara, Rasna and Kulanjana are two different plants. According to P.V. Sharma, Alpinia galanga is Malayavaca or Kulanjana. | ||||
| References | Reference book Tips! | [2] Indian Medicinal Plants - A Compendium of 500 species, Varier, P.S., Orient Longman Ltd. Chennai (Madras) Vol. 1 (Repr.1996), p 106. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants, 1956. Chopra, R.N., Nayar, S.L. and Chopra, I.C., Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, New Delhi. - New Edition (1996) National Institute Science Communication; Supplement p 13. Illustrated Manual of Herbal Drugs Used in Ayurveda, 1996. Sarin, Y.K., Council of Scientific & Industrial Research and Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi p 60. Ayurvedic Drugs and Their Plant Sources, 1994. Sivarajan, V.V. and Balachandran, I., Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi p 398-400. Plants in Ayurveda (A Compendium of Botanical and Sanskrit Names), 1997. Abdul Kareem, M., Foundation for Revitalisation of Local Health Traditions, Bangalore 95. Dravyagunavijnana, Vols. 1-5, reprint 1998. Sharma, P.V., Chowkhambha Bharati Academy, Varanasi Vol. 2, pp 304-306. | |||
| Research paper | *C1 Barik, B. R., Kundu, A. B. and Dey, A. K,; Phytochemistry, 26, 2126-27 (1987). *C2 Murakami, A.,and Ohigashi, H.; Sejinbyo Yobo Shokuhin no Kaihatsu, Niki. E., Toshikawa, T., Osawa, T. and Shi, E. S. Ed.: Tokyo, Japan, pp. 142-48 (1998). *C3 Samasundar, K. V., Ramesh, S. and Chandrasekhara, R. S.; J. Med. Arom. Plant Sci., 22, 646-48 (2000). *C4 Someya, Y., Kobayashi, A., Kubota, K.; Biosci. Biotech. Biochem., 65, 950-53 (2001). *C5 Kubota, K., Someya, Y., Kurobayashi, Y. and Kobayashi, A.; Flavor Chem. Ethn. Foods, [Proc. Meet. 5th Chem. congr. North Am.], 97-104 (1997). *C6 Kubota, K., Nakamura, K., Kobayashi, A. and Amaike, M.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 46, 5244-47 (1998). *C7 Murakami, A., Nakamura, Y., Ohigashi, H. and Koshimizu, K.; Mem. Sch. Biol. -Oriented Sci., Technol. Kinki Univ. 1, 1-23 (1997). *C8 Yamahara, J.; Jpn. Kokai Tokkyo Koho JP 10087418 A2, 5pp, Heisei (1998). *C9 Ohigashi, H., Nakamura, Y. and Murakami, A; Food Style 21, 2, 31-35 (1998). *C10 Mori, H., Kubota, K. and Kobayashi, A.; Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kaishi, 42, 989-95 (1995). *C11 Matsuda, H., Pongpiriyadacha, Y., Morikawa, T, Ochi, M. and Yoshikawa, M.; J. Pharmacol. 13, 59-67 (2003). *C12 Matsuda, H., Morikawa, T, Managi, H. and Yoshikawa, M.; Biorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 13, 3197-3202 (2003). *C13 Jirovetz, L., Buchbauer, G. Shafi, M. P. and Leela, N, K.; Acta. Pharm. 53, 73-81 (2003). | ||||
| Remarks | The plant is a constituent of a herbal drug formulation used against rheumatoid arthritis. In South India, the drug Kulanjana is called Rasna by the Ayurvedic practitioners. | ||||
| Last renewal date | 2024/04/08 | ||||