Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
36.061089
103.83430299999998
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Gansu Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 黄耆, Huangqi, Astragali Radix (JP18), (CP2020), Astragalus Root (JP18), Milkvetch Root (CP2020) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 綿黄耆, 小綿耆, 北耆 | ||||||
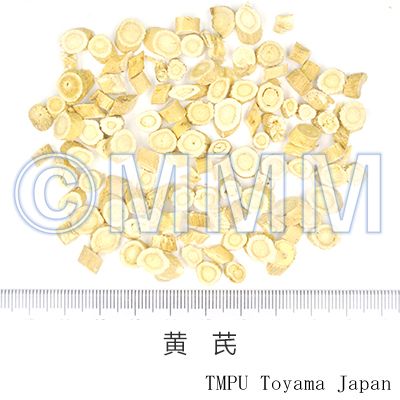
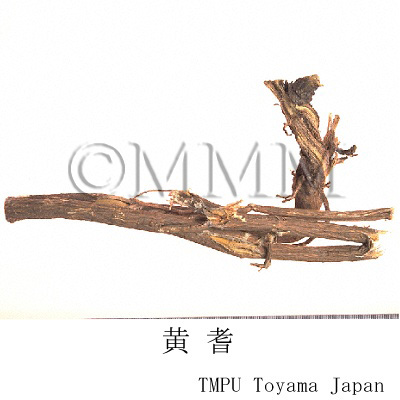
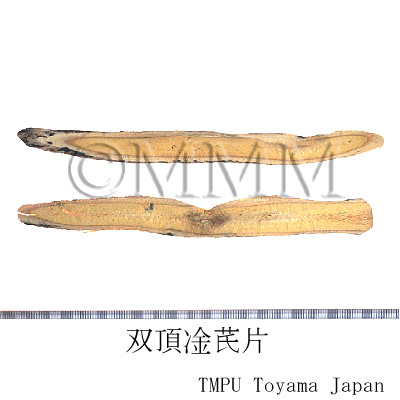
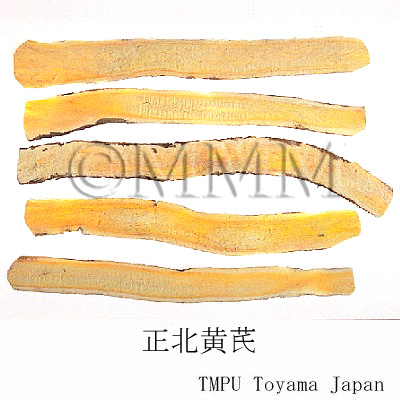
| crude drug image |
| ||||||
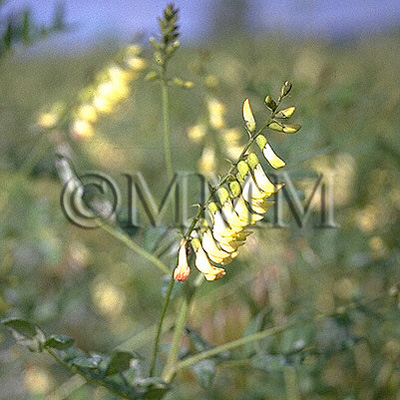
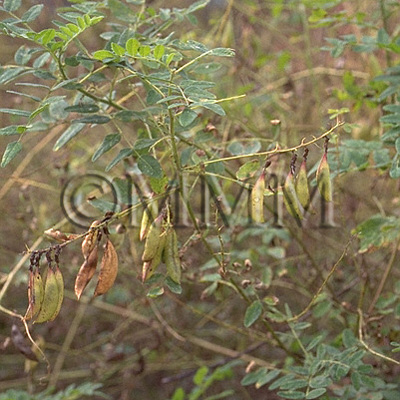
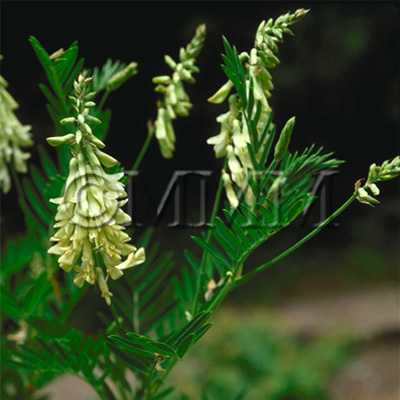
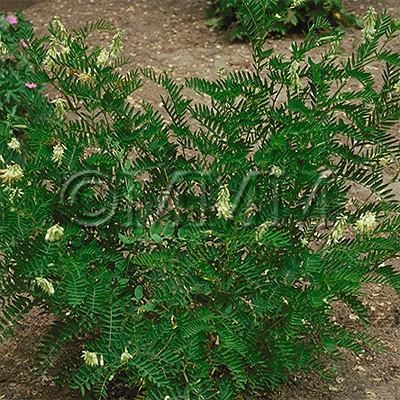
| Original plant name | Astragalus membranaceus Bunge1 or Astragalus mongholicus Bunge, (Kibanaōgi1) | ||||||
| original plant image |
| ||||||
| Family name | Leguminosae | ||||||
| Used part | root | ||||||
| Quality for selection | Good Huangqi is thick and columnar like a rod. The outside is pale brown or yellowish brown, and the inside is pale yellow with sweet aroma. (TN) | ||||||
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) | ||||||
| Clinical application | As a tonic, cardiotonic, diuretic and anhidrotic, huangqi is applied for valetudinarianism, dystrophy, dysfunction of sweating and acute or chronic nephritis. | ||||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | ||||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Drugs for replenishing Qi (vital energy) | |||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild warm; sweet. [Meridian Tropism] Lung and spleen meridians. [Actions] To tonify qi and upraise yang, secure the exterior, check sweating, promote urination, alleviate edema, engender fluid, nourish the blood, move stagnation, relieve impediment, expel toxin and pus, promote wound healing and tissue regeneration. [Indications] Qi deficiency and lack of strength, reduced food intake, sloppy stool, sunken middle qi, chronic diarrhea, prolapse of the rectum, bloody stool, menstrual flooding and spotting, exterior deficiency with spontaneous sweating, qi deficiency edema, interior heat wasting-thirst, blood deficiency and sallow complexion, hemiplegia, arthralgia, numbness, abscesses and cellulitis difficult to suppurate and perforate, or difficult to heal. | ||||||
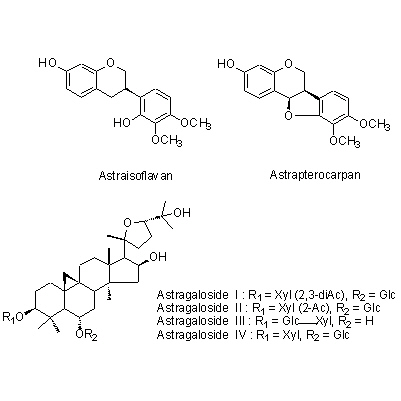
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids (*C2): Linoleic acid, Linoleinic acid Monosaccharides (*C2): D-Glucose, D-Fructose Oligosaccharides (*C2): Sucrose Triterpenoid saponins (*C1): Astragaloside I, Astragaloside II, Astragaloside III, Astragaloside IV, Astragaloside V, Astragaloside VI, Astragaloside VII, Astragaloside VIII, Soyasaponin I Sterols (*C2): β-Sitosterol Isoflavones (*C2): Formononetin, 3'-Hydroxyformononetin, 2',3'-Dihydroxy-7,4'-dimethoxyisoflavone, 7,3'-Dihydroxy-4'-methoxyisoflavone 7-O-glucoside, Astraisoflavan, 7,2'-Dihydroxy-3',4'-dimethoxyisoflavane 7-O-glucoside, Astrapterocarpan 7-hydroxy-3',4'-dimethoxypterocarpan 7-O-glucoside, Isoliquiritigenin Amino acids (*C1,C2): I-Canavanine, Betaine, γ-Aminobutyric acid Other nitrogen containing compounds (*C2): Choline | ||||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | ||||||
| Pharmacological effect | Diuretic and hypotensive (water extract and ethanol extract) | ||||||
| DNA sequence | AF121675, AF239711, AF239712, AF239712; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | ||||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") | 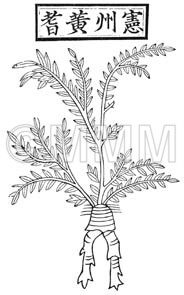 ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | ||||||
| Disease | Lack of energy, Fatigable, Shortness of breath, Anorexia, Chill, Descent of the uterus, Chronic diarrhea, Hematochezia, Irregular vaginal bleeding, Numbness, Partial paralysis, Night sweats, Pyogenic dermatosis, Edema, Spontaneous sweating, Proctoptosis, Polyposia, Polyuria, Internal bleeding, Acute nephritis, Chronic nephropathy, Proteinuria, Diabetes mellitus | ||||||
| Formulation | Ioto, Ishoho, Uzuto, Ekkiyoeito, Ogikeishigomotsuto, Ogikenchuto, Ogishakuyakukeishikushuto, Ogibekkoto, Orenshodokuin, Kamikihito, Kigikenchuto, Kikyogedokuto, Kihito, Kyukihochuto, Gyokuheifusan, Keishikaogito, San'oto, Shikonboreito, Shichikensan, Shichimotsukokato, Juzentaihoto, Jumizasan, Jurokumiryukiin, Shunrinshakusekishito, Joshitsuhokito, Joyowaketsuto, Seishoekkito, Seishinto, Seishinrenshiin, Daibofuto, Jiohanho, Tokiinshi, Tokito, Tokirokuoto, Naitaku-san, Naitaku-san, Ninjinsan, Ninjin-yoei-to, Hangebyakujutsutemmato, Fuhishomyakusankabyakukyu, Boiogito, Boibukuryoto, Hojinto, Botanpisan, Hochuekkito, Mibakuekkito | ||||||
| Related drugs | Jinqi, Hongqi (see "Remarks") | ||||||
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1) The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 149-150. C2) Outline of Pharmacognosy, a Textbook, pp 281-282. | ||||||
| Remarks | Huangqi is the chief remedy for tonifying. It tonifies the qi of exterior (skin, hypodermis), and is used to treat insufficiency syndrome in the exterior. On the contrary, Ginseng tonifies the qi of the Five Viscera and is used to treat deficiency syndrome in the interior. Excess use causes itching paresthesia and rash. In China, "Junpi (晋耆)" or "Hongqui (紅耆)", both refers the root of Hedysarum polybotrys Hand.-Mazz., and are most appreciated and valued. | ||||||
| Last renewal date | 2025/12/25 | ||||||