Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
Production area information
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937378
135.50216509999996
Collection information
Japan,Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
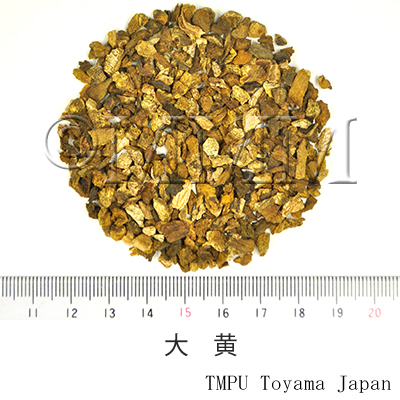
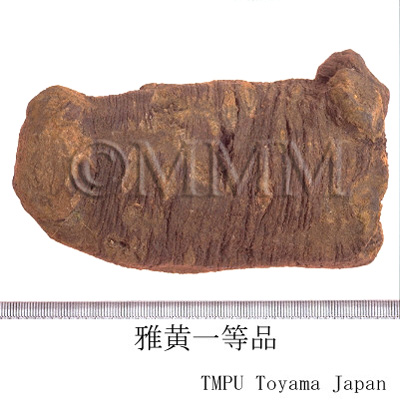
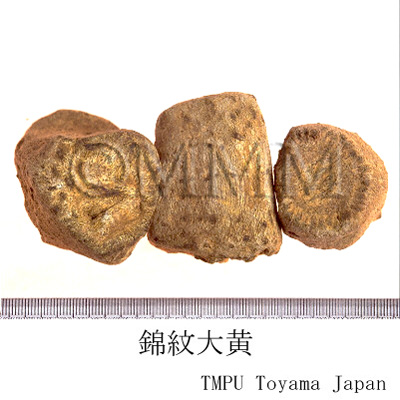
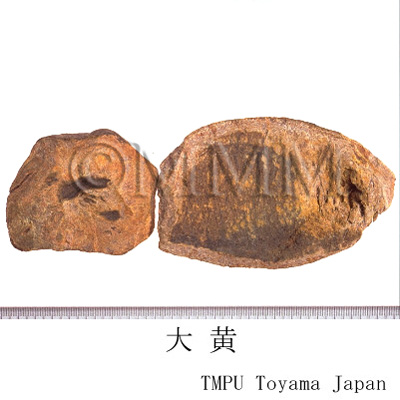
| Common name | 大黄, Dahuang, Rhei Rhizoma (JP18), Rhei Radix et Rhizoma (CP2020), Rhubarb (JP18), (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 青海大黄, 西寧大黄, 甘粛大黄, 雅黄, 馬蹄大黄 | ||||||
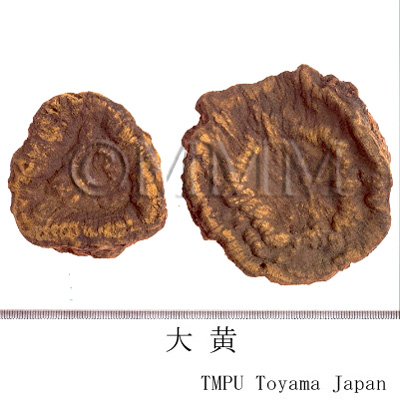
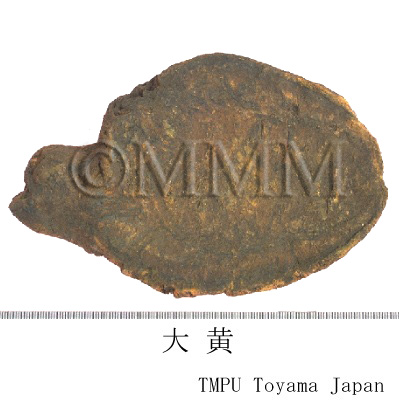
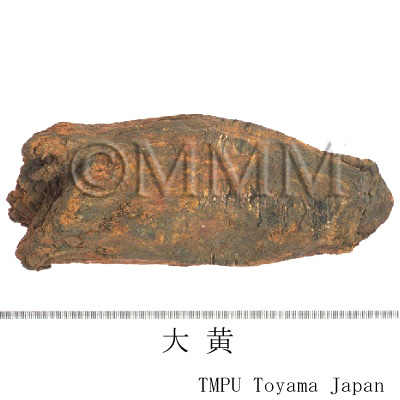
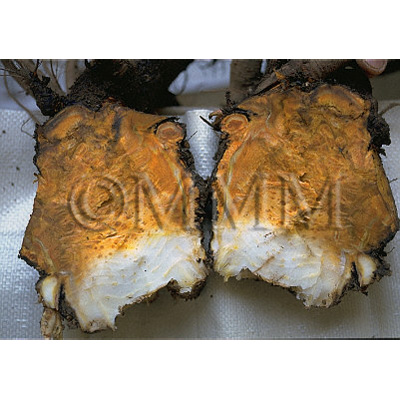
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
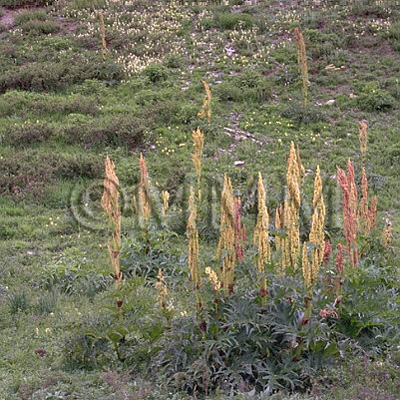
| Original plant name | Rheum palmatum Linn., Rheum tanguticum Maximowicz, Rheum officinale Baillon, Rheum coreanum Nakai, or their interspecific hybrids | ||||||
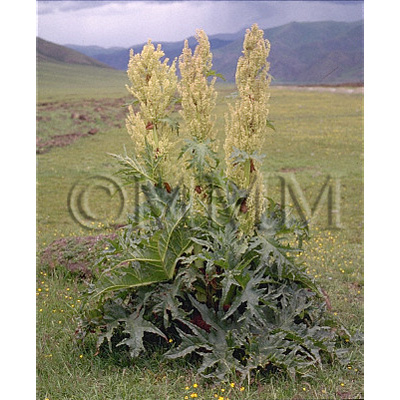
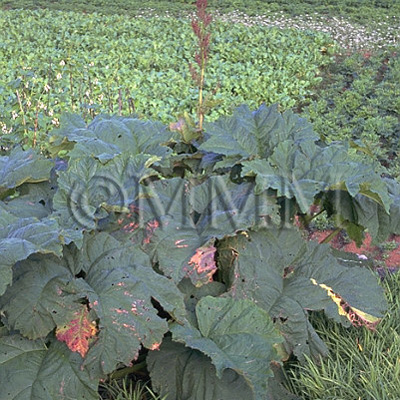
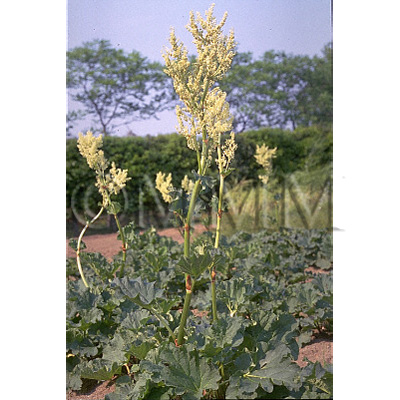
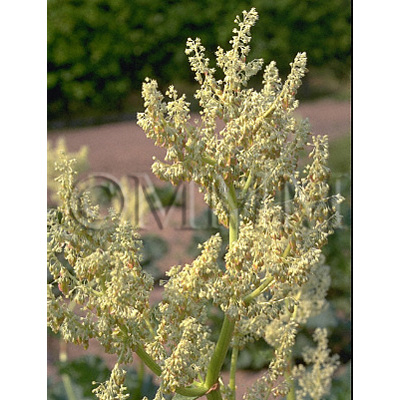
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Polygonaceae | ||||||
| Used part | rhizome | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Dahuang has a characteristic golden yellow pattern and star-like spots. The internal part is stiff and contains oil with a clean aroma. It is sticky when chewed. (NI) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | A mild laxative, stomachic and removing blood stasis drug. In Chinese medicine, Dahuang removes poison of excess syndrome, promotes bowel movement, cures stomachache of constipation, and festering swelling. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Purgatives, cathartics | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Cold; bitter. [Meridian Tropism] Spleen, stomach, large intestine, liver and pericardium meridians. [Actions] To remove accumulation with purgation, clear heat, purge fire, cool the blood, remove toxin, expel stasis, unblock the meridians, drain dampness to abate jaundice. [Indications] Accumulation, stagnation and constipation caused by excess heat, hematemesis caused by blood heat, red eyes and swollen throat, swelling abscess, deep-rooted boil and sore, abdominal pain caused by intestinal abscess, blood-stasis amenorrhea, postpartum stasis and obstruction, injuries from falls and fights, dampness-heat dysentery, jaundice and red urine, stranguria, edema; topical application for burn and scald. | ||||||
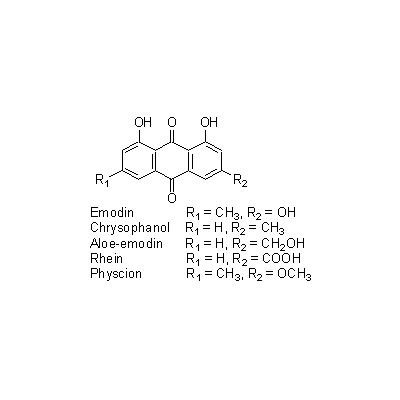
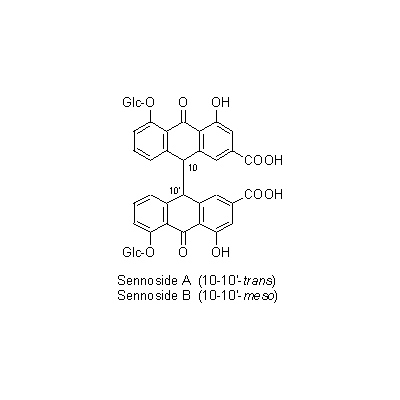
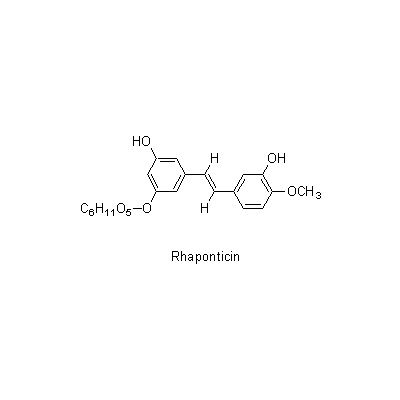
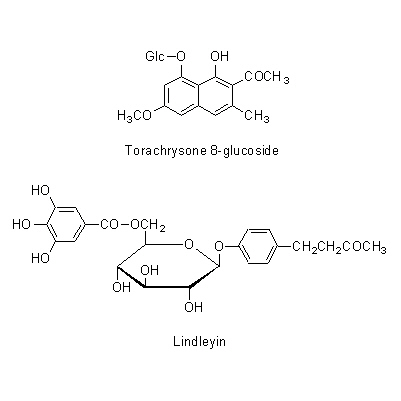
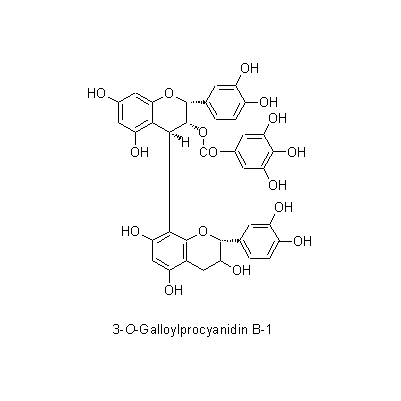
| Chemical constituent | Anthraquinones (*C1-C10): Chrysophanol, Emodin, Rhein, Aloe-emodin, Physcion, Physcion-monoglucoside, Aloe-emodin-8-monoglucoside, Chrysophanol-1-monoglucoside, Emodin-monoglucoside, Rhein-8-monoglucoside, Sennidin A, Sennidin B, Sennidin C, Rheidin A, Rheidin B, Rheidin C, Palmidin A, Palmidin B, Palmidin C, Palmidin D, Sennoside A, Sennoside B, Sennoside C, Sennoside D, Sennoside E, Sennoside F, Dirhein, Anthrone, Chrysophanol anthrone, Rheinosides, 以下代謝物/followings are the metabolites 8-Glucosylrheinanthrone, Rheinanthrone, Sennidin A-8-monoglucoside, Sennidin B-8-monoglucoside, Sennidin B-8'-monoglucoside, Rhein dianthrone diglucoside Tannins (*C1): Rhatannin I, Rhatannin II, Torachrysone 8-glucoside, 6-Hydroxymusizin, Lindleyin, Procyanidin B-1 3-O-gallate, (+)-Catechin, (-)-Epicatechin, Epicatechin gallate, Gallocatechin, Gallocatechin gallate, Glucogallin, 2'-O-Cinnamoylglucogallin, Gallic acid, Tetrarin (その他/Others): (-)-Epicatechin 3-O-gallate, Procyanidin B-2 3,3'-di-O-gallate, RG-tannin (*C11): 1,2,6-Trigalloyl-glucose, 3-O-Galloylprocyanidin B-1 Stilbenes Sect.Rhapontica, Sect.Ribesifornia(*C1): Rhaponticin, 3,5-Dihydroxy-4-methoxy stilbene glucoside, Piceid (*C11): 3,5,4'-Trihydroxystilbene 4'-glucoside およびその/and its 6''-O-gallate Naphthalenes (*C11): Torachrysone 8-glucoside, 6-Hydroxymusizin およびその/and its 6'-O-oxalate | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Cathartic [extract, rhubarb (dahuang) powder, sennoside A)]. Antibacterial (water extract, aloe-emodin), antifungal (catechin). Decreases urea nitrogen in the blood (rhatannin). Decreases MG level in the blood and the urine (water extract, epicatechin 3-O-gallate, procyanidin B-2 3,3'-di-O-gallate). antiinflammatory, analgesic (lindleyin). anticholera toxin. | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AF093392, AF094558, AF204860, M77702 | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Constipation, Abdominal pain, High fever, Disturbance of consciousness, Diarrhea, Tenesmus, Full stomach, Chill, Red eye, Swelling and pain of the throat, Toothache, Nasal hemorrhage, Hematemesis, Appendicitis, Pyogenic dermatosis, Amenorrhea, Hyperemesis after childbirth | ||||||
| Formulation | Inchinkoto, Unpito, Otsujito, Kagawagedokuzai, Kagenryokakusan'ippo, Katsuketsugedokuto, Katsuketsusan'oto, Kamijokito, Kankyoto, Kanrento, Kanrendaioto, Kanrendaiokasekkoto, Kikyogedokuto, Kijitsushishidaioshito, Kijitsudaioto, Kippi-daio-bokusho-to, Kyoseihatekigan, Kumibinroto, Keishikashakuyakudaioto, Keishikadaioto, Keimeisan, Gohekiin, Kobokusammotsuto, Kowashakuyakuto, Gomotsudaioto, Saikokaryukotsuboreito, San'oshashinto, San'oshashinto (brewing), Shishidaioto, Shijunseiryoin, Shakukan'oshinbuto, Shakuyakuto, Shakuyakutokadaio, Shakuyakukanzobushidaioto, Sekishozuto, Shadojindaioto, Junchoto, Shogedokuto, Jingyobofuto, Seiinrikakuto, Daiokanzoto, Daiobushito, Daiobotampito, Daibyakuchuin, Jiohanho, Jishusabiho, Jidabokuippo, Jizusoippo, Jizutsuippo, Chuseito, Choijokito, Tsudosan, Tokakujokito, Toryuto, Naisoorento, Nyoshinsan, Hachimisenkiho, Hachimitaikaho, Binrojunkito, Bofutsushosan, Honposhakuyakuto, Ryokakusan, Ryokankyomishingeninoto, Rengyoto, Rengyoto, Compound Rhubarb and Sennna Powder, Fuinto | ||||||
| Related drugs | Tudahuang, Wadaio | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 16-20. C2)Planta Med.,40,225(1980). C3)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,30,1338(1982). C4)J.Pharmaco-bio-Dyn.,8,800(1985). C5)Chem.Pharm.Bull.,35,1998(1987). C6)Pharmacology,36,172(1988). C7)Appl.Envir.Microbiol.,60,1041(1994). C8)Biol.Pharm.Bull.,19,701(1996). C9)Biol.Pharm.Bull.,19,705(1996). C10)Biol.Pharm.Bull.,19,136(1996). C11)Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, pp 315-316. | ||||||
| Remarks | The active ingredient of catharsis is sennosaide. Sennosaide A, metabolized by enteric bacteria in the colon, is transformed into Rhein anthrone which accelerates peristalsis of the intestine and induces catharsis. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/11/02 | ||||||