※Click on the image to enlarge it.
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Guangxi Zhuangzu Autonomous Region
| Common name | 菊花, Juhua, Chrysanthemi Flos (JP18) (CP2020), Chrysanthemum Flower (JP18) (CP2020) |
|---|
| Synonyms | 苦薏, 甘菊, 白菊花 |
|---|
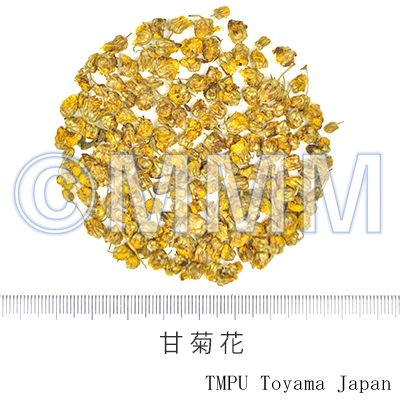
| crude drug image |  |
※Click on the image to enlarge it. |
|
|---|
| Original plant name | Chrysanthemum indicum Linn.1 or Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramatulle2, (Shimakangiku1 or Kiku2) |
|---|
| original plant image |  |
※Click on the image to enlarge it. |
|
|---|
| Family name | Compositae |
|---|
| Used part | capitulum |
|---|
| Quality for selection | Good juhua is bulky, yellow and has a lot of petals. The newer the better. (NI) |
|---|
| Official compendium | JP XVIII, CP (2020 ed.) |
|---|
| Clinical application | As an antifebrile, antidote, painkiller, anti-inflammation drug, it is applied to relieve cold, fever, chill, headache, red painful eyes, dizziness and vertigo and swellings. Compouding with Lonicerae Flos, it is applied to treat arterial sclerosis and high cholesterol. It is also taken as medicinal tea. |
|---|
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine |
|---|
Drug effect in
traditional medicine | Traditional
classification | Diaphoretics with cold property |
|---|
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Mild cold; bitter, pungent.
[Meridian Tropism] Liver and heart meridians.
[Actions] To clear heat and remove toxin, purge fire and pacify the liver.
[Indications] Deep-rooted boil and sore, swelling abscess, red painful swelling eyes, headache and dizziness. |
|---|
| Chemical constituent | Fatty acids
C. morifolium (*C1):
Acetic acid, Propionic acid
Monosaccharides
C. morifolium (*C1):
花/flower: Fructose, Glucose, Arabinose, Galactose, Rhamnose, Ribose
Oligosaccharides
C. morifolium (*C1):
Sucrose (花/flower)
Monoterpenoids
C. morifolium (*C1):
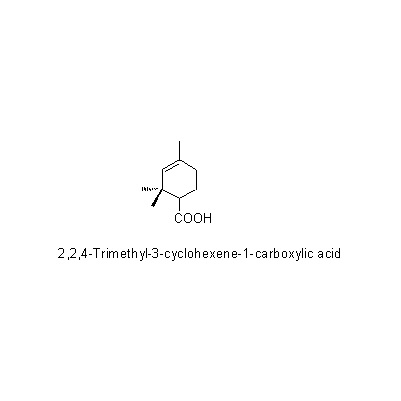
2,2,4-Trimethyl-3-cyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid (花/flower), Borneol, Bornyl acetate, Camphor, α-Thujione
Flavones & Flavonols
C. morifolium (*C1):
Apigeninglucoside (花/flower)
Other aromatic derivatives
C. morifolium (*C1):
Benzoic acid, Benzaldehyde, Anisaldehyde
Simple nitrogen containing compounds
C. morifolium (*C1):
Adenine, Choline (花/flower)
unknown
C. morifolium (*C1):
Acacetin-7-rhamnoglucoside (花/flower), Stachydrine, Chrysanthenone
|
|---|
| Chemical structure | |
|---|
| Pharmacological effect | Decreases bodily temperature slightly (malfunction of the circulatory system in large dose). Strengthens capillary resistance. Antibacterial (Kangjuhua: various dermal fungi). |
|---|
| DNA sequence | AF218883, L13648 |
|---|
Classical reference
(Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image |
|---|
| Disease | Fever, Headache, Cough, Sore throat, Red eye, Bleary eyes, Decreaced vision, Vertigo, Stagger |
|---|
| Formulation | Seijokentsuto, Chotosan, Jijinmeimokuto (Jinkimeimouto), Senkanmeimokuto, Jinkimeimokuto, Mankeishisan, Meiganippo, Kogikujiogan |
|---|
| References | JP18: The 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia.
CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi.
C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. II, pp 122-125. |
|---|
| Remarks | It has many synonyms such as 白菊花 (white chrysanthemum flower) and 甘菊 (sweet chrysanthemum) literally. |
|---|
| Last renewal date | 2022/09/30 |
|---|
| | |
|---|