Crude drug sample data base
※Click on the image to enlarge it.
The capital city, provincial capital city or the representative
location of its administrative area is indicated.
location of its administrative area is indicated.
30.572815
104.06680099999994
Production area information
People's Republic of China,Sichuan Prov.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_san.png
34.6937249
135.5022535
Collection information
Japan(ToS),Osaka Pref.
https://ethmed.toyama-wakan.net/img/pin_nyu.png
Scientific information data base
| Common name | 青皮, Qingpi, Citri Unshiu Pericarpium Immaturus (Non-JPS2022), Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium Viride (CP2020), Immature Citrus Unshiu Peel (Non-JPS2022), Green Tangerine Peel (CP2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | 四花青皮, 個青皮 | |||||
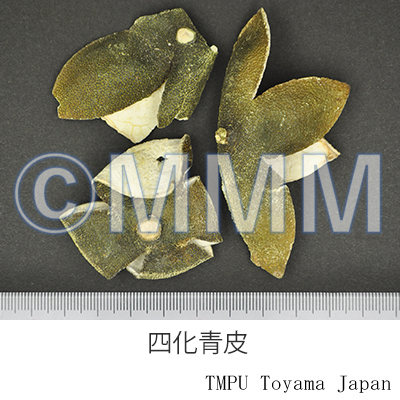
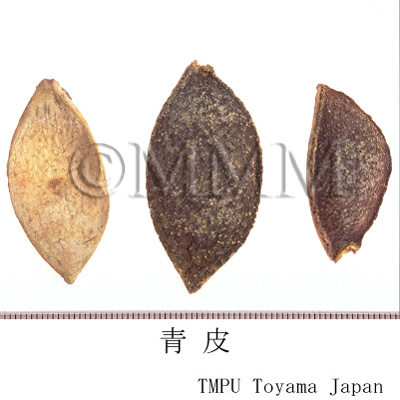
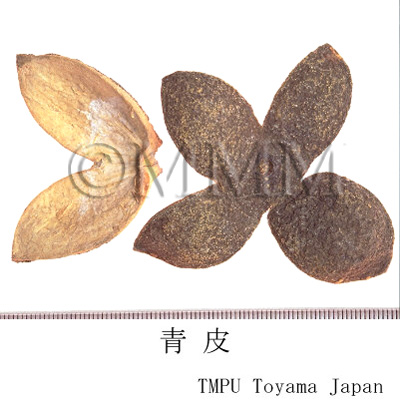
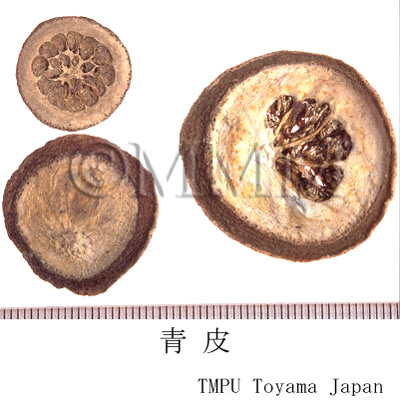
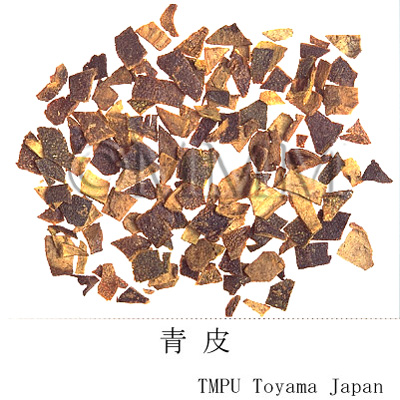
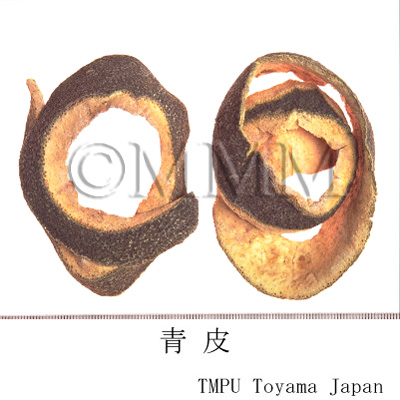
| crude drug image |
| |||||
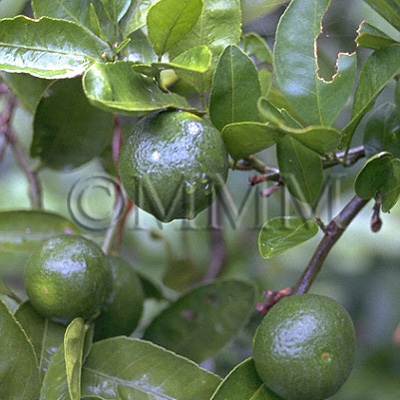
| Original plant name | Citrus unshiu Marcowicz1 or Citrus reticulata Blanco, (Unshūmikan1) | |||||
| original plant image |
| |||||
| Family name | Rutaceae | |||||
| Used part | pericarp of young fruit or unripe fruit | |||||
| Quality for selection | The surface of good one is grayish blue in color. The stronger bluish tone is preferable. The cavernous tissue of the back side is white. The taste and flavors should be as fresh as possible. (NI) | |||||
| Official compendium | Non-JPS (2022), CP (2020 ed.) | |||||
| Clinical application | As an aromatic stomachic, it is applied to treat indigestion and abdominal pain. It enters the qi system of liver and gall bladder. It is a stronger medicine than chenpi in promoting excretion, activating qi and relieving pain. It is used to both upper and lower energizer. | |||||
| Medical system | Traditional Chinese medicine | |||||
| Drug effect in traditional medicine | Traditional classification | Carminatives for regulating flow of Qi | ||||
| Beneficial effect | [Property and Flavor] Warm; bitter and pungent. [Meridian Tropism] Liver, gallbladder and stomach meridians. [Actions] To soothe the liver and break qi, eliminate accumulation and resolve stagnation. [Indications] Distending pain in the chest and the hypochondrium, pain caused by genital disease, mammary hyperplasia, acute mastitis, food accumulation and qi stagnation, distending pain in the epigastrium and abdomen. | |||||
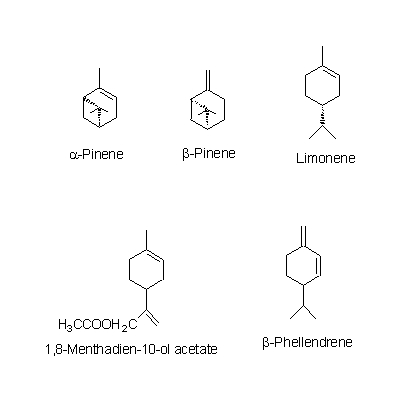
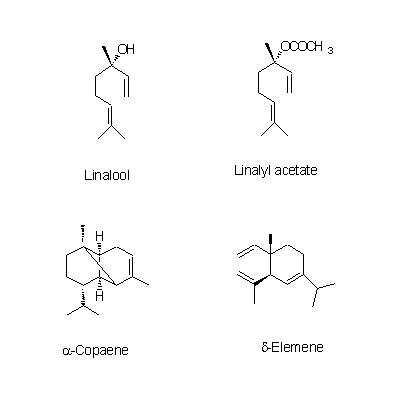
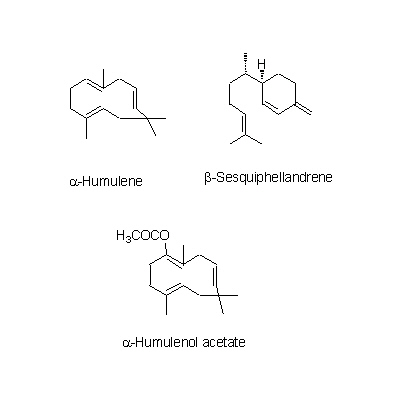
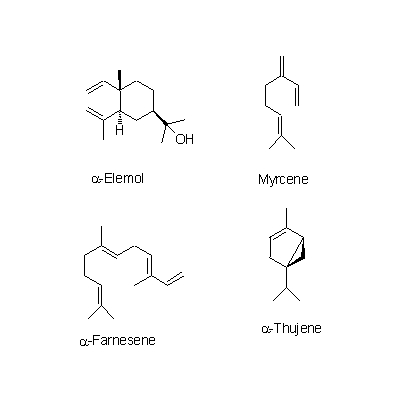
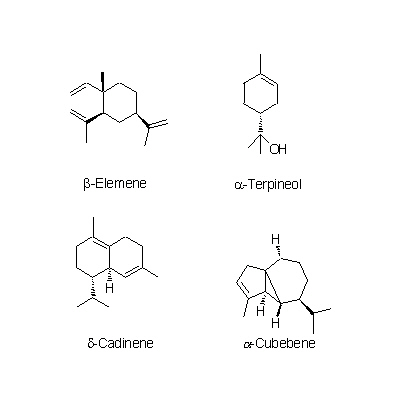
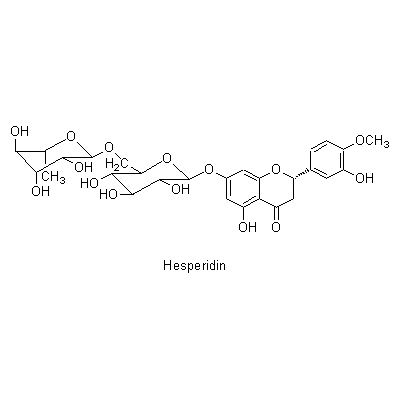
| Chemical constituent | Other aliphatic and related compounds C. unshiu (*C1): クエン酸 / citric acid Monosaccharides C. unshiu (*C1): Vitamin C Monoterpenoids C. unshiu (*C1): Limonene, α-Terpinene, α-Pinene, β-Pinene, Linalool, α-Cubebene, α-Thujene, α-Terpineol Sesterterpenoids C. unshiu (*C1): δ-Elemene, α-Copaene, β-Sesquiphellandrene, 1,8-Menthadien-10-ol acetate, α-Elemol, Myrcene, α-Farnesene, β-Elemene, δ-Cadinene Flavones & Flavonols C. reticulata (*C2,C4): Isosinensetin, Sinensetin, 5,7,8,4'-Tetramethoxyflavone, Nobiletin, Tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, 3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone, Tangeretin, 5-Demethylnobiletin C. unshiu (*C2,C3,C4,C5): Isosinensetin, Sinensetin, 5,7,8,4'-Tetramethoxyflavone, Nobiletin, Tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, 3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone, Tangeretin, Rhoifolin, 5-Demethylnobiletin C. sinensis (*C2): Isosinensetin, Sinensetin, Nobiletin, Tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, 3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone, Tangeretin, 5-Demethylnobiletin C. aurantium (*C2): Nobiletin, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, 3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone, Tangeretin, 5-Demethylnobiletin C. natsudaidai (*C2): Nobiletin, Tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 3,5,6,7,8,3',4'-Heptamethoxyflavone, 3-Hydroxy-5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone, Tangeretin Flavanones & Dihydroflavonols C. unshiu (*C2,C3,C4,C5): Hesperidin, Naringenin, Narirutin, Naringin C. reticulata (*C2,C4): Naringenin, Hesperetin, Narirutin, Hesperidin, Naringin, Isoimperatorin C. sinensis (*C2): Narirutin, Hesperidin C. aurantium (*C2): Poncirin, Naringenin, Narirutin, Naringin, Neohesperidin C. natsudaidai (*C2): Poncirin, Naringenin, Hesperetin, Narirutin, Naringin, Hesperidin, Neohesperidin Coumarins C. aurantium (*C2): Meranzin hydrate, Marmin, 5-[(6,7-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-2-octenyl) oxy]-Psoralen C. natsudaidai (*C2): Meranzin hydrate, Marmin, Isomeranzin, Isoimperatorin C. reticulata (*C4): Oxypeucedanin | |||||
| Chemical structure |
※画像をクリックすると、拡大して表示されます。 | |||||
| Pharmacological effect | Sympathomimetic action (synephrine), antiulcer (nobiletin), antiinflammatory (naringin,neohesperidin,nobiletin,tangeretin,sinensetin,xanthotoxin), antiallergy (nobiletin,tangeretin,3-methoxynobiletin,sinensetin), inhibition of c-AMP phosphodiesterase (nobiletin,tangeretin,3-demethylnobiletin), capillary reinforcement (hesperidin), antioxidation (3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid), sedation, central inhibition, contraction of removed ileum, uterus and peripheral blood vessel, mucosa and local stimulation, increase the pressure in gall bladder in vivo and myotony of the sphincter of Oddi, increase in bile secretion, enhanced intestinal movement in vivo, decrease in the level of cholesterol in the liver and serum (d-limonene). | |||||
| DNA sequence | U38312, AF312228; Traditioal Medical & Parmaceutical Database. | |||||
| Classical reference (Chinese Herbal Classic "Zhenglei bencao") |  ※Click this image to see the actual image ※Click this image to see the actual image | |||||
| Disease | Pain due to flatulence of hypochondrium, Depression, Restlessness, Mastitis, Hernia, Dyspepsia | |||||
| Formulation | Kagenshahakusan, Saikosokanto, Bunshinkiin | |||||
| Related drugs | Citri Unshiu Pericarpium, Tachibana Pericarpium, Aurantii Pericarpium, Aurantii Fructus Immaturus, Aurantii Fructus | |||||
| References | Non-JPS2022: The Japanese standards for non-Pharmacopoeial crude drugs 2022. CP2020: Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2020 edi. C1)The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku with Color Pictures Vol. I, pp 257-260. C2)Nat.Med.,51,231(1997). C3)Nat.Med.,51,84(1997). C4)Nat.Med.,50,114(1996). C5)Nat.Med.,51,205(1997). C6)Shoyakugaku Zasshi,46,150(1992). | |||||
| Remarks | The fallen young fruits are collected in May and June, and dried in the sun (known as Geqingpi [個青皮]). The immature fruits are collected in July and August, and a slit is made in the peal then the calyx is removed. It is known as Sihuaqingpi (四花青皮 or 四化青皮). The immature fruit has more flavonoid glycoside and synephrine. It also has more antioxidant properties. | |||||
| Last renewal date | 2022/07/20 | |||||